Chaubisi rajya
Chaubisi Rajya (Nepali: चौबीसी राज्य, literally "24 principalities") were sovereign and intermittently allied petty kingdoms on the Indian subcontinent, ruled by Khass from medieval India, located around the Gandaki River Basin, a major Himalayan tributary of the Ganges.
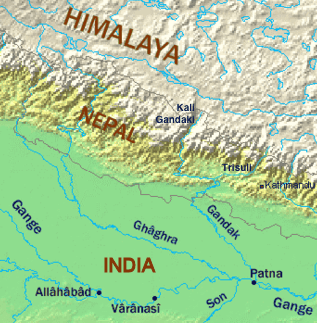
The 24 principalities were:
Prithvi Narayan Shah ascended the throne of Gorkha Kingdom in 1743, then proceeded to build the Kingdom of Nepal. The Chaubisi were annexed during the unification of Nepal from 1744 to 1810. Prithvi Narayan Shah unified about half the 24 principalities, the entire Kathmandu Valley around the present-day Nepali capital Kathmandu and additional principalities further east before dying in 1775. Annexation of the rest of the 24 proceeded under his son Pratap Singh Shah (ruled 1775-77) and grandson Rana Bahadur Shah (ruled 1777-1799). The Shah dynasty was outmaneuvered by another Chaubisi family, the Rana dynasty or Kunwar family of Kaski and Lamjung, in 1846 and reduced to figureheads until 1953.
A parallel group of 22 small kingdoms, Baise Rajya (Nepali: बाइसे राज्य), existed to the west of the Gandaki Basin. These were also annexed by the Shah dynasty before 1799.