Beechcraft Queen Air
The Beechcraft Queen Air is a twin-engined light aircraft produced by Beechcraft in several versions from 1960 to 1978. Based upon the Twin Bonanza, with which it shared key components such as wings, engines, and tail surfaces, but featuring a larger fuselage, it served as the basis for the highly successful King Air series of turboprop aircraft. It is often used as a private aircraft, a utility, or a small commuter airliner. Production ran for 17 years.
| Queen Air | |
|---|---|
.jpg) | |
| Bemidji Airlines Beech 65-A80 | |
| Role | Utility aircraft Airliner |
| Designer | Beech Aircraft Corporation |
| First flight | August 28, 1958 |
| Introduction | 1960 |
| Status | Active service |
| Produced | 1960-1978 |
| Number built | 930[1] |
| Unit cost | |
| Developed into | Beechcraft King Air Beechcraft Model 99 |
Design and development
The company's Twin Bonanza was reaching the limits of development so Beechcraft decided to develop a design with a larger fuselage and new tail which it designated the Beech 65. Early in development the United States Army which had been a customer of the Twin Bonanza (which it called the L-23 Seminole), ordered 68 aircraft under the designation L-23F. The prototype Beech 65 first flew on August 28, 1958.
The Queen Air is a twin-engined nine-seat low-wing cantilever cabin monoplane with a retractable landing gear with a nose wheel. It was initially powered by two 340 hp (250 kW) Lycoming IGSO-480 six-cylinder, horizontally opposed piston engine.
The Model 65 received a Federal Aviation Authority type certificate on February 4, 1959 and the first deliveries were made soon after. On February 8, 1960 a Queen Air achieved a new height record of 34,862 feet.
The basic Model 65 was in production until 1967 when the improved Model A65 with a swept rather than vertical tail was introduced. Production continued with further variants introducing pressurisation and turboprop engines.
Variants

65
This is the Queen Air powered by two Lycoming IGSO-480s producing 340 hp (250 kW) with a 1400-hour TBO. It had a gross weight of 7,700 lb (3,500 kg) with useful loads around 2,000 lb (910 kg). It is easily recognized by its straight unswept tail. Usually referred to as a "straight 65". Produced from 1960 to 1966.
A65
First produced in 1967 the A65 is very similar to the straight 65. The major change was the addition of a swept tail giving the aircraft a much more modern appearance. Available fuel was also increased to 264 gal with the extended wing. The Lyc. IGSO480 engines produced 340 HP @ 3400 rpm with 48 inches of manifold pressure. The gross weight was also increased to 8200 lbs (A65-8200). A few models were produced with a cargo door, next to the airstair door with provided a 48-inch opening. Production ended in 1971. This aircraft was used in Canada by Perimeter Airlines from 1968 to 1998.
70
Introduced in 1968. This aircraft is similar to the A65 in that it is powered by the 340 hp (250 kW) Lycoming IGSO-480, however it has the longer wing of the 80 series. This allows the 70 to have a greater lifting ability than the 65 but a lower fuel burn than the 80. It is, essentially, an A65 with the B80 wing. Its gross weight is 8,200 lb (3,700 kg) and useful loads can be as high as 2,400 lb (1,100 kg). Production ended in 1971.
80
First flying on June 22, 1961 and certified on February 20, 1962,[3] the Queen Air 80 was the first of the Queen Airs to have the more modern swept tail. It was powered by a larger Lycoming IGSO-540 which produced 380 hp (280 kW). Gross weight on the 80 is 8,000 lb (3,600 kg).
A80
The Queen Air A80 was introduced in 1964, and had a new wing, wingspan increasing from 45 feet 10 1⁄2 inches (13.98 m) to 50 feet 3 inches (15.32 m).[3] Other major changes to the A80 included a redesign of the aircraft nose, and a 500-pound increase in takeoff weight to 8,500 lb (3,900 kg) gross weight.
B80
Introduced in 1966 the B80 was to be the final production model. The B80 was by far the longest produced Queen Air with production lasting some 12 years. Its major improvement was the increased gross weight to a 8,800 lb (4,000 kg). This gave the B80 a useful load of well over 3,000 lb (1,400 kg). Production ended in 1978.
88

Introduced in 1965 the model 88 is a pressurized version of the Queen Air. This aircraft featured round cabin windows that make the 88 look quite similar to a 90 series King Air. It also shares the engines and long wing of the B80. Sales were slack due to its higher sales price and lower useful load as compared to the B80. Only 47 examples were ever produced of which two were converted to King Air standard and the model 88 aircraft was removed from production in 1969. The first two models of the King Air's official designation were BE65-90 and BE65-A90 owing to its Queen Air heritage.
Excalibur

