ActivityPub
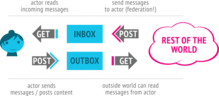
ActivityPub is an open, decentralized social networking protocol based on Pump.io's ActivityPump protocol.[1] It provides a client/server API for creating, updating and deleting content, as well as a federated server-to-server API for delivering notifications and content.
| Communication protocol | |
 | |
| Developer(s) | World Wide Web Consortium |
|---|---|
| Introduced | January 23, 2018 |
| Website | activitypub |
Project status
ActivityPub is a standard for the Internet in the Social Web Networking Group of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). At an earlier stage, the name of the protocol was "ActivityPump", but it was felt that ActivityPub better indicated the cross-publishing purpose of the protocol. It learned from the experiences with the older standard called OStatus.
In January 2018, the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) published the ActivityPub standard as a Recommendation.[2]
Former Diaspora community manager Sean Tilley wrote an article that suggests ActivityPub protocols may eventually provide a way to federate Internet platforms.[3]
Notable implementations
Federated (server-to-server) protocol
- Mastodon, a social networking software, implemented ActivityPub in version 1.6, released on 10 September 2017. It is intended that ActivityPub offer more security for private messages than the previous OStatus protocol does.[4]
- Misskey, a social networking software implementing ActivityPub.
- Pleroma, a social networking software.
- Nextcloud, a federated service for file hosting.
- PeerTube, a federated service for video streaming.[4]
- Friendica, a social networking software, implemented ActivityPub in version 2019.01.[5]
- Hubzilla has compatibility with ActivityPub with the plugin PubCrawl, from version 2.8 (October 2017).[6] Default protocol is Zot6.[7]
- Zap, a social networking software implementing Zot6 & ActivityPub.
- go-fed implements Server-to-Server and Client-to-Server ActivityPub in a Go library.[8]
- Pixelfed, a federated photo sharing platform.
- WriteFreely, a federated blogging platform.[9]
- Mobilizon, an event planner software from Framasoft.[10]
- LearnAwesome, a social network for sharing reviews about learning resources, implemented ActivityPub support in 2020.[11]
Client-to-server protocol
Client implementation
The following solutions are clear client based implementations of ActivityPub:[4]
- dokieli a client side editor using WebAnnotation and ActivityPub.[12]
Server implementation
The following solutions are clear server based implementations of ActivityPub:[8]
See also
References
- "Sandstorm and the Social Web". zenhack.net.
- "W3C Recommendation 23 January 2018".
- Tilley, Sean (23 September 2017). "A quick guide to The Free Network".
- "Server-Server - ActivityPub implementation reports". Retrieved 2019-01-02.
- "Friendica 2019.01 released". Retrieved 2019-01-24.
- "ChangeLog". GitHub.
- "4.0.3". Framagit.
- "ActivityStreams & ActivityPub in golang, oh my!". Retrieved 2019-01-02.
- "WriteFreely - IndieWeb". Retrieved 2019-11-27.
- actu@nextinpact.com. "Mobilizon de Framasoft gère maintenant la fédération des installations - Next INpact". www.nextinpact.com (in French). Retrieved 2019-12-19.
- "LearnAwesome implements ActivityPub broadcast of reviews". Retrieved 2020-06-21.
- "dokieli - homepage". Retrieved 2019-01-02.
- "microblog.pub - homepage". Retrieved 2019-01-02.
- "distbin - about page". Archived from the original on 2018-08-19. Retrieved 2019-01-02.
External links
- "Socialwg - W3C Wiki". www.w3.org. Retrieved 2017-11-05.
- "ActivityPub". www.w3.org. Retrieved 2017-11-05.
- "ActivityPub Rocks!". activitypub.rocks. Retrieved 2017-11-05.
- "ActivityPub: Specification", GitHub, World Wide Web Consortium, 2017-11-02, retrieved 2017-11-05