World War II reparations
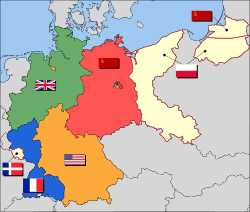
After World War II, both West Germany and East Germany were obliged to pay war reparations to the Allied governments, according to the Potsdam Conference. Other Axis nations were obliged to pay war reparations according to the Paris Peace Treaties, 1947.
Early propositions
An early plan for a post-war Germany was the Morgenthau plan with terms that would have essentially transformed Germany to an agrarian society. The French Monnet Plan would have transferred the Ruhr Area to France. This position was completely changed by the London Agreement on German External Debts, also known as the London Debt Agreement (German: Londoner Schuldenabkommen) of 1953.
Recipients
Greece

As a result of the Nazi German occupation, much of Greece was subjected to enormous destruction of its industry (80% of which was destroyed), infrastructure (28% destroyed), ports, roads, railways and bridges (90%), forests and other natural resources (25%)[1][2][3] and loss of civilian life (7.02–11.17% of its citizens).[4][5] The occupying Nazi regime forced Greece to pay the cost of the Nazi occupation in the country and requisite raw materials and food for the occupation forces, creating the conditions for the Great Famine. Furthermore, in 1942, the Greek Central Bank was forced by the occupying Nazi regime to loan 476 million Reichsmarks at 0% interest to Nazi Germany.
After the war, in 1960, Greece accepted 115 million Marks from West Germany as compensation for Nazi crimes. Nevertheless, past Greek governments have insisted that this was only a down-payment, not complete reparations.[6] In 1990, immediately prior to German reunification, West Germany and East Germany signed the Two Plus Four Agreement with the former Allied countries of the United States, United Kingdom, France, and the Soviet Union, but not Greece. Since that time, Germany has unilaterally insisted that all matters concerning World War II, including further reparations to Greece, are closed. On 8 February 2015, the Greek Prime Minister, Alexis Tsipras demanded that Germany pay the complete reparations to Greece.[7] On 6 April 2015, Greece evaluated the war reparations to be the equivalent of 279 billion euros. Germany replied that the reparations issue was resolved in 1990.[8]
Israel and Jews, in general
West Germany paid reparations to Israel and the World Jewish Congress for confiscated Jewish property under Nuremberg laws, forced labour and persecution. However, no reparations were paid for killed Jews during the Holocaust.
The Netherlands
The Netherlands demanded reparations, but later desired to annex a large part of German territory. They eventually annexed 69 km2 in 1949, bought back by West Germany in 1960.
Poland
As a consequence of aggression by Nazi Germany, much of Poland was subjected to enormous destruction of its industry (62% of which was destroyed), its infrastructure (84%) and loss of civilian life (16.7% of its citizens during the war). Material recompensation incurred by Germany has been estimated as approximately €1.5 billion to 2006 exchange values.
On 23 August 1953, the Soviet-imposed communist Polish regime under pressure and control of the Soviet Union announced it would unilaterally waive its right to war reparations from East Germany on 1 January 1954, with the exception of reparations for Nazi oppression and atrocities. East Germany in turn had to accept the Oder-Neisse border, which gave around 1/4 of Germany in its 1937 borders (see Former eastern territories of Germany) to Poland and Russia. West Germany hadn't paid reparations to non-Jewish recipients for the damage inflicted in Poland. Gierek-Schmidt agreement signed in 1975 in Warsaw, stipulated that 1.3 billion DM will be paid to Poles who, during Nazi occupation, had paid into Germany's social security system without receiving pension.[9]
After German reunification in 1990, Poland demanded reparations again, as a reaction to claims made by German refugee organizations demanding compensation for property and land repossessed by the new Polish state that they were forcibly deported from as a stipulation of the Potsdam Agreement and the priorly mentioned Oder-Neisse border. In 1992, the Foundation for Polish-German Reconciliation was founded by the Polish and German governments, and as a result Germany paid Polish sufferers ca. 4.7 billion zł. There is an ongoing debate among Polish international law experts whether Poland still has the right to demand war reparations, with many arguing that the 1954 declaration wasn't legal as Poland wasn’t a sovereign state.[10]
Reparations issue arose again in 2017 with comments made on the side of Polish government officials from Law and Justice political party. According to a statement made by the German government on the issue, the reparations issue was resolved in 1953 as Poland declined receiving any payments from Germany. This claim is being countered by Polish commentators, stating that the then Polish government was under control and heavy pressure from the Soviet Union and that its 1953 refusal is non-binding.[11] The Roman Catholic Church did not support Polish claims on reparations, saying "not to destroy the hard-earned trust [between Poland and Germany]".[12]
In my opinion, Poland has the right to this (reparations) and the Polish state has the right to ask for them.
Poland resigned from reparations in 1953 and had since repeatedly confirmed this. There is no reason to question the effectiveness of the 1953 resignation.
Jarosław Kaczyński, leader of the Law and Justice party, has been making comments on reparations issue ever since he brought them up.[15] Sigmar Gabriel, Foreign Minister of Germany rejected the reparations issue again on behalf of the German government.[16]
Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia received a value of US$36 million, in industrial equipment from the dismantled German factories. West Germany also paid 8 million German marks as reparations for forced human experimentation on Yugoslav citizens.
