Zakir Husain Delhi College
 | |
Former names | Delhi College, Zakir Husain College, Anglo Arabic College[1] |
|---|---|
| Motto | Live By Love |
| Established | 1692[1] |
| Principal | Dr. Sulekh Chandra |
| Location | New Delhi, India |
| Affiliations | University of Delhi |
| Website |
www |
Zakir Husain Delhi College, formerly Zakir Husain College, Anglo Arabic College and Delhi College, founded in 1692, is the oldest existing educational institution in Delhi, and is a constituent college of the University of Delhi, offering undergraduate and post graduate courses in Arts, Commerce and Sciences.[2] It has had a considerable influence on modern education as well as Urdu and Islamic learning in India, and today remains the only Delhi University college offering BA (Hons) courses in Arabic and Persian.[3]
History
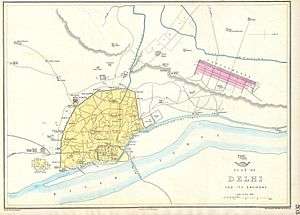
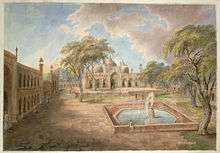
It was initially founded by Ghaziuddin Khan, a general of Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb, a leading Deccan commander and the father of Qamar-ud-din Khan, Asaf Jah I, the founder of the Asaf Jahi dynasty of Hyderabad, also known as the first Nizam of Hyderabad, in 1690s, and was originally termed Madrasa Ghaziuddin Khan after him. However, with a weakening Mughal Empire, the Madrasa closed between 1790 and 1791, but with the support of local nobility, an oriental college for literature, science and art, was established at the site in 1792.[1][3]
It stood just outside the walled city of Delhi outside the Ajmeri Gate, near Paharganj close to the New Delhi railway station. It was originally surrounded by a wall and connected to the walled city fortifications and was referred to as the College Bastion.[4][5]
It was reorganized as the 'Anglo Arabic College' by the British East India Company in 1828 to provide, in addition to its original objectives, an education in English language and literature. The object was “to uplift” what the Company saw as the “uneducated and half-barbarous people of India.” Behind the move was Charles Trevelyan, the brother-in-law of Thomas Babingdon Macaulay, the same infamous Macaulay whose famously declared that “a single shelf of a good European library was worth the whole native literature of India and Arabia”.[6]
Rev. Jennings started secret Bible classes in the officially secular Delhi College. In July 1852, two prominent Delhi Hindus, Dr. Chaman Lal, one of Zafar’s personal physicians, and his friend Master Ramchandra,[7] a mathematics lecturer at the Delhi College, baptised a public ceremony at St. James' Church, Delhi.[3]
Dr. Sprenger, then principal, presided over the founding of the college press, the Matba‘u ’l-‘Ulum and founded the first college periodical, the weekly Qiranu ’s-Sa‘dain, in 1845.
Another cultural intermediatory was Mohan Lal Kashmiri, diplomat, and author, who worked for the East India Company and was educated at the college.
It was renamed Zakir Husain College in 1975 by Indira Gandhi government after Dr. Zakir Husain, a distinguished educator and a President of India.[2] The college was later shifted to its present building outside Turkman Gate in 1986, the old structure in the Madrasa Ghaziuddin complex, still houses a hostel for the college.[5] It was declared a heritage monument by the ASI in 2002. Then in 2008, a separate archive on its history was set up within the college library, with centuries-old books and documents on display, chronicling its 300-year-old history.[1]
Alumni and impact
It has had a number of distinguished alumni. Sir Syed Ahmed Khan, the founder of Aligarh Muslim University, Maulana Mohammed Hussain Azad, the father of Urdu prose, Deputy Nazir Ahmed, the Urdu essayist and ICS, poets, Ali Sardar Jafri and Akhtar ul-Iman, Mirza M N Masood, an Indian hockey olympian, eminent linguist and the 5th Vice-Chancellor of Jamia Millia Islamia Professor Emeritus Masud Husain Khan, Khwaja Ahmed Farooqui (literature), Professor A N Kaul (pro-vice chancellor, Delhi University), J N Dixit (Defence Analyst), Professor Gopi Chand Narang (world-renowned Urdu/Persian critic), Pankaj Vohra (Associate Editor, Hindustan Times), B N Uniyal, Shahid Siddiqui, Manmohan, Mukul Vyas, Chandra Prabha, Habib Akhtar, M Afzal (journalists) and politicians like Jagdish Tytler and Sikandar Bakht.[1][3]
Among the greats of Delhi College was Professor Bhisham Sahni of the English department who was a noted writer and dramatist. Professor Sahni was the brother of actor Balraj Sahni.
