Vogel (lunar crater)
 LRO WAC mosaic | |
| Coordinates | 15°06′S 5°54′E / 15.1°S 5.9°ECoordinates: 15°06′S 5°54′E / 15.1°S 5.9°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 27 km |
| Depth | 2.8 km |
| Colongitude | 354° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Hermann C. Vogel |
Vogel is a small lunar impact crater located to the southeast of Albategnius, and is named after the German astronomer Hermann Carl Vogel.[1] It is the smallest member of a trio of craters that increase in size from north to south, consisting of Vogel, Argelander and Airy. To the west is the remnant of the crater Parrot. Also northeast is the smaller Burnham.
Both the northern and southern ends of Vogel's rim are interrupted by smaller craters. Vogel B to the north is overlain in turn along its northern rim by an even smaller crater, thus forming a cluster of interconnected craters with Vogel being the largest. The rim of Vogel is otherwise relatively intact and not significantly worn.
Satellite craters
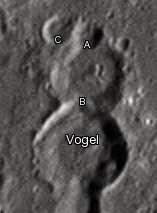

By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Vogel.
| Vogel | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 14.1° S | 5.6° E | 9 km |
| B | 14.4° S | 5.7° E | 22 km |
| C | 14.1° S | 5.3° E | 10 km |
Notes
- ↑ "Vogel". usgs.gov. Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. International Astronomical Union. Retrieved September 20, 2017.
References
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Vogel (crater). |