Tax buoyancy
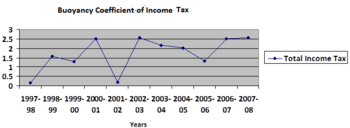
Buoyancy coefficient of income tax in India during 1997-98 to 2007-08 (Source:Compiled from reports of Comptroller and Auditor General of India for relevant years)
Tax buoyancy is an indicator to measure efficiency and responsiveness of revenue mobilization in response to growth in the Gross domestic product or National income.[1]
A tax is said to be buoyant if the tax revenues increase more than proportionately in response to a rise in national income or output.
A tax is buoyant when revenues increase by more than, say, 1 per cent for a 1 per cent increase in GDP.
Usually, tax elasticity is considered a better indicator to measure tax responsiveness.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Growth of Income Tax Revenue in India" (PDF). Retrieved 19 November 2012.
- ↑ Jane H. Leuthold and Tchetche N'Guessan. "Tax buoyancy" (PDF). Tax buoyancy vs. elasticity in a developing economy. University of Illinois at Urbana-champaign. Retrieved 19 November 2012.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.