This is a modification performed in the aftermarket by supplemental type certificates (STCs) to the BE65. It resolves the biggest issue of the Queen Air design, the engines. This is accomplished by replacing the rather cantankerous (if operated incorrectly) six-cylinder Lycoming IGSO-480s and Lycoming IGSO-540s, with the far more robust eight-cylinder Lycoming IO-720. This presents the major advantage of not having a gearbox or superchargers to cause maintenance and reliability problems. However the loss of the supercharger does limit the cruising altitude to below fifteen thousand feet. The other advantages gained are the overall increase in power to 400 hp (300 kW) per engine as well as a gross weight increase in most models. The gross weights are increased to 8,000 lb (3,600 kg) in all the short-wing aircraft (65, A65, 80), 8,200 lb (3,700 kg) in the 70, and 8800 in the other long-wing aircraft (A80, B80, 88). The US Army National Guard installed this modification on some of their aircraft. The Excalibur Queen Air can be recognized by the noticeably smaller engine cowlings and lower-set engines. This STC was originally designed and produced by Ed Swearingen who was well known for his work on the Twin Bonanza, Queen Air, and later Swearingen aircraft (Merlin and Metro). The ownership of this STC has changed hands many times over the years. The current owner is Bemidji Aviation which operates a fleet of Excalibur Queen Airs as well as other aircraft in the charter and freight role in the upper mid-west of the United States.
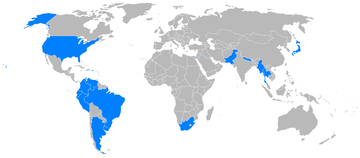
Military operators
_(cropped).jpg)
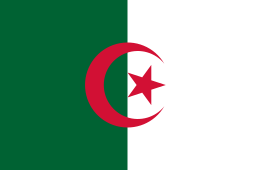
- Algerian Air Force - 3 B80s in service as of 1986.[5]

- Argentine Army Aviation[6]
- Argentine Naval Aviation - 5 B80s as of 1986.[7]



- Colombian Air Force[8]

- Air Force of the Dominican Republic[9]

- Ecuadorian Army[10]

- Border Security Force[11]

- Israeli Air Force

- Haiti Air Corps
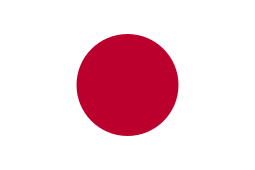
- Japan Air Self-Defense Force
- Japan Maritime Self Defense Force[12]



- Peruvian Air Force acquired 18 Queen Airs in 1965–1966.[13]
- Peruvian Army[14]
Specifications (Queen Air B80)
Data from Janes's All The World's Aircraft 1976-77.[20]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1–2
- Capacity: 4–9 passengers
- Length: 35 ft 6 in (10.82 m)
- Wingspan: 50 ft 3 in (15.32 m)
- Height: 14 ft 2 1⁄2 in (4.331 m)
- Wing area: 293.9 sq ft (27.30 m2)
- Airfoil: NACA 23020 at root, NACA 23012 at tip
- Empty weight: 5,277 lb (2,394 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 8,800 lb (3,992 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 214 US gal (178 imp gal; 810 L) normal, 264 US gal (220 imp gal; 1,000 L) with optional auxiliary tanks
- Powerplant: 2 × Lycoming IGSO-540 A1D supercharged, air-cooled flat-6 engines, 380 hp (280 kW) each
- Propellers: 3-bladed Hartzell constant speed
Performance
- Maximum speed: 215 kn (247 mph, 398 km/h) at 11,500 ft (3,500 m)
- Cruise speed: 159 kn (183 mph, 294 km/h) at 15,000 ft (4,600 m), 45% power (econ cruise)
- Stall speed: 71 kn (82 mph, 131 km/h) wheels and flaps down, IAS
- Range: 1,317 nmi (1,516 mi, 2,439 km) at 15,000 ft (4,600 m), 45% power
- Service ceiling: 26,800 ft (8,200 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,275 ft/min (6.48 m/s)
- Takeoff distance to 50 ft (15m): 2,556 ft (779 m)
- Landing distance from 50 ft (15m): 2,572 ft (784 m)
See also
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Beechcraft Queen Air. |
Notes
- General Aviation Manufactures Association Archived November 14, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- Flying Magazine: 23. November 2012. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - Taylor 1971, p. 234.
- Hawker Beechcraft Commercial Genealogy Serialization 1945-2007, p.32-36. June 2007.
- Hatch Flight International 29 November 1986, p. 32.
- "Back to 1987: Don Torcuato’s 40th anniversary air show" - Gaceta Aeronautica 28 October 2013 (accessed April 16, 2016)
- Hatch Flight International 29 November 1986, p. 34.
- Hatch Flight International 29 November 1986, p. 46.
- Hatch Flight International 29 November 1986, p. 49.
- Hatch Flight International 29 November 1986, p. 50.
- "Indian Border Security Force official website". Archived from the original on August 20, 2014. Retrieved January 30, 2016.
- Taylor 1971, p. 233.
- Air International May 1988, pp. 231–232.
- Hatch Flight International 29 November 1986, p. 78.
- Hatch Flight International 29 November 1986, p. 92.
- Harding 1990, pp. 14–15.
- Hatch Flight International 29 November 1986, p. 102.
- Hatch Air Pictorial April 1984, p. 127.
- Hatch Flight International 29 November 1986, p. 103.
- Taylor 1976, pp. 217–218.
Bibliography
- "Andean Air Power...The Peruvian Air Force". Air International, May 1988. Vol. 34, No. 5. pp. 224–235, 240.
- Harding, Stephen. U.S. Army Aircraft Since 1947. Shrewsbury, UK: Airlife Publishing Ltd., 1990. ISBN 1-85310-102-8.
- Hatch, Paul F. "Air Forces of the World: Venezuelan Army Air Arm (Aviación del Ejercito Venezolana)". Air Pictorial, April 1994, Vol. 46 No. 4. p. 127.
- Hatch, Paul F. "World's Air Forces 1986". Flight International, 29 November 1986, Vol. 130, No. 4039. pp. 30–104. ISSN 0015-3710.
- Taylor, John W.R. Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1971–72. London: Sampson Low, Marston & Co. Ltd., 1971. ISBN 0-354-00094-2.
- Taylor, John W.R. Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1976-77. London:Jane's Yearbooks, 1976. ISBN 0-354-00538-3.