BM-24
The BM-24 is a multiple rocket launcher designed in the Soviet Union. It is capable of launching 240mm rockets from 12 launch tubes. Versions of the BM-24 have been mounted on the ZIL-151 6x6 Truck chassis and the AT-S tracked artillery tractor, forming the BM-24T from the latter. Production began out of Automotive Factory no. 2 in 1947 Moscow.[3] Israel operated one battalion, consisting of vehicles captured from Egypt in the Six-Day War. The battalion took part in the Yom Kippur War and the 1982 Lebanon War.[4]
| BM-24M | |
|---|---|
BM-24M on a ZIL-157 chassis. Technical Museum of Togliatti. | |
| Type | Multiple rocket launcher |
| Place of origin | USSR |
| Production history | |
| Produced | 1947–58 |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 8,680 kg (19,140 lb) |
| Length | 6.7 m (22 ft 0 in) |
| Width | 2.3 m (7 ft 7 in) |
| Height | 2.9 m (9 ft 6 in) |
| Crew | 6[1] |
| Caliber | Diameter: 240 mm (9.4 in)
|
| Barrels | 12 in two rows |
| Elevation | +65°/0° |
| Traverse | 140° |
| Muzzle velocity | 465 m/s (1,530 ft/s) |
| Maximum firing range | Long rocket: 10.2 km (6.3 mi) Short rocket: 6.6 km (4.1 mi)[1] |
| Engine | ZIL-157 109HP 6-cylinder petrol |
| Suspension | Wheeled ZIL-157 6x6 chassis |
Operational range | 430 km (270 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 65 km/h (40 mph)[1] |
| BM-24T | |
|---|---|
 BM-24T on a AT-S tractor chassis. | |
| Type | Multiple rocket launcher |
| Place of origin | USSR |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 15,240 kg (33,600 lb) |
| Length | 5.8 m (19 ft 0 in) |
| Width | 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) |
| Height | 3.1 m (10 ft 2 in) |
| Crew | 6[2] |
| Caliber | Diameter: 240 mm (9.4 in)
|
| Barrels | 12 in two rows |
| Elevation | +45°/0° |
| Traverse | 210° |
| Muzzle velocity | 465 m/s (1,530 ft/s) |
| Maximum firing range | Long rocket: 10.2 km (6.3 mi) Short rocket: 6.6 km (4.1 mi)[1] |
| Engine | V-54-T 250HP 12-cylinder diesel |
| Suspension | Tracked |
Operational range | 380 km (240 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 35 km/h (22 mph)[1] |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to BM-24. |
Variants
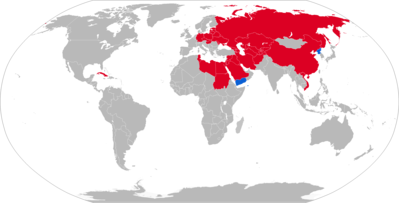
Operators
See also
Photo Gallery
 Reload drill
Reload drill BM-24 at Batey Haosef Museum
BM-24 at Batey Haosef Museum The Israeli 36 rocket MAR-240 on a Sherman tank chassis at Yad la-Shiryon Museum
The Israeli 36 rocket MAR-240 on a Sherman tank chassis at Yad la-Shiryon Museum
References
- Foss, Christopher (1977). Jane's pocket book of towed artillery. New York: Collier. p. 179. ISBN 0020806000. OCLC 911907988.
- Foss, Christopher (1977). Jane's pocket book of towed artillery. New York: Collier. p. 181. ISBN 0020806000. OCLC 911907988.
- "BM-24 (Katyusha) 6x6 Wheeled Multiple Launch Rocket System". Retrieved 2017-09-01.
- Prenatt 2016, p. 25.
- Prenatt 2016, p. 24.
- Military Balance 2016, p. 320.
- Military Balance 2016, p. 429.
- Diplomat, Ankit Panda, The. "South Korea's Joint Chiefs Want to Intercept North Korean Rocket Artillery Volleys". thediplomat.com. Retrieved 20 April 2018.
- Military Balance 2016, p. 265.
- Military Balance 2016, p. 324.
- Military Balance 2016, p. 334.
- Prenatt 2016, p. 30.
- Prenatt, Jamie; Hook, Adam (2016). Katyusha – Russian Multiple Rocket Launchers 1941–Present. New Vanguard 235. Oxford: Osprey Publishing Ltd. ISBN 978-1-4728-1086-1.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (February 2016). The Military Balance 2016. 116. Routlegde. ISBN 9781857438352.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.