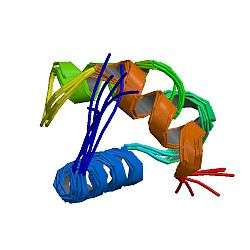
TERF2IP
Telomeric repeat-binding factor 2-interacting protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TERF2IP gene.[5][6]
Interactions
TERF2IP has been shown to interact with Ku80,[7] Rad50[7] and TERF2.[5][7][8]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000166848 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000033430 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 Li B, Oestreich S, de Lange T (July 2000). "Identification of human Rap1: implications for telomere evolution". Cell. 101 (5): 471–83. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80858-2. PMID 10850490.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: TERF2IP telomeric repeat binding factor 2, interacting protein".
- 1 2 3 O'Connor, Matthew S; Safari Amin; Liu Dan; Qin Jun; Songyang Zhou (July 2004). "The human Rap1 protein complex and modulation of telomere length". J. Biol. Chem. United States. 279 (27): 28585–91. doi:10.1074/jbc.M312913200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 15100233.
- ↑ Zhu, X D; Küster B; Mann M; Petrini J H; de Lange T (July 2000). "Cell-cycle-regulated association of RAD50/MRE11/NBS1 with TRF2 and human telomeres". Nat. Genet. UNITED STATES. 25 (3): 347–52. doi:10.1038/77139. ISSN 1061-4036. PMID 10888888.
Further reading
- Zhu XD, Küster B, Mann M, et al. (2000). "Cell-cycle-regulated association of RAD50/MRE11/NBS1 with TRF2 and human telomeres". Nat. Genet. 25 (3): 347–52. doi:10.1038/77139. PMID 10888888.
- Hanaoka S, Nagadoi A, Yoshimura S, et al. (2001). "NMR structure of the hRap1 Myb motif reveals a canonical three-helix bundle lacking the positive surface charge typical of Myb DNA-binding domains". J. Mol. Biol. 312 (1): 167–75. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4924. PMID 11545594.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Loayza D, De Lange T (2003). "POT1 as a terminal transducer of TRF1 telomere length control". Nature. 423 (6943): 1013–8. Bibcode:2003Natur.423.1013L. doi:10.1038/nature01688. PMID 12768206.
- Li B, de Lange T (2004). "Rap1 affects the length and heterogeneity of human telomeres". Mol. Biol. Cell. 14 (12): 5060–8. doi:10.1091/mbc.E03-06-0403. PMC 284807. PMID 14565979.
- Zhu XD, Niedernhofer L, Kuster B, et al. (2004). "ERCC1/XPF removes the 3' overhang from uncapped telomeres and represses formation of telomeric DNA-containing double minute chromosomes". Mol. Cell. 12 (6): 1489–98. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00478-7. PMID 14690602.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- O'Connor MS, Safari A, Liu D, et al. (2004). "The human Rap1 protein complex and modulation of telomere length". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (27): 28585–91. doi:10.1074/jbc.M312913200. PMID 15100233.
- Liu D, Safari A, O'Connor MS, et al. (2004). "PTOP interacts with POT1 and regulates its localization to telomeres". Nat. Cell Biol. 6 (7): 673–80. doi:10.1038/ncb1142. PMID 15181449.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10112130B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Ye JZ, Donigian JR, van Overbeek M, et al. (2004). "TIN2 binds TRF1 and TRF2 simultaneously and stabilizes the TRF2 complex on telomeres". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (45): 47264–71. doi:10.1074/jbc.M409047200. PMID 15316005.
- Liu D, O'Connor MS, Qin J, Songyang Z (2005). "Telosome, a mammalian telomere-associated complex formed by multiple telomeric proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (49): 51338–42. doi:10.1074/jbc.M409293200. PMID 15383534.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Wan D, Gong Y, Qin W, et al. (2004). "Large-scale cDNA transfection screening for genes related to cancer development and progression". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (44): 15724–9. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10115724W. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404089101. PMC 524842. PMID 15498874.
- Antoine K, Ferbus D, Kolahgar G, et al. (2005). "Zinc finger protein overexpressed in colon carcinoma interacts with the telomeric protein hRap1". J. Cell. Biochem. 95 (4): 763–8. doi:10.1002/jcb.20487. PMID 15838871.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Gerber SA, et al. (2006). "A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization". Nat. Biotechnol. 24 (10): 1285–92. doi:10.1038/nbt1240. PMID 16964243.
- Wu Y, Zacal NJ, Rainbow AJ, Zhu XD (2007). "XPF with mutations in its conserved nuclease domain is defective in DNA repair but functions in TRF2-mediated telomere shortening". DNA Repair (Amst.). 6 (2): 157–66. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.09.005. PMID 17055345.
- Bae NS, Baumann P (2007). "A RAP1/TRF2 complex inhibits nonhomologous end-joining at human telomeric DNA ends". Mol. Cell. 26 (3): 323–34. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.03.023. PMID 17499040.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.