3200 Phaethon
3200 Phaethon /ˈfeɪ.əθɒn/ (previously sometimes spelled Phaeton), provisional designation 1983 TB, is an active[6] Apollo asteroid with an orbit that brings it closer to the Sun than any other named asteroid (though there are numerous unnamed asteroids with smaller perihelia, such as (137924) 2000 BD19).[7] For this reason, it was named after the Greek myth of Phaëthon, son of the sun god Helios. It is 5.8 km (3.6 mi) in diameter[4] and is the parent body of the Geminids meteor shower of mid-December. With an observation arc of 35+ years, it has a very well determined orbit.[1] The 2017 Earth approach distance of about 10 million km was known with an accuracy of ±700 m.[1]
 Radar image of 3200 Phaethon taken by Arecibo, December 17, 2017 | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | |
| Discovery date | October 11, 1983 |
| Designations | |
| (3200) Phaethon | |
| Pronunciation | /ˈfeɪ.əθɒn/ |
Named after | Phaëthon |
| 1983 TB | |
| |
| Adjectives | Phaethonian /feɪəˈθoʊniən/[2] |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch April 27, 2019 (JD 2458000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 12,941 days (35.43 yr) |
| Aphelion | 2.4028 AU (359 million km) |
| Perihelion | 0.13998 AU (20.9 million km) |
| 1.2714 AU (190 million km) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.88990 |
| 523.6 days (1.434 yr) | |
Average orbital speed | 19.9 km/s (45,000 mph) |
| 313.94° | |
| 0° 41m 15.108s / day | |
| Inclination | 22.260° |
| 265.22° | |
| 322.19° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.01955 AU (2.92 million km) |
| Venus MOID | 0.0469 AU (7.02 million km)[3] |
| Jupiter MOID | 2.7375 AU (410 million km) |
| TJupiter | 4.510 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 5.8 km (3.6 mi)[4] |
| 3.604 hours (0.1502 d)[1] | |
| 0.1066±0.011[1] | |
| F-type asteroid[1][5] | |
| 10.7 (December 14, 2017) | |
| 14.6[1] | |
Discovery
Phaethon was the first asteroid to be discovered using images from a spacecraft. Simon F. Green and John K. Davies discovered it in images from October 11, 1983, while searching Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS) data for moving objects. It was formally announced on October 14 in IAUC 3878 along with optical confirmation by Charles T. Kowal, who reported it to be asteroidal in appearance. Its provisional designation was 1983 TB, and it later received the numerical designation and name 3200 Phaethon in 1985.
Orbital characteristics
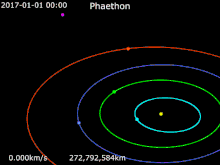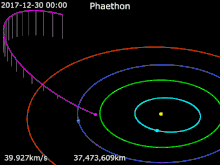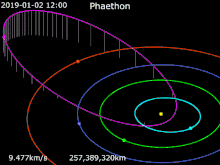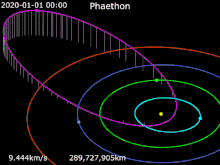
Sun · Mercury · Venus · Earth · Mars · 3200 Phaethon
Phaethon is categorized as an Apollo asteroid, as its orbital semi-major axis is greater than that of the Earth's at 1.27 AU (190 million km; 118 million mi). It is also suspected to be a member of the Pallas family of asteroids.[8]
Its most remarkable distinction is that it approaches the Sun closer than any other named asteroid: its perihelion is only 0.14 AU (20.9 million km; 13.0 million mi) — less than half of Mercury's perihelial distance. It is a Mercury-, Venus-, Earth-, and Mars-crosser as a result of its high orbital eccentricity. The surface temperature at perihelion could reach around 1,025 K (750 °C; 1,390 °F).