It's said that Ghalib was once a candidate for the Persian post for Delhi College. However, the administrator conducting the interview failed to come out to greet him, and an offended Ghalib left.[3]
Mamluk Ali Nanutavi, the distinguished scholar, who descendants founded Darul Uloom Deoband, taught Arabic here in 1830s.[3]
Zakir Husain Delhi College offers science, humanities and commerce as well as language courses. One important feature of the college is that it is (at least used to be) the only college in Delhi which offers Graduation courses to male students in Psychology. All other colleges which offer this course are exclusively for female students.
Zakir Husain Memorial Trust
Zakir Husain Delhi College is run by the Zakir Husain Memorial Trust since 1975.[2][5]
Mirza Mehmood Begg Library & Book Bank
The College has a library possessing about 1,18,462 books. It runs on open shelf system but some important text books are also kept in reserve section.It not only caters to the academic requirements but also houses leisure books and books to increase general awareness.The Library is named after the college principal Mirza Mehmood Begg.
Salman Gani Hashmi Auditorium
The College has an auditorium with a seating capacity of 417 persons. Various cultural programmes, lectures and college annual function are also organised in this auditorium. This auditorium is named after the former college principal Salman Gani Hashmi.
College Archives
The Delhi College Archives, situated in a section of the M. M. Begg Library, was inaugurated by Professor Sabyasachi Bhattacharya, Chairman, Indian Council of Historical Research, on February 18, 2008.
The archives contain a large number of files relating to the college and significant developments in higher education in Delhi and North India from 1823 onwards. These have been located within the National Archives of India and the Delhi Archives, and analyzed over the last couples of years.
Original writings by teachers and alumni of the college in Urdu, Persian and English are also available in the archives. Text bookbs prepared and/or used during the 19th Century for instruction in mathematics, history, geography, philosophy, literature etc., are on display. The archives also contains secondary sources and books relating to Delhi College and the intellectual ferment in Delhi region during the 18th and 19th centuries.
Zakir Husain Memorial Lecture
A major annual event in the college calendar is the Zakir Husain Memorial Lecture to commemorate Dr. Zakir Husain. The speaker is an eminent personality of his field. It is organized in the 1st week of February. Zakir Husain Memorial Lecture is organized since 2006 annually. The lecture has been delivered by the following persons so far:
- Aruna Roy (2006)
- Professor Sukhadeo Thorat (2007)
- Intizar Hussain (2008)
- Hamid Ansari (2009)
- Professor B. B. Bhattacharya (2010)
- Soli Sorabjee (2011)
- Professor C. M. Naim (2012)
- Professor V.S. Chauhan (2013)
Convocation Ceremony
This is the only college in the Delhi University which holds convocation ceremony.
See also
- Mohan Lal (Zutshi)
- List of colleges affiliated with the University of Delhi
- Anglo Arabic Senior Secondary School another descedent of the original institution
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Firoz Bakht Ahmad (31 December 2003). "Anglo Arabic School: an academic legacy of the Mughals". The Milli Gazette (newspaper). Retrieved 12 January 2018.
- 1 2 3 Zakir Hussain College to get a new name Times of India (newspaper), Published 26 December 2011, Retrieved 12 January 2018
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Gail Minault. "Delhi College and Urdu" (PDF). Retrieved 12 January 2018.
- ↑ "Plan of Delhi and its environs," by Edward Weller, for the "Weekly Dispatch," published in 1857, Retrieved 12 January 2018
- 1 2 3 Two Circle News (29 July 2010). "New name for Zakir Hussain College". Retrieved 12 January 2018.
- ↑ The Delhi College Traditional Elites, the Colonial State, and Education before 1857, The Madrasa of Ghaziu'd-Din Khan at Delhi, Ebba Koch
- ↑ http://minds.wisconsin.edu/handle/1793/18323 Minault, Gail. Master Ramchandra of Delhi College: Teacher, Journalist, and Cultural Intermediary. Annual of Urdu Studies vol. 18 (2003), Retrieved 12 January 2018
External links
- Official website Zakir Husain Delhi College
