Buggy (automobile)
Buggy is generally used to refer to any lightweight automobile with off road capabilities and sparse bodywork. Most are built either as a kit car or from scratch.
| Buggy | |
|---|---|
 Citroën Méhari, a French buggy | |
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Many |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | Lightweight |
| Related | Horse and buggy |
History
Originally used to describe very lightweight horse-drawn vehicles for one or two persons,[1] the term was extended to lightweight automobiles as they became popular.[2][3] As automobiles became increasingly sophisticated, the term briefly dropped out of use before being revived to describe more specialised off road vehicles.[4][5][6]
Types
- Bennett buggy, a Canadian, depression era term for an automobile pulled by a horse
- Dune buggy, designed for use on sand dunes
- Baja Bug, a modified Volkswagen Beetle
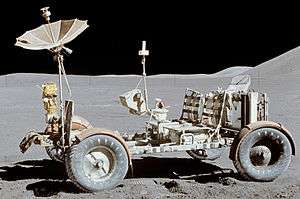
- Moon buggy, the vehicle used on the moon in the Apollo program
- Sandrail, a variant of the dune buggy
- Swamp buggy, designed for use in swamps
See also
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dune buggies. |
- Felton, William (1794–1795). "A treatise on carriages". London: printed for and sold by the author; by J. Debrett; R. Fadlder [sic]; J. Egerton; J. White; W. Richardson; and A. Jameson. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Advantages of the automobile buggy". Popular Mechanics. July 1909. p. 72. Retrieved 14 August 2013.
- "untitled". Logansport (Indiana) Daily Reporter. 4 December 1901. p. 3.
He is catapulted through space by the explosion of a ‘gasoline buggy’.
- "Amphibian 'Marsh buggy' used to hunt oil". Popular Mechanics. April 1937. p. 529. Retrieved 14 August 2013.
- "Jungle Buggy packs a load". Popular Science. May 1948. p. 122. Retrieved 14 August 2013.
- Hunn, Max (October 1954). "Swamp-buggy Steeplechase". Popular Mechanics. p. 137. Retrieved 14 August 2013.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.