Phaethon is a possible candidate for detecting general relativistic and/or solar oblateness effects in its orbital motion due to the frequent close approaches to the Sun.[9]
Potentially hazardous asteroid
Phaethon is categorized as a potentially hazardous asteroid (PHA),[1][10] but that does not mean there is a near-term threat of an impact. It is a potentially hazardous asteroid merely as a result of its size (absolute magnitude H ≤ 22) and Earth minimum orbit intersection distance (Earth MOID ≤ 0.05 AU).[11] The Earth minimum orbit intersection distance (E-MOID) is 0.01945 AU (2,910,000 km; 1,808,000 mi), which is defined by the shortest distance between the orbit of Phaethon and the orbit of Earth.[1] With a 30+ year observation arc, the orbit of Phaethon is very well understood with very small uncertainties.[1] Close approaches of Phaethon are well constrained for the next 400 years.[9]
| PHA | Date | Approach distance in lunar distances | Abs. mag (H) |
Diameter (C) (m) |
Ref (D) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal (B) | Minimum | Maximum | |||||
| (143651) 2003 QO104 | 1981-05-18 | 2.761 | 2.760 | 2.761 | 16.0 | 1333–4306 | data |
| 2014 LJ21 | 1989-08-01 | 7.034 | 6.843 | 7.224 | 16.0 | 1333–4306 | data |
| 4179 Toutatis | 1992-12-08 | 9.399 | 9.399 | 9.399 | 15.30 | 2440–2450 | data |
| 4179 Toutatis | 2004-09-29 | 4.031 | 4.031 | 4.031 | 15.30 | 2440–2450 | data |
| (159857) 2004 LJ1 | 2038-11-16 | 7.719 | 7.719 | 7.719 | 15.4 | 1746–4394 | data |
| (4953) 1990 MU | 2058-06-05 | 8.986 | 8.984 | 8.988 | 14.1 | 3199–10329 | data |
| 4179 Toutatis | 2069-11-05 | 7.725 | 7.724 | 7.725 | 15.30 | 2440–2450 | data |
| (52768) 1998 OR2 | 2079-04-16 | 4.611 | 4.611 | 4.612 | 15.8 | 1462–4721 | data |
| (415029) 2011 UL21 | 2089-06-25 | 6.936 | 6.935 | 6.938 | 15.7 | 1531–4944 | data |
| 3200 Phaethon | 2093-12-14 | 7.714 | 7.709 | 7.718 | 14.6 | 4900–5300 | data |
| (52768) 1998 OR2 | 2127-04-16 | 6.536 | 6.510 | 6.563 | 15.8 | 1462–4721 | data |
| (A) This list includes near-Earth approaches of less than 10 lunar distances (LD) of objects with H brighter than 16. (B) Nominal geocentric distance from the center of Earth to the center of the object (Earth has a radius of approximately 6,400 km). (C) Diameter: estimated, theoretical mean-diameter based on H and albedo range between X and Y. (D) Reference: data source from the JPL SBDB, with AU converted into LD (1 AU≈390 LD) (E) Color codes: unobserved at close approach observed during close approach upcoming approaches | |||||||
Physical characteristics
Phaethon is an asteroid with fairly unusual characteristics in that its orbit more closely resembles that of a comet than an asteroid; it has been referred to as a "rock comet".[12] In recent studies performed by NASA's STEREO spacecraft, dust tails have been observed,[13] and in 2010, Phaethon was detected ejecting dust.[14] It is possible that the Sun's heat is causing fractures similar to mudcracks in a dry lake bed.[14] This occurs because Phaethon's orbit takes it closer to the Sun than any other named asteroid (0.14 AU at perihelion) causing extreme heating and enough solar radiation pressure to push any separated pieces off the asteroid's surface. Since its discovery, several other objects were found exhibiting mixed cometary and asteroidal features, such as 133P/Elst–Pizarro, leading to a new class of objects dubbed "active asteroids".[6]
In 2018, observations revealed that Phaethon was blue in color, which is an extremely rare occurrence among asteroids. In contrast, most asteroids tend to be grey or red.[15][16] In 2020, polarimentric study revealed Phaeton has a surface with steep slopes covered by a mix of regolith with larger pebbles.[17] Phaethon's composition fits the notion of its cometary origin; it is classified as a F-type asteroid because it is composed of dark material.[1][5]
Meteor shower
Shortly after its discovery, Fred Whipple observed that the "orbital elements of 1983 TB shown on IAUC 3879 are virtually coincident with the mean orbital elements of 19 Geminid meteors photographed with the super-Schmidt meteor cameras".[18] In other words, Phaethon is the long-sought parent body of the Geminids meteor shower of mid-December.
Planned flyby
DESTINY+ (Demonstration and Experiment of Space Technology for INterplanetary voYage Phaethon fLyby dUSt science) is a planned mission to flyby 3200 Phaethon, as well as various minor bodies originating from it. The spacecraft is being developed by the Japanese space agency JAXA, and will demonstrate advanced technologies for future deep space exploration. DESTINY+ is planned to be launched in 2022.
Close approaches
Phaethon approached to 0.120895 AU (18,085,600 km; 11,237,900 mi) of Earth on December 10, 2007,[1] and was detected by radar at Arecibo.[9] When Phaethon came to perihelion in July 2009, it was found to be brighter than expected.[19][20] During its approach, the STEREO-A spacecraft detected an unexpected brightening, roughly by a factor of two.[12]
2010 approach

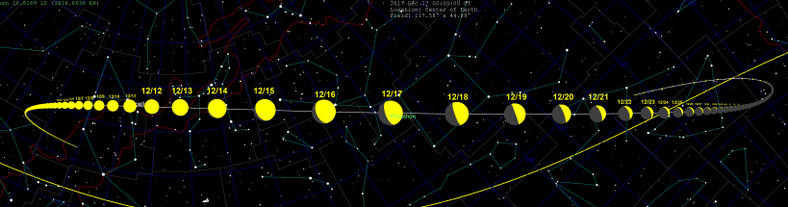
2017 approach
On December 16, 2017, at 23:00 UT, Phaethon passed 0.06893169 AU (10,312,034 km; 6,407,601 mi) from Earth (27 lunar distances).[1] The Earth approach distance was known with a 3-sigma accuracy of ±700 m.[1][lower-alpha 1] This was the best opportunity to date for radar observations by Goldstone and Arecibo, with a resolution of 75 meters/pixel (246 feet/pixel).[9]
The asteroid was bright enough to see in small telescopes, peaking at magnitude 10.8 between December 13–15 while dimming slightly to magnitude 11 on December 16 at closest approach.[21] Arecibo made observations of Phaethon from December 15–19.[4] It will not make an Earth approach closer than the 2017 passage until December 14, 2093, when it will pass 0.01981 AU (2,964,000 km; 1,841,000 mi) from Earth.[1][22]
Notes
- In 2014, JPL 374 (solution date 2014-Sep-12) showed a 2017 Earth approach distance with an accuracy of ±80 km. Math: (MAX−MIN) * AU / 2
References
- "3200 Phaethon (1983 TB)". JPL Small-Body Database. Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Archived from the original on June 5, 2019. Retrieved June 5, 2019.
