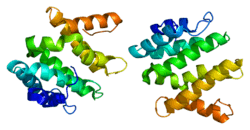TOM1
Target of Myb protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TOM1 gene.[5][6][7]
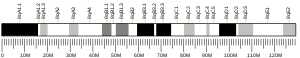
The specific function of this gene has not yet been determined, yet it may involve the translocation of growth factor receptor complexes to the lysosome for degradation. This gene is localized to 22q13.1, with HMOX1 and MCM5 distally and HMG2L1 proximally positioned.[7]
Interactions
TOM1 has been shown to interact with TOLLIP[8] and ZFYVE16.[9]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000100284 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000042870 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Seroussi E, Kedra D, Kost-Alimova M, Sandberg-Nordqvist AC, Fransson I, Jacobs JF, Fu Y, Pan HQ, Roe BA, Imreh S, Dumanski JP (Aug 1999). "TOM1 genes map to human chromosome 22q13.1 and mouse chromosome 8C1 and encode proteins similar to the endosomal proteins HGS and STAM". Genomics. 57 (3): 380–8. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5739. PMID 10329004.
- ↑ Katoh Y, Shiba Y, Mitsuhashi H, Yanagida Y, Takatsu H, Nakayama K (May 2004). "Tollip and Tom1 form a complex and recruit ubiquitin-conjugated proteins onto early endosomes". J Biol Chem. 279 (23): 24435–43. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400059200. PMID 15047686.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: TOM1 target of myb1 (chicken)".
- ↑ Yamakami, Megumi; Yoshimori Tamotsu; Yokosawa Hideyoshi (Dec 2003). "Tom1, a VHS domain-containing protein, interacts with tollip, ubiquitin, and clathrin". J. Biol. Chem. United States. 278 (52): 52865–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306740200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 14563850.
- ↑ Seet, Li-Fong; Liu Ningsheng; Hanson Brendon J; Hong Wanjin (Feb 2004). "Endofin recruits TOM1 to endosomes". J. Biol. Chem. United States. 279 (6): 4670–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M311228200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 14613930.
Further reading
- Dunham I, Shimizu N, Roe BA, et al. (1999). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 22". Nature. 402 (6761): 489–95. Bibcode:1999Natur.402..489D. doi:10.1038/990031. PMID 10591208.
- Misra S, Beach BM, Hurley JH (2000). "Structure of the VHS domain of human Tom1 (target of myb 1): insights into interactions with proteins and membranes". Biochemistry. 39 (37): 11282–90. doi:10.1021/bi0013546. PMID 10985773.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Clark HF, Gurney AL, Abaya E, et al. (2003). "The secreted protein discovery initiative (SPDI), a large-scale effort to identify novel human secreted and transmembrane proteins: a bioinformatics assessment". Genome Res. 13 (10): 2265–70. doi:10.1101/gr.1293003. PMC 403697. PMID 12975309.
- Yamakami M, Yoshimori T, Yokosawa H (2004). "Tom1, a VHS domain-containing protein, interacts with tollip, ubiquitin, and clathrin". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (52): 52865–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306740200. PMID 14563850.
- Seet LF, Liu N, Hanson BJ, Hong W (2004). "Endofin recruits TOM1 to endosomes". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (6): 4670–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M311228200. PMID 14613930.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Collins JE, Wright CL, Edwards CA, et al. (2005). "A genome annotation-driven approach to cloning the human ORFeome". Genome Biol. 5 (10): R84. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r84. PMC 545604. PMID 15461802.
- Seet LF, Hong W (2005). "Endofin recruits clathrin to early endosomes via TOM1". J. Cell Sci. 118 (Pt 3): 575–87. doi:10.1242/jcs.01628. PMID 15657082.
- Schmid EM, Ford MG, Burtey A, et al. (2007). "Role of the AP2 beta-appendage hub in recruiting partners for clathrin-coated vesicle assembly". PLoS Biol. 4 (9): e262. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040262. PMC 1540706. PMID 16903783.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
External links
- TOM1 human gene location in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- TOM1 human gene details in the UCSC Genome Browser.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.