Soviet Union
Other countries who were not subject to German reparations
- Czechoslovakia
- Denmark
- UK or Commonwealth countries
- Norway
- Finland
- Austria
- Luxembourg
- Belgium
Other forms of payment
According to the Yalta Conference, no reparations to Allied countries would be paid in money. Instead, much of this value consisted of German industrial assets, as well as forced labour to Russia.[17]
Annexation of territories
Soviet Union annexed the German territories east of the Oder-Neisse, leading to the expulsion of 12 million Germans. These territories were incorporated into communist Poland and the Soviet Union respectively and resettled with citizens of these countries. In the case of communist Poland, the majority of settlers were people expelled from eastern Polish territories annexed by the Soviet Union.
France controlled the Saar protectorate from 1947 to 1956, with the intention of using its coal deposits and possibly annexing the region to France permanently. The same mines had been under French control from the end of the First World War until 1935. Following the results of a plebiscite, France had to relinquish its control of the Saar region on 1 January 1957, however it continued to extract coal from the area's mines until 1981.
The Netherlands annexed approximately 69 km2 of German territory in 1949, nearly all of which was given back to the West Germany Government in 1957. Under the Dutch-German treaty made in The Hague on 8 April 1960, West Germany agreed to pay to The Netherlands the sum of 280 million German marks in compensation for the return.
Dismantling of industries
At the beginning of the occupation, the Allies started dismantling the remnants of German industries. The Western Allies later abandoned this plan in favour of the Marshall Plan.
Intellectual property
The Allies confiscated significant values of German patents, copyrights and trademarks.
Forced labour
See German prisoners of war in the Soviet Union, Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union and Forced labor of Germans after World War II.
See also
References
- ↑ Vallianatos, Evaggelos. "The Math of Mass Starvation and Murder: Germany in Greece During World War II". Truthout. Retrieved 2017-11-30.
- ↑ "Τα ερείπια της γερμανικής κατοχής στην Ελλάδα (μέρος 2ο)". Retrieved 2017-11-30.
- ↑ "Οι μεγάλες καταστροφές και το γερμανικό χρέος στην Ελλάδα μέσα από ντοκουμέντα". Newsbeast.gr (in Greek). 2015-03-05. Retrieved 2017-11-30.
- ↑ "Council for Reparations from Germany, ''Black Book of the Occupation''(In Greek and German) Athens 2006 p. 1018-1019" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-21. Retrieved 2011-06-15.
- ↑ Gregory, Frumkin. Population Changes in Europe Since 1939, Geneva 1951. pp. 89-91
- ↑ Nikos Christodoulakis (2014). Germany’s War Debt to Greece: A Burden Unsettled. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 13. ISBN 9781137441959.
[A] Special Report published by the Bank of Greece in 1962 ... specified the amount outstanding to be ... more than tenfold the sum dispensed by Germany.
- ↑ "Payback time? Greek PM seeks reparations over Nazi occupation & war-time loan". Russia Today. 8 February 2015. Retrieved 7 April 2015.
- ↑ "Greece Nazi occupation: Athens asks Germany for 279bn euros". BBC News. 7 April 2015. Retrieved 7 April 2015.
- ↑ Reluctant Realists: The Christian Democrats and West German Ostpolitik, Clay Clemens Duke University Press Books (27 July 1989) Page 160.
- ↑ Sprawy Międzynarodowe, 2005, nr 1 Problem reparacji, odszkodowań i świadczeń w stosunkach polsko-niemieckich 1944–2004. Tom I – Witold M. Góralski (red. naukowa): Studia, str. 427; tom II – Sławomir Dębski, Witold M. Góralski: Dokumenty, str. 621. Polski Instytut Spraw Międzynarodowych. Warszawa 2004
- ↑ WELT, DIE (2017-08-02). "Zweiter Weltkrieg: Polens Regierung prüft Reparationsforderungen an Deutschland". DIE WELT. Retrieved 2017-11-30.
- ↑ (www.dw.com), Deutsche Welle. "Deutschland lehnt Zahlung weiterer Reparationen an Polen ab | Aktuell Europa | DW | 08.09.2017". DW.COM (in German). Retrieved 2017-11-30.
- ↑ "Poland 'ready' to demand WWII reparations from Germany: PM". 8 September 2017. Retrieved 30 November 2017.
- ↑ (www.dw.com), Deutsche Welle. "Deutschland lehnt Zahlung weiterer Reparationen an Polen ab - Aktuell Europa - DW - 08.09.2017". DW.COM. Retrieved 30 November 2017.
- ↑ Trzaska, Izabela (2017-09-25). "Reparacje wojenne. Prezes Kaczyński szykuje się do walki na forum międzynarodowym". WP money (in Polish). Retrieved 2017-11-30.
- ↑ "German FM rejects war reparations for Poland: report". Polskie Radio dla Zagranicy. Retrieved 2017-11-30.
- ↑ Pavel Polian-Against Their Will: The History and Geography of Forced Migrations in the USSR Central European University Press 2003 ISBN 963-9241-68-7 P.244-249