Unicast
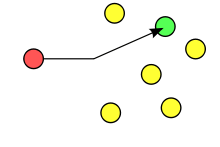
In computer networking, unicast refers to a one-to-one transmission from one point in the network to another point; that is, one sender and one receiver, each identified by a network address.[1]
Addressing methods
| Routing schemes
|
|---|
| Unicast
|
| Broadcast
|
| Multicast
|
| Anycast
|
| Geocast
|
The Internet Protocol and other network addressing systems recognize five main addressing methods:
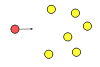
- Unicast addressing uses a one-to-one association between a sender and destination: each destination address uniquely identifies a single receiver endpoint.
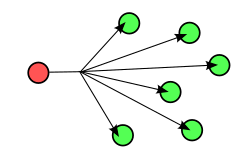
- Broadcast uses a one-to-all association; a single datagram from one sender is routed to all of the possibly multiple endpoints associated with the broadcast address. The network automatically replicates datagrams as needed to reach all the recipients within the scope of the broadcast, which is generally an entire network subnet.
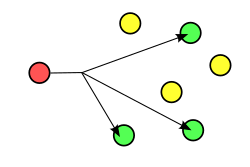
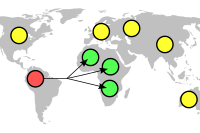
- Multicast addressing uses a one-to-many-of-many or many-to-many-of-many association; datagrams are routed simultaneously in a single transmission to many recipients. It differs from broadcast in that the destination address designates a subset, not necessarily all, of the accessible nodes.
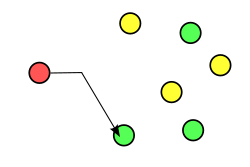
- Anycast addressing is a one-to-one-of-many association where datagrams are routed to any single member of a group of potential receivers that are all identified by the same destination address. The routing algorithm selects the single receiver from the group based on which is the nearest according to some distance measure.
- Geocast refers to the delivery of information to a group of destinations in a network identified by their geographical locations. It is a specialized form of multicast addressing used by some routing protocols for mobile ad hoc networks.
See also
References
- ↑ Godred Fairhurst. "Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast".
External links
- "Differences Between Multicast and Unicast". Microsoft. Retrieved 2008-02-04.
- "What Is Unicast IPv4 Routing?". Microsoft. Retrieved 2010-09-30.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.