- "phaeton". Oxford English Dictionary (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. September 2005. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- "(3200) Phaethon Orbit". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved June 5, 2019.
- Agle, D. C.; Brown, Dwayne; Farukhi, Suraiya (December 22, 2017). "Arecibo Radar Returns with Asteroid Phaethon Images". NASA. Retrieved January 8, 2018.
- Kartashova, A.; Husarik, M.; Ivanova, O.; Kokhirova, G.; Bakanas, E.; Sokolov, I.; Khamroev, U. Kh.; Ibragimov, A. A. (June 5, 2019), Photometric observations of the asteroid 3200 Phaethon using small and middle telescopes, arXiv:1906.01064
- Jewitt, David; Hsieh, Henry; Agarwal, Jessica (2015). Michel, P.; et al. (eds.). "The Active Asteroids" (PDF). Asteroids IV. University of Arizona: 221–241. doi:10.2458/azu_uapress_9780816532131-ch012. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- "JPL Small-Body Database Search Engine — Constraints: asteroids and q < 0.141 (au)". JPL Small-Body Database. Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved September 5, 2011. Take notice of the orbit condition number (the lower the number, the lower the orbit's uncertainty).
- Jaggard, Victoria (October 12, 2010). "Exploding Clays Drive Geminids Sky Show?". National Geographic. Archived from the original on August 11, 2017. Retrieved August 10, 2017.
- Benner, Lance A. M. (2017). "Goldstone Radar Observations Planning: Asteroid 3200 Phaethon". NASA/JPL Asteroid Radar Research. Retrieved November 26, 2017.
- Phillips, Tony (December 3, 2007). "Asteroid Shower". Science@NASA. NASA. Retrieved April 4, 2017.
- "NEO Groups". Near Earth Object Program. NASA. Archived from the original on November 2, 2016.
- Jewitt, David; Li, Jing (2010). "Activity in Geminid Parent (3200) Phaethon". The Astronomical Journal. 140 (5): 1519. arXiv:1009.2710. Bibcode:2010AJ....140.1519J. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/140/5/1519.
- Jewitt, David; Li, Jing; Agarwal, Jessica (2013). "The Dust Tail of Asteroid (3200) Phaethon". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 771 (2). L36. arXiv:1306.3741. Bibcode:2013ApJ...771L..36J. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/771/2/L36.
- Sutherland, Paul (September 10, 2013). "Why an asteroid is crumbling into meteor dust". Skymania.com. Archived from the original on February 22, 2015. Retrieved September 10, 2013.
- Eleanor Imster (November 1, 2018). "Rare blue asteroid sometimes behaves like a comet". EarthSky. Retrieved April 6, 2019.
- Eric Mack (October 23, 2018). "A look at 3200 Phaethon: A big, bizarre, blue asteroid we plan to visit". CNET. Retrieved April 6, 2019.
- Golubeva, L. F.; Shestopalov, D. I.; Kvaratskhelia, O. I. (2020). "Polarimetric properties of asteroid 3200 Phaethon". arXiv:2001.00789 [astro-ph.EP].
- Whipple, F. L. (October 25, 1983). Marsden, B. G. (ed.). "1983 TB and the Geminid Meteors". IAU Circular. 3881. 1. Bibcode:1983IAUC.3881....1W.
- Shanklin, Jonathan (2009). "Comet Section: 2009 News". British Astronomical Association. Retrieved September 20, 2009.
- Battams, K.; Watson, A. (June 2009). "(3200) Phaethon". IAU Circular. 9054. 3. Bibcode:2009IAUC.9054....3B.
- "(3200) Phaethon: Ephemerides for December 2017". NEODyS-2. University of Pisa Department of Mathematics. Retrieved November 26, 2017.
- "(3200) Phaethon: Close Approaches". NEODyS-2. University of Pisa Department of Mathematics. Retrieved May 18, 2009.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 3200 Phaethon. |
- (3200) Phaethon by the Associazione Friulana di Astronomia e Meteorologia
- "The 2004 Geminid Meteor Shower" by Science@NASA
- "ScienceCasts: Rock Comet Meteor Shower" by Science@NASA on YouTube.com
- Phaethon orbit and observations at IAU Minor Planet Center
- 3200 Phaethon at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- Ephemeris · Obs prediction · Orbital info · MOID · Proper elements · Obs info · Close · Physical info · NEOCC
- 3200 Phaethon at the JPL Small-Body Database

.gif)
