Tritrichomonas
| Tritrichomonas | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| (unranked): | Excavata |
| Phylum: | Metamonada |
| Class: | Parabasalia |
| Order: | Tritrichomonadida |
| Family: | Tritrichomonadidae |
| Genus: | Tritrichomonas Kofoid, 1920 |
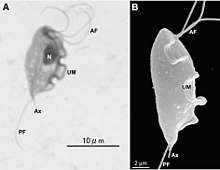
Tritrichomonas is a genus of single celled flagellated parasitic excavates, some of whose species are known to be pathogens of the bovine reproductive tract as well as the intestinal tract of felines.[1]
Species
Example species within the Tritrichomonas genus are Tritrichomonas augusta and Tritrichomonas foetus, the latter of which characteristically interacts with bacteria that reside in the intestinal tract by adhering to the intestinal epithelium of the host. Tritrichomonas augusta have been observed in the amphibian Rough-skinned Newt, Taricha granulosa, in certain Northern California coastal counties in the United States.[2]
References
Line notes
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.