Alexandra Land
Alexandra Land (Russian: Земля Александры, Zemlya Aleksandry) is a large island located in Franz Josef Land, Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russian Federation. Not counting detached and far-lying Victoria Island, it is the westernmost island of the Franz Josef Archipelago. It is the site of a Russian military base that was reopened in 2017.
| Земля Александры | |
|---|---|
Location of Alexandra Land in the Franz Josef Archipelago | |
 Alexandra Land | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Arctic |
| Coordinates | 80.6339°N 46.5839°E |
| Archipelago | Franz Josef Archipelago |
| Area | 1,050 km2 (410 sq mi) |
| Length | 70 km (43 mi) |
| Width | 30 km (19 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 382 m (1,253 ft) |
| Highest point | Kupol Lunny |
| Administration | |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 5 (2007) |

Geography
The highest point of the island, 382 m (1,253 ft), is the summit of Kupol Lunny (Купол Лунный) "Dome of the Moon", a large ice dome covering most of the western part of the island.[1] At the western end of the western glaciated area lies the Nordenskiöld Glacier;[2] other glaciers in the island are the Worcester Glacier (HMS Worcester Glacier)[3] and the Payer Glacier. The northern part of the island is unglacierized and its eastern end forms a peninsula stretching southwards, the Polyarnykh Letchikov Peninsula.[4] This peninsula is covered by Kupol Kropotkina (Купол Кропоткина), a smaller ice dome.[5] There are three large lakes on the island, including the Utinoye Lake (Duck Lake) and the Ledyanoye Lake (Ice Lake).
Dezhnev Bay (Zaliv Dezhneva) lies between the western part of the island and the Polyarnykh Letchikov Peninsula. Cape Thomas (Mys Tomasa) is the southernmost headland of the peninsula. Cambridge Channel (Proliv Kambritch) is a wide sound between Alexandra Land and Zemlya Georga.
At the southern end this island has two capes pointing southwestwards in its southernmost coast: Cape Lofley and Cape Ludlow. Cape Mary Harmsworth, the cape pointing westwards is the westernmost point of the Franz Josef Archipelago proper.
History and ecology
The English explorer Benjamin Leigh Smith, sighted Alexandra Land in 1880, but did not land. He named the area for Alexandra, then Princess of Wales.[6] An alternative account states that the name "Alexandra Land" commemorates Grand Duchess Alexandra Pavlovna of Russia (1783–1801), who became Archduchess of Austria in 1799 upon her marriage to Archduke Joseph of Austria, Palatine of Hungary (1776-1847).
Alexandra Land is home to Nagurskoye military base, Russia's northernmost military base, built in the 1950s.
Russian navigator Valerian Albanov of the Svyataya Anna reached Cape Mary Harmsworth in Alexandra Land in 1914 after his ordeal on the polar ice. Cape Mary Harmsworth was named after Alfred Harmsworth's wife Mary. Alfred Harmsworth, fellow of the Royal Geographical Society, was the main sponsor of the 1894 Jackson-Harmsworth Polar Expedition to Franz Josef Land.
The polar bear, Ursus maritimus, is found on Alexandra Land. The polar bear population in this region, as in other Arctic subregions, is genetically distinct from other polar bear subpopulations in differing Arctic subregions.[7]
During World War II, the Germans established an ill-fated meteorological station on the island, called Schatzgräber ("Treasure Hunter"). Most of the members were stricken with trichinosis after eating raw polar bear meat. The survivors were removed and the project abandoned.[8][9]
Nagurskoye
Nagurskoye is a Russian base located on the island at 80°49′N 47°25′E, on the site of the former meteorological station. It was named after pioneer pilot Jan Nagórski (1888-1976) and served as one of the most important meteorological stations in the archipelago during the Cold War. This base has a 1,500 m (4,900 ft) snow runway. An Antonov An-72 cargo aircraft crashed while landing at Nagurskoye on 23 December 1996.
A major new base, named the "Arctic Trefoil" (Arkticheskiy trilistnik) for its three-lobed structure, was constructed at Nagurskoye. It can house 150 soldiers for 18 months and has an area of 14,000 square metres (150,000 sq ft).[10]
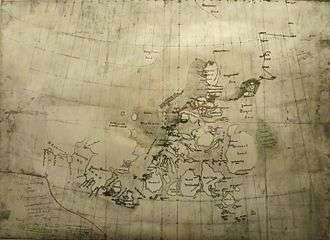 Original map of the route taken by Nansen and Johansen during their 1895–96 North Pole expedition: The "Alexandra" southern coast is included in the west. |
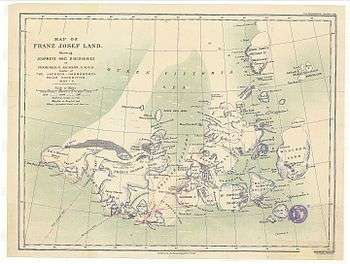 Alexandra Land in an 1898 map of Franz Josef Land showing the explorations of Frederick G. Jackson |
See also
- List of islands of Russia
- List of glaciers of Russia
- Queen Victoria Sea
References
- "Kupol Lunny". Mapcarta. Retrieved 6 October 2016.
- "Alexandra Land – Franz-Joseph-Land". Franz-Joseph-Land Info. Retrieved 8 October 2016.
- "Popular Science Monthly/Volume 55/September 1899/Scientific Literature". Wikisource. Retrieved 11 October 2016.
- "Poluostrov Polyarnykh Letchikov". Mapcarta. Retrieved 6 October 2016.
- "Kupol Kropotkina, Russia - Geographical Names, map, geographic coordinates". geographic.org.
-
Mills, William James (2003). "Alexandra Land (Franz Josef Land)". Exploring Polar Frontiers: A Historical Encyclopedia. 1. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. p. 9. ISBN 9781576074220. Retrieved 2 October 2019.
[...] discovery is generally credited to Benjamin Leigh Smith in 1880, who named it for Princess Alexandra, wife of Edward, Prince of Wales.
- C. Michael Hogan. Nicklas Stromberg (ed.). "Polar Bear: Ursus maritimus". Globaltwitcher.com. Archived from the original on 8 March 2012.
- Warnes, Indra (22 October 2016). "Secret NAZI ice-base ordered by Adolf Hitler discovered in Arctic". The Express. Retrieved 22 October 2016.
- Dege, Wilhelm (2003). War North of 80: The Last German Arctic Weather Station of World War II. Translated by William Barr. University of Calgary Press. ISBN 1-55238-110-2.
- Russia Builds Second Military base to Support Arctic Ambitions
Further reading
- Valerian Albanov, In the Land of White Death ISBN 9780679783619
External links

- Jackson-Harmsworth Polar Expedition