Buhl-Verville CA-3 Airster
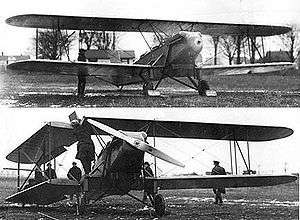
The Buhl-Verville CA-3 Airster (also known as the J4 Airster, after its engine), was a utility aircraft built in the United States in 1926, notable as the first aircraft to receive a type certificate in the US,[2][3][4] (i.e. A.T.C. No. 1) issued by the Aeronautics Branch of the Department of Commerce on March 29, 1927.[5] It was a conventional single-bay biplane with equal-span unstaggered wings and accommodation for the pilot and passengers in tandem open cockpits. Marketed for a variety of roles including crop-dusting, aerial photography, and freight carriage, only a handful were built, some with water-cooled engines as the CW-3, and others with air-cooled engines as the CA-3 . One CA-3 placed second in the 1926 Ford National Reliability Air Tour.[6]
| CA-3 Airster | |
|---|---|
| Role | Utility aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Buhl |
| Designer | Alfred Verville, Etienne Dormoy |
| First flight | 1926 |
| Number built | 20[1] |
1926 Ford Air Tour, piloted by Louis Meister, and another (designated the CA-3A) placed third in the 1927 Air Derby, piloted by Nick Mamer. One CW-3 and one CA-3 each were evaluated by the United States Army as trainers, but neither were purchased.
Versions
CA
- CA-3 Airster (1926) aka J4 Airster or B-V Airster
- 200 hp Wright J-4 (a.k.a. J-4 Whirlwind)
- Folding wings
- awarded the first ATC ever issued, March 1927 (ATC 1, 2-6)
- one modified under ATC 2-6 as 2p with 220 hp Wright J-5 as a trainer for Army trials
- CA-3A Airster (1926)
- 225 hp Wright J-5
- 3 built
- cost: $9,300
- CA-3B Airster (1926)
- one built
CW
- CW-3 OX5 Airster (1925)[7]
- 90hp Curtiss OX-5
- useful load: 770 lbs
- range: 475 miles
- Folding wings
- three built
- CW-3 Wright Trainer (1926)
- 220 hp Wright J-5
- useful load: 885 lbs
- range: 450 miles
- one built for unsuccessful military trainer trials
Specifications (CA-3A)
Data from Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1928[8]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Capacity: 2 pax, max useful load 885 lb (401 kg)
- Length: 24 ft 7.5 in (7.506 m)
- Wingspan: 35 ft 8 in (10.87 m)
- Height: 8 ft 10 in (2.69 m)
- Wing area: 303 sq ft (28.1 m2)
- Empty weight: 1,550 lb (703 kg)
- Gross weight: 2,995 lb (1,359 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 40 US gal (33.3 imp gal; 151.4 l) fuselage main tank and 22 US gal (18.3 imp gal; 83.3 l) centre-section gravity tank
- Powerplant: 1 × Wright J-5 Whirlwind 9-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engine, 225 hp (168 kW)
- Propellers: 2-bladed wooden fixed-pitch propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 125 mph (201 km/h, 109 kn)
- Range: 475 mi (764 km, 413 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 16,000 ft (4,900 m)
- Rate of climb: 950 ft/min (4.8 m/s)
- Time to altitude: 7,250 ft (2,210 m) in 10 minutes
See also
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
(Partial listing, only covers most numerous types)
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Buhl-Verville CA-3 Airster. |
Citations
- "Verville Sport Trainer AT". Aviation-history.com. Retrieved 2014-05-09.
- "The First Federal Aircraft Type Certificate" (PDF). www.faa.gov. 1927.
- "ATCs". Aerofiles.com. Retrieved 2014-05-09.
- http://www.hoaircraft.com/VintageBuhlpdf.pdf
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-01-28. Retrieved 2015-02-23.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Forden, Lesley. The Ford Air Tours: 1925-1931. New Brighton Minnesota: Aviation Foundation of America, 2003, First edition 1972. No ISBN.
- "Flight Global Magazine, April 8th, 1927, page 209". Flightglobal.com. 1926-04-08. Retrieved 2014-05-09.
- Grey, C.G., ed. (1928). Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1928. London: Sampson Low, Marston & company, ltd. p. 203c.
Bibliography
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. p. 216.
- http://www.aerofiles.com/_buhl.html
- Federal Aviation Administration history page
