Trou au Natron

Trou au Natron (French: "hole of natron") or Doon Orei (Teda: "big hole")[1] is a volcanic caldera of the Tibesti Massif in the nation of Chad in Northern Africa.[2][3] The volcano is extinct. It is unknown when it last erupted.[4][5] Its volcano number is 0205–01.[6] Trou au Natron is located just south-east of Toussidé, the westernmost volcano of the Tibesti Mountains. Its edge cuts into the nearby Yirrigue caldera.
The caldera sits at an elevation of 2,450 m (8,040 ft).[7] It has an irregular diameter of approximately 6–8 km (4–5 mi) and is up to 1,000 m (3,300 ft) deep.[2] Four smaller volcanic cones, made of scoria or andesitic tuff sit on the floor of the caldera.[2][8] Numerous smaller vents and hot springs on the caldera's floor emit hot steam and mineral water.[2]
Because of its irregular shape, it has been theorized that the caldera was formed as a result of multiple massive explosions, each of which deepened the enormous pit.[2] During these explosions, chunks of debris up to 5 m3 (180 cu ft) in size may have been hurled up to 10 km (6.2 mi) from the crater.[2] Its exact period of formation is unconfirmed, although a Pleistocene formation has been suggested.[6] It is known to be one of the youngest formations on the Tibesti Massif.[4]
Soda lake
Much of the surface of the caldera is lined with a white crust of carbonate salts such as sodium carbonite and natrolite.[8] This substance is also known as natron, leading to the French name for the site. This crust is sometimes known as the Tibesti Soda Lake.[2][9] The crusts are formed when mineral-rich steam is emitted from small vents on the crater's floor. When this water evaporates in the desert heat, the minerals remain behind as part of the crust.[2]
Gallery
_ASTER.jpg) Satellite image of Trou au Natron via Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER)
Satellite image of Trou au Natron via Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) Satellite image of the Tousside volcano (large dark area in centre). Trou au Natron is visible above and to the left (smaller white area).
Satellite image of the Tousside volcano (large dark area in centre). Trou au Natron is visible above and to the left (smaller white area).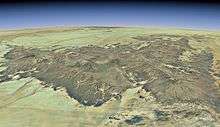 Satellite overview of the Tibesti Massif. Trou au Natron is located to the left; it is highlighted in the full-size view of the image.
Satellite overview of the Tibesti Massif. Trou au Natron is located to the left; it is highlighted in the full-size view of the image.
References
- ↑ Beltrami, Vanni; Proto, Harry (2007). Il Sahara centro-orientale dalla preistoria ai tempi dei nomadi Tubu (in Italian). Archaeopress. ISBN 9781407301020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Scheffel, Richard L.; Wernet, Susan J., eds. (1980). Natural Wonders of the World. United States of America: Reader's Digest Association, Inc. p. 377. ISBN 0-89577-087-3.
- ↑ al-Arḍ, Jamʻīyah al-Lībīyah li-ʻUlūm (1966). Annual Field Conference. Earth Sciences Society of the Libyan Arab Republic.
The Trou au Natron has a caldera diameter of six to eight km...
- 1 2 "Global Volcanism Program | Tarso Toussidé". volcano.si.edu. Retrieved 2017-10-03.
- ↑ "VOGRIPA". www.bgs.ac.uk. Retrieved 2017-10-03.
- 1 2 Siebert, Lee; Simkin, Tom; Kimberly, Paul (2011-02-09). Volcanoes of the World: Third Edition. University of California Press. ISBN 9780520947931.
- ↑ Barry, Roger Graham (1981). Mountain Weather and Climate. CUP Archive. ISBN 9780416737301.
- 1 2 Green, Jack; Short, Nicholas Martin (2012-12-06). Volcanic Landforms and Surface Features: A Photographic Atlas and Glossary. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9783642651502.
- ↑ Goudie, Andrew (2002). Great Warm Deserts of the World: Landscapes and Evolution. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199245154.
Coordinates: 20°59′00″N 16°32′00″E / 20.98333°N 16.53333°E