von Kármán–Gabrielli diagram
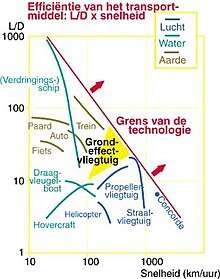
Example of a von Kármán–Gabrielli diagram (however in Dutch).
is here replaced by
is here replaced by
The von Kármán–Gabrielli diagram (also Gabrielli–von Kármán diagram, GvK diagram) is a diagram which compares the efficiency of transportation methods by plotting specific tractive force, or specific resistance (ε = P/mgv = E/mgd) against velocity (v). It was first used by Theodore von Kármán and Giuseppe Gabrielli in their 1950 paper on this subject.[1][2][3]
The basic idea is that formally, 1 kWh/ 100 km is equivalent to a force (see Work (physics)#Work and energy), a resistance force amounting to 36 N[4].
See also
References
- ↑ "What price speed? Specific power required for propulsion of vehicles", G. Gabrielli and Th. von Kármán, Mechanical Engineering 72 (1950), #10, pp. 775-781.
- ↑ "What Price Speed - Revisited", The Railway Research Group, Imperial College, Ingenia 22 (March 2005). PDF with the graphs
- ↑ pp. 385-386, Springer Handbook of Robotics, eds. Bruno Siciliano and Oussama Khatib, Springer, 2008, ISBN 978-3-540-23957-4, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-30301-5.
- ↑ Useful data - Cambridge repository website repository.cam.ac.uk; see page 328.
External links
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.