AMX 40 (1940)
The AMX 40 was a prototype of French Cruiser tank.
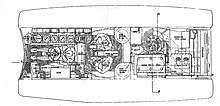
| AMX 40 (1940) | |
|---|---|
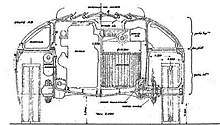
 AMX 40 Blueprint | |
| Type | Medium tank |
| Place of origin | France |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Joseph Molinié |
| Designed | 1938-1940 |
| Manufacturer | Ateliers de construction d'Issy-les-Moulineaux |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 16 t (35,000 lb)-18 t (40,000 lb) |
| Length | 5.33 m (17 ft 6 in) |
| Width | 2.45 m (8 ft 0 in) |
| Height | 2.37 m (7 ft 9 in) |
| Crew | 3 (commander/gunner, driver, loader) |
| Armor | 60 mm equivalent (turret front) 30-50 mm (hull sides) + 15 mm sponsons 40 mm (lower hull) sides + 15 mm side skirts 25 mm (double bottom) |
Main armament | 47 mm SA35 gun (176 rounds) |
Secondary armament | 7.5 mm MAC 1931 coaxial machine gun, 7.5 mm MAC 1934 anti-aircraft machine gun (4000 rounds) |
| Engine | Aster two-stroke diesel engine 160 hp (4-cylinder) or 220 hp (6-cylinder) |
| Transmission | RVR automatic |
| Suspension | Christie |
| Fuel capacity | 400 liters |
Operational range | >500 km (310 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 45–50 km/h (28–31 mph) |
Steering system | controlled differential |
History
In April 1939, a French military mission led by the General Martin visited the British military. They were impressed by the British Cruiser Mk III and decided to make an improved cavalry tank based on it which will later be known as AMX 40.[1][2]
After the start of World War 2, development of the AMX 40 commenced in March 1940 under the leadership of Joseph Molinié from Ateliers de construction d'Issy-les-Moulineaux. The AMX 40 was a Cruiser tank, planned to be a successor to the SOMUA S35 and Somua S40.[3] However, in July 1940, design was discontinued after the Fall of France.[3][4]
Development
The AMX 40 was to replace the obsolete SOMUA S35 and Somua S40 tanks.
Design
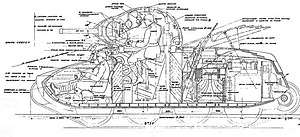
The AMX 40 was ahead of its time in some aspects; the hull and turret were well sloped and had no straight angles. The tank was manned by a crew of 3.[3]
Turret
The two-man egg-shaped turret had two openings for the optical rangefinder. The turret ring diameter was of only 90 cm. There was a circular access hatch of 60 cm in diameter at the rear of the turret.
There were no vision slits for the turret of the AMX 40. Vision was achieved by a panoramic periscope located on the top of the turret.[3]
Armament
The planned main armament was a 47 mm SA35 gun gun. 176 rounds were stowed in the fighting compartment in rotary and tilting magazines in order to be reached quickly.
Secondary armament included two 7.5mm machine guns; one coaxial machine gun and one anti-aircraft defence machine gun mounted on a ball joint behind the turret.[3]
Hull
The hull had rounded armor everywhere which increased the armor protection of the tank.[3]
Engine
The AMX 40 was supposed to use a 160 hp two-stroke Aster diesel engine similar to the one used on the AMX 38. The choice of diesel fuel significantly increased safety by preventing ignition at room temperature.[3]
The engine horsepower was noticeably less than the SOMUA S-35 (190 hp) and SOMUA S-40 (220 hp), despite the fact that the tank's weight was close to the SOMUA S-35. A 220 hp, six-cylinder version of the Aster engine was under development
Running gear
The chassis had 8 road wheels of 82 cm in diameter. There were no return rollers. The road wheels were protected by 15 mm steel side skirts.
The AMX 40 was a "convertible tank", in the event of a broken track[3] the crew could remove the tracks and use the two rear wheel drive, allowing the tank to travel at high speeds on roads. In wheeled mode, the tank was steered by pivoting the two front road wheels.
Communications
The AMX 40 was to be equipped with a radio.[5]
References
- Joseph Molinié,Les engins blindés du monde 1917-1967, 1981, Argout Editions, pg 14-15
- Stéphane Ferrard,GBM n°95, 2011, pg 78-86
- "1940 AMX 40 MEDIUM TANK" (in French). Retrieved 2020-02-28.
- "AMX 40 Medium Tank". Retrieved 2020-02-28.
- "AMX 40". Retrieved 2020-02-28.