Vestibule (architecture)
A vestibule /ˈvɛstɪbjuːl/ is an anteroom (antechamber) or small foyer leading into a larger space,[1] such as a lobby, entrance hall, passage, etc., for the purpose of waiting, withholding the larger space view, reducing heat loss, providing space for outwear, etc. The term applies to structures in both modern and historical architecture since ancient times. In modern architecture, vestibule typically refers to a small room next to the outer door and connecting it with the interior of the building. In ancient Roman architecture, vestibule (Latin: vestibulum) referred to a partially enclosed area between the interior of the house and the street.[2]
Modern usage

In contemporary usage, a vestibule constitutes an area surrounding the exterior door. It acts as an antechamber between the exterior and the interior structure. Often it connects the doorway to a lobby or hallway. It is the space one occupies once passing the door, but not yet in the main interior of the building
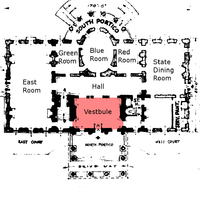
Although vestibules are common in private residences, as a modified mud room, they are especially prevalent in more opulent buildings, such as government ones, designed to elicit a sense of grandeur by contrasting the vestibule's small space with the following greater one, and by adding the aspect of anticipation. The residence of the White House in the United States is such an example, but somewhat confusing. At the north portico, it contains a tiny vestibule now between the doors flushed with the outer and inner faces of the exterior wall of, and in the past inside, the Entrance Hall (called incorrectly Vestibule) separated from the not much bigger Cross Hall by just 2 double columns. The difference in sizes between a vestibule and the following space is better illustrated by the—so called—entrance (15) to the main gallery in the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum by Frank Lloyd Wright. Many government buildings mimic the classical architecture from which the vestibule originates.
A purely utilitarian use of vestibules in modern buildings is to create an "air lock" entry. Such vestibules consist of merely a set of inner doors and a set of outer doors, the intent being to reduce air infiltration to the building by having only one set of doors open at any given time.[3]
ATM vestibule
An ATM vestibule is an enclosed area with automated teller machines that is accessible from the outside of a building, but typically features no further entrance beyond the vestibule. There may be a secure entrance to the vestibule which requires a card to open.[4]
Between the priorities financial institutions had for 2020, in Europe and USA implementing new technology was in the top 3. Since the customers were most affected by criminal activity in the last years, and with a lot of the incidents happening at or around ATMs and ATM Vestibules, law enforcement agencies are working alongside the banks to develop new ways to improve the security. Even now, most of these designated areas are equipped with close-circuit monitoring system, panic and fire alarms and restriction access systems. The latter is where most of the improvements are being made nowadays, as new technology is developed year by year. If until recent days’ access in the ATM Vestibules was made with the help of the magnetic band of the credit card, now we have access control devices such as PASSCHIP which are using a technology dedicated to CHIP based cards. This is bringing new hurdles on criminal’s path and an increased sense of security for the self-banking process, which should make customers feel more secure whilst carrying out their transactions.[5]
Railroad use
The vestibule on a railroad passenger car is an enclosed area at the end of the carbody, usually separated from the main part of the interior by a door, which is power-operated on most modern equipment. Entrance to and exit from the car is through the side doors, which lead into the vestibule. When passenger cars are coupled, their vestibules are joined by mating faceplate and diaphragm assemblies to create a weather-tight seal for the safety and comfort of passengers who are stepping from car to car. In British usage the term refers to the part of the carriage where the passenger doors are located; this can be at the ends of the carriage (on long-distance stock) or at the 1/4 and 3/4 of length positions (typical on modern suburban stock).
Ancient usage
Ancient Greece
Vestibules were common in ancient Greek temples. Due to the construction techniques available at the time, it was not possible to build large spans. Consequently, many entrance ways had two rows of columns that supported the roof and created a distinct space around the entrance.[6]
In ancient Greek houses, the prothyrum was the space just outside the door of a house, which often had an altar to Apollo or a statue, or a laurel tree.[7]
In elaborate houses or palaces, the vestibule could be divided into three parts, the prothyron (πρόθυρον), the thyroreion (θυρωρεῖον, lit. 'porter's lodge'), and the proaulion (προαύλιον).[8]
Ancient Rome
In ancient Roman architecture, where the term originates, a vestibule was a space between the interior of a building and the street.[7] Upon entering a Roman house or domus, one would have to pass through the vestibule before entering the atrium.[9]
The structure was a mixture between a modern hall and porch.
Church architecture
From the 5th century on vestibules were used in churches in both the east and west.[10]
See also
| Look up vestibule in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikisource has the text of a 1913 Catholic Encyclopedia article about Vestibule. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Vestibule. |
- Genkan
- Propylaeum
- Antarala, vestibule in certain Hindu temples
References
- ↑ Harris, Cyril (2005). Dictionary of Architecture and Construction (4 ed.). McGraw Hill Professional. p. 1044. ISBN 0071589015. Archived from the original on 2016-05-18.
- ↑ Vestibule. The Oxford English Dictionary. Common people refer to a vestibule as being a porch.http://www.oed.com Archived 2008-01-11 at the Wayback Machine. Online edition, December 2006
- ↑ "Why do some public buildings have two layers of doors? [Archive] - Absolute Write Water Cooler". absolutewrite.com. Archived from the original on 7 May 2017. Retrieved 1 May 2018.
- ↑ Kovacs, Eduard (7 February 2012). "Fraudsters Install Skimmer on ATM Vestibule Door". Softpedia. Archived from the original on 13 December 2013. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ↑ "PASSCHIP". passchip.com. Retrieved 2018-07-20.
- ↑ Tarbel, F.B. "A History of Ancient Greek Art". Retrieved 2006-03-02.
- 1 2 John William Mollett, An Illustrated Dictionary of Words Used in Art and Archaeology, [https://books.google.com/books?id=joqfAAAAMAAJ&pg=PA267&lpg=PA267 s.v.
- ↑ Emile Isambert, Orient, Grèce, et Turquie d'Europe, Guides Joanne, 1881, p. 771
- ↑ McManus, Barbara. "Sample Plan of a Roman House". VRoma. The College of New Rochelle. Archived from the original on 2006-02-09. Retrieved 2006-03-02.
- ↑
