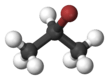
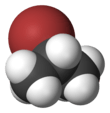
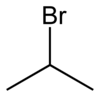
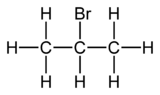
2-Bromopropane
2-Bromopropane, also known as isopropyl bromide and 2-propyl bromide, is the halogenated hydrocarbon with the formula CH3CHBrCH3. It is a colorless liquid. It is used for introducing the isopropyl functional group in organic synthesis. 2-Bromopropane is prepared by heating isopropanol with hydrobromic acid.[3]
 | |||
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Bromopropane[1] | |||
| Other names
Isopropyl bromide[2] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 741852 | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.778 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| MeSH | 2-bromopropane | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2344 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H7Br | |||
| Molar mass | 122.993 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.31 g mL−1 | ||
| Melting point | −89.0 °C; −128.1 °F; 184.2 K | ||
| Boiling point | 59 to 61 °C; 138 to 142 °F; 332 to 334 K | ||
| 3.2 g L−1 (at 20 °C) | |||
| log P | 2.136 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 32 kPa (at 20 °C) | ||
Henry's law constant (kH) |
1.0 μmol Pa−1 mol−1 | ||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.4251 | ||
| Viscosity | 0.4894 mPa s (at 20 °C) | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C) |
135.6 J K mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−129 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−2.0537–−2.0501 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |   | ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H225, H360, H373 | ||
| P210, P308+313 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 19 °C (66 °F; 292 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanes |
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Preparation
2-Bromopropane is commercially available. It may be prepared in the ordinary manner of alkyl bromides, by reacting isopropanol with phosphorus and bromine,[4] or with phosphorus tribromide.[5]
Safety
Short-chain alkyl halides are often carcinogenic.
The bromine atom is at the secondary position, which allows the molecule to undergo dehydrohalogenation easily to give propene, which escapes as a gas and can rupture closed reaction vessels. When this reagent is used in base catalyzed reactions, potassium carbonate should be used in place of sodium or potassium hydroxide.
Further reading
- M G. Gergel “Excuse Me Sir, Would You Like to Buy a Kilo of Isopropyl Bromide?” Pierce Chemical Co. (1979). (story of start-up chemical company).
References
- "2-bromopropane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 27 March 2005. Identification. Retrieved 15 June 2012.
- Wilfred L.F. Armarego and Christina Li Lin Chai, Purification of laboratory chemicals, 7th edition, Butterworth-Heinemann, 2013, p. 176
- Merck Index of Chemicals and Drugs, 9th ed. Monograph 5071
- Oliver Kamm and C. S. Marvel (1941). "Alkyl and alkylene bromides". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 1, p. 25
- C. R. Noller and R. Dinsmore (1943). "Isobutyl bromide". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 2, p. 358