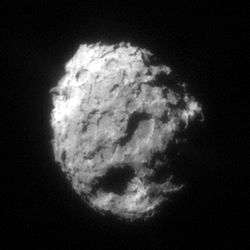
76P/West–Kohoutek–Ikemura
76P/West–Kohoutek–Ikemura is a Jupiter-family periodic comet in the Solar System with a current orbital period of 6.48 years.[1]
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Richard M. West at the European Southern Observatory Sky Atlas Laboratory, Geneva, Lubos Kohoutek at the Hamburg Observatory, Germany and Toshihiko Ikemura in Shinshiro, Japan |
| Discovery date | January–March 1975 |
| Orbital characteristics A | |
| Epoch | 2014-Dec-9 |
| Aphelion | 5.345 AU |
| Perihelion | 1.6012 AU |
| Semi-major axis | 3.4707 AU |
| Eccentricity | 0.5387 |
| Orbital period | 6.48 yr |
| Inclination | 30.48° |
| Last perihelion | 26 Oct 2019[1] 7 May 2013 |
| Next perihelion | 2026-04-13[1] |
The comet was initially spotted on a photographic plate by Richard M. West at the European Southern Observatory Sky Atlas Laboratory, Geneva in January 1975, when it had a brightness of magnitude 12.[2] Inability to predict its movement from a single image meant the comet had to be presumed lost.
In late February it was accidentally rediscovered by Lubos Kohoutek at the Hamburg Observatory, Germany and independently on 1 March by Toshihiko Ikemura in Shinshiro, Japan. After further observations the comets parabolic orbit was computed, which gave a perihelion date of 23 March 1975 and proved that all three sightings were of the same object, which was accordingly designated 76P/West–Kohoutek–Ikemura.
Further calculations by Brian G. Marsden determined the comet's elliptical orbit and revealed that it had passed only 0.012 AU from Jupiter on 22 March 1972. This close approach had reduced its orbital frequency from some 30 years to the current 6.48 years and its perihelion distance from 4.78 AU to 1.60 AU.
The comet has been observed at its successive returns in 1987, 1993, 2000, 2006 and 2013.
See also
References
- "76P/West-Kohoutek-Ikemura Orbit". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 2019-02-24.
- Kronk, Gary W. "76P/West-Kohoutek-Ikemura". Archived from the original on 2009-08-08. Retrieved 2019-02-26. (Cometography Home Page)
External links
- Orbital simulation from JPL (Java) / Horizons Ephemeris
- 76P/West-Kohoutek-Ikemura – Seiichi Yoshida @ aerith.net
| Numbered comets | ||
|---|---|---|
| Previous 75D/Kohoutek |
76P/West–Kohoutek–Ikemura | Next 77P/Longmore |