Casuarinaceae
The Casuarinaceae are a family of dicotyledonous flowering plants placed in the order Fagales, consisting of four genera and 91 species[2] of trees and shrubs native to eastern Africa, Australia, Southeast Asia, Malesia, Papuasia, and the Pacific Islands. At one time, all species were placed in the genus Casuarina. Lawrence Alexander Sidney Johnson separated out many of those species and renamed them into the new genera of Gymnostoma in 1980 and 1982,[3][4] Allocasuarina in 1982,[4] and Ceuthostoma in 1988, with some additional formal descriptions of new species in each other genus.[5] At the time, it was somewhat controversial. The monophyly of these genera was later supported in a 2003 genetics study of the family.[6] In the Wettstein system, this family was the only one placed in the order Verticillatae. Likewise, in the Engler, Cronquist, and Kubitzki systems, the Casuarinaceae were the only family placed in the order Casuarinales.
| Casuarinaceae | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Common ironwood (Casuarina equisetifolia) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Casuarinaceae R.Br.[1] |
| Type genus | |
| Casuarina | |
| Genera | |
| |
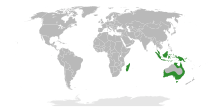 | |
| The range of Casuarinaceae | |
Members of this family are characterized by drooping equisetoid (meaning "looking like Equisetum"; that is, horsetail) twigs, evergreen foliage, monoecious or dioecious and infructescences ('fruiting bodies') cone-like, meaning combining together many outward-pointing valves, each containing a seed, into roughly spherical, cone-like, woody structures. The roots have nitrogen-fixing nodules that contain the soil actinomycete Frankia.
In Australia the most widely used common name for Casuarinaceae species is sheoak or she-oak (a comparison of the timber quality with English oak). Male specimens bear no fruit and are perhaps therefore colloquially referred to as sheoak. Other common names in Australia include ironwood, bull-oak or buloke, beefwood,[7] or cassowary tree.[8]
The Shire of Buloke in Victoria, Australia, is named after the species Allocasuarina luehmannii.
References
- Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (2009). "An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG III". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society. 161 (2): 105–121. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.2009.00996.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 22 Dec 2013.
- Christenhusz, M. J. M. & Byng, J. W. (2016). "The number of known plants species in the world and its annual increase". Phytotaxa. 261 (3): 201–217. doi:10.11646/phytotaxa.261.3.1.
- Johnson, Lawrie A. S. (1980). "Notes on Casuarinaceae". Telopea. (Online page archive version, link via APNI Gymnostoma ref's). 2 (1): 83–84. doi:10.7751/telopea19804114. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 22 Dec 2013.
- Johnson, Lawrie A. S. (23 Dec 1982). "Notes on the Casuarinaceae II" (PDF). Journal of the Adelaide Botanic Gardens. 6 (1): 73–87. Retrieved 22 Dec 2013.
- Johnson, Lawrie A. S. (1988). "Notes on Casuarinaceae III: The new genus Ceuthostoma". Telopea. (Online page archive version, link via APNI Ceuthostoma ref's). 3 (2): 133–137. doi:10.7751/telopea19884801. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-06-10. Retrieved 22 Dec 2013.
A synoptic key for the four genera of the family is given.
- Steane, Dorothy A.; Wilson, Karen L.; Hill, Robert S. (2003). "Using matK sequence data to unravel the phylogeny of Casuarinaceae" (PDF). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 28 (1): 47–59. doi:10.1016/S1055-7903(03)00028-9. PMID 12801471.
- Cox, P., & Freeland, J. 1969. Rude timber buildings in Australia. Thames and Hudson. ISBN 0-500-34035-8 page 18. Cox states that the name 'she-oak' is derived from Native America sheac - beefwood.
- Partridge, Eric (2013). Origins: A Short Etymological Dictionary of Modern English. Routledge. p. 82. ISBN 9781134942176. Retrieved 22 Dec 2013.
- Xiang X-G, Wang W, Li R-Q, Lin L, Liu Y, Zhou Z-K, Li Z-Y, Chen Z-D (2014). "Large-scale phylogenetic analyses reveal fagalean diversification promoted by the interplay of diaspores and environments in the Paleogene". Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics. 16 (3): 101–110. doi:10.1016/j.ppees.2014.03.001.
External links


- Research team from IRD working on Frankia-Casuarinaceae mycorrhizal and nitrogen-fixing symbioses