19521 Chaos
19521 Chaos is a cubewano, a Kuiper-belt object not in resonance with any planet. It is a likely dwarf planet. Chaos was discovered in 1998 by the Deep Ecliptic Survey with Kitt Peak's 4 m telescope. Its albedo is 0.050+0.030
−0.016,[7] making it, with its absolute magnitude (H) of 4.8,[4] 600+140
−130 km in diameter.[7] It is named after the primeval state of existence in Greek mythology, from which the first gods appeared.
 19521 Chaos as imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope in September 2001 | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Deep Ecliptic Survey |
| Discovery date | 19 November 1998 |
| Designations | |
| (19521) Chaos | |
| Pronunciation | /ˈkeɪ.ɒs/ |
Named after | Chaos |
| 1998 WH24 | |
| TNO (cubewano)[1][2] | |
| Adjectives | Chaotian /keɪˈoʊʃən/[3] |
| Orbital characteristics[4] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 3 | |
| Observation arc | 5902 days (16.16 yr) |
| Earliest precovery date | 17 October 1991 |
| Aphelion | 50.636 AU (7.5750 Tm) |
| Perihelion | 40.957 AU (6.1271 Tm) |
| 45.796 AU (6.8510 Tm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.10567 |
| 309.92 yr (113199 d) | |
Average orbital speed | 4.3931 km/s |
| 337.2998° | |
| 0° 0m 11.449s / day | |
| Inclination | 12.0502° |
| 50.0239° | |
| 58.4097° | |
| Jupiter MOID | 35.8 AU (5.36 Tm) |
| Neptune MOID | 12.5 AU (1.87 Tm)[5] |
| TJupiter | 5.884 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 615± ? [6] 600+140 −130 km [7] ~665 [8] |
| 3.985 d | |
| 0.050+0.030 −0.016 [7] | |
| B–V=0.95±0.03 [8] V–R=0.63±0.03 [8] V–I=1.25±0.04 [8] | |
| 4.8 [4] 5.0 [6][8] | |
Orbit
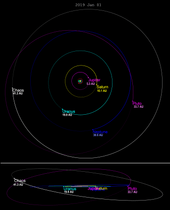
19521 Chaos has an orbital period of approximately 309 years. Its orbit is longer, but less eccentric than the orbit of Pluto. 19521 Chaos's orbit is inclined approximately 12° to the ecliptic. Its orbit never crosses the orbit of Neptune. Currently, the closest approach possible to Neptune (MOID) is 12.5 AU (1.87 billion km).[5]
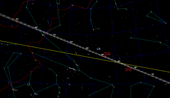
Chaos is at perihelion around 2035, coming as close as 40 AUs from Earth. Its brightest magnitude will be 20.8.
Physical characteristics
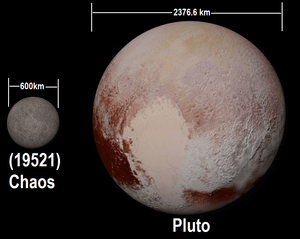
Chaos is a dark object, with an albedo estimated at 5%, implying a diameter of 600 km. It rotates slowly in 3.985 days. According to Brown, it is a likely dwarf planet.[6]
References
- "MPEC 2008-O05 : Distant Minor Planets (2008 AUG. 2.0 TT)". Minor Planet Center. 17 July 2008. Retrieved 8 January 2011.
- Buie, Marc W. (9 November 2004). "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 19521". Space Science Department. SwRI. Retrieved 28 September 2008.
- Thayer (1994). Gray World, Green Heart.
- "19521 Chaos (1998 WH24)". JPL Small-Body Database Browser (2007-12-14 last obs). Retrieved 11 April 2016.
- "(19521) Chaos = 1998 WH24 orbit". IAU Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- Brown, Michael E. "How many dwarf planets are there in the outer solar system? (updates daily)". California Institute of Technology. Retrieved 25 December 2018.
- Vilenius, E.; Kiss, C.; Mommert, M.; Müller, T.; Santos-Sanz, P.; Pal, A.; et al. (2012). ""TNOs are cool": A survey of the trans-Neptunian region VI. Herschel / PACS observations and thermal modeling of 19 classical Kuiper belt objects". arXiv:1204.0697v1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201118743. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Doressoundiram, A.; Peixinho, N.; de Bergh, C.; Fornasier, S.; Thébault, Ph.; Barucci, M.A.; Veillet, C. (October 2002). "The color distribution in the Edgeworth-Kuiper Belt". The Astronomical Journal. 124 (4): 2279–2296. arXiv:astro-ph/0206468. Bibcode:2002AJ....124.2279D. doi:10.1086/342447.
External links
- "Original Minor Planet Electronic Circular (1998-X08) for 19521 Chaos".
- "Revised Minor Planet Electronic Circular (1999-V03) 19521 Chaos".
- 19521 Chaos at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 19521 Chaos at the JPL Small-Body Database

_(cropped).jpg)
