Tufted titmouse
| Tufted titmouse | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Adult singing | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Paridae |
| Genus: | Baeolophus |
| Species: | B. bicolor |
| Binomial name | |
| Baeolophus bicolor (Linnaeus, 1766) | |
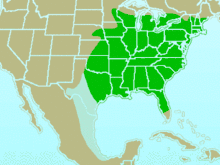 | |
| Combined range of tufted titmouse and black-crested titmouse | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Parus bicolor Linnaeus, 1766 | |
The tufted titmouse (Baeolophus bicolor) is a small songbird from North America, a species in the tit and chickadee family (Paridae). The black-crested titmouse, found from central and southern Texas southwards, was included as a subspecies but is now considered a separate species B. atricristatus.
These small birds are approximately 6 inches in length, with a white front, and grey upper body outlined with rust colored flanks.[2] Other characteristics include their black forehead, and the tufted grey crest on their head.[2]
The song of the tufted titmouse is usually described as a whistled peter-peter-peter, though this song can vary in approximately 20 notable ways.[3]
Their habitat is deciduous and mixed woods as well as gardens, parks and shrubland. Though the tufted titmouse is non-migratory and originally native to Ohio and Mississippi, factors such as bird feeders have caused these birds to occupy a larger amount of territory across the United States and stretching into Ontario, Canada.[2][4]
The tufted titmouse forages actively on branches, sometimes on the ground, mainly eating insects, especially caterpillars, but also seeds, nuts and berries. They will store food for later use. They tend to be curious about their human neighbors and can sometimes be spotted on window ledges peering into the windows to watch what's going on inside. They are more shy when seen at bird feeders; their normal pattern there is to scout the feeder from the cover of trees or bushes, fly to the feeder, take a seed, and fly back to cover to eat it.
Tufted titmice nest in a hole in a tree, either a natural cavity, a man-made nest box, or sometimes an old woodpecker nest.[5] They line the nest with soft materials, sometimes plucking hair from a live animal such as a dog.[6] If they find shed snake skin, they will try to incorporate pieces of it in their nest.[7] Their eggs are under an inch long and are white or cream-colored with brownish or purplish spots.
The lifespan of the tufted titmouse is approximately 2.1 years, though they can live for more than 10 years.[8] These birds will on average have a clutch size of 5 to 7 eggs.[9] Unlike many birds, the offspring of tufted titmice will often stay with their parents during the winter, and even after the first year of their life.[10] Sometimes, a bird born the year before will even help its parents raise the next year's young.
See also
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2012). "Baeolophus bicolor". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- 1 2 3 McCommons, James (2003). "Tufted Titmouse". Emmaus. 50: 16 – via ProQuest. (Registration required (help)).
- ↑ Grubb, Thomas C. (1998). Tufted Titmouse. Stackpole Books. ISBN 9780811729673.
- ↑ "Tufted Titmouse" (PDF). Ohio Birds. Retrieved May 4, 2018.
- ↑ Laskey, Amelia. "Some Tufted Titmouse Life Historu" (PDF). Retrieved May 4, 2018.
- ↑ "Tufted Titmouse, Audubon Field Guide". Retrieved 2015-08-17.
- ↑ Medlin, Elizabeth C.; Risch, Thomas S. (2006). "AN EXPERIMENTAL TEST OF SNAKE SKIN USE TO DETER NEST PREDATION". The Condor. 108 (4): 963. doi:10.1650/0010-5422(2006)108[963:aetoss]2.0.co;2. ISSN 0010-5422. Lay summary.
- ↑ Elder, William H. (1985). "Survivorship in the Tufted Titmouse" (PDF). Wilson Bull. 97: 517–524 – via ProQuest.
- ↑ Laskey, Amelia R. (July 1957). "Some Tufted Titmouse Life History" (PDF). Bird Banding. 28: 135–145 – via ProQuest.
- ↑ Pravosudova, Elena V.; Grubb, Thomas C.; Parker, Patricia G.; Doherty, Paul F. (1999). "Patch Size and Composition of Social Groups in Wintering Tufted Titmice". The Auk. 116 (4): 1152–1155. doi:10.2307/4089699. JSTOR 4089699.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tufted titmouse. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Baeolophus bicolor |
- "Tufted titmouse media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Tufted titmouse species account – Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- Tufted titmouse – Baeolophus bicolor – USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter
- Tufted titmouse photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)