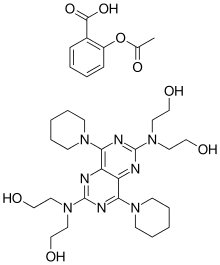
Acetylsalicylic acid/dipyridamole
The combination drug acetylsalicylic acid/dipyridamole (trade names Aggrenox, Asasantin) is a drug combination of:[1]
- Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin) - An extremely common NSAID that has anticoagulant effects
- Dipyridamole, a drug that inhibits platlet activation[2] when given chronically and causes vasodilation when given at high doses over short time.
 | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Acetylsalicylic acid | Anticoagulant |
| Dipyridamole | Anticoagulant |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Aggrenox, Asasantin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | UK Drug Information |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
The combination acts as an extended release formulation and is primarily used for platelet inhibition in patients suffering, or at risk from, acute coronary events and stroke.[3] Its use has been shown to be better than the use of either dipyridamole or aspirin alone.[4]
References
- FASS (the Swedish official drug catalog) > Asasantin Last update: 2009–08–17
- "Dipyridamole" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- Malinin, Alex I.; Eisert, Roswith M.; Atar, Dan; Barkagan, Zinoviy; Serebruany, Victor L. (2002). "Aggrenox (Extended-Release Dipyridamole and Low-Dose Aspirin in Combination): Protecting Platelets from Excessive Activation in Patients with Vascular Events". Heart Drug. 2 (2): 93–104. doi:10.1159/000063427.
- Serebruany, Victor L.; Malinin, Alex I.; Sane, David C.; Jilma, Bernd; Takserman, Aviv; Atar, Dan; Hennekens, Charles H. (September 2004). "Magnitude and time course of platelet inhibition with Aggrenox and Aspirin in patients after ischemic stroke: the AGgrenox versus Aspirin Therapy Evaluation (AGATE) trial". European Journal of Pharmacology. 499 (3): 315–324. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.07.114. PMID 15381054.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.