Subclinical diabetes
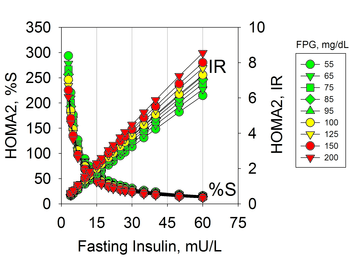
Subclinical diabetes is a stage of hyperinsulinemia due to insulin resistance in normoglycemic individuals and, therefore, not diagnosed for hyperglycemic states characteristic of diabetes mellitus. It anticipates the prediabetes and diabetes stages characterized by hyperglycemia among other glucocentric biomarkers.[1] Insulin resistance can be diagnosed by measures of plasma insulin, both fasting or during a glucose tolerance test – as originally reported by the pathologist Dr. Joseph R. Kraft. [2] and Prof. Gerald Reaven.[3] It has been endorsed by the American Diabetes Association in the Consensus Development Conference on Insulin Resistance,[4] where they state that "if the assay for fasting insulin was reliable, it would be useful to detect insulin resistance early (i.e., before or soon after the pubertal period, which itself causes insulin resistance) and before clinical disease appears".
The implications of a permanent hyperinsulinemic stage is the risk of comorbidities related to diabetes observed in subclinical diabetic individuals[5][6][7][1] including cardiovascular diseases,[8][9][10] retinopathy,[11] cancer,[12][13][14] and dementia.[15][16]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Lima, Luis Mauricio TR (2017). "Subclinical Diabetes" (PDF). An Acad Bras Cienc. 89 (1): 591–614. doi:10.1590/0001-3765201720160394. PMID 28492735.
- ↑ Kraft, JR (1975). "Detection of Diabetes Mellitus In Situ (Occult Diabetes)". Laboratory Medicine. 6 (2): 10–22. doi:10.1093/labmed/6.2.10.
- ↑ Reaven, GM; Lerner, RL; Stern, MP; Farguhar, JW (1967). "Role of insulin in endogenous hypertriglyceridemia" (PDF). The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 46 (11): 1756–67. doi:10.1172/JCI105666. PMC 292926. PMID 6061748.
- ↑ Association, American Diabetes (1998). "Consensus Development Conference on Insulin Resistance: 5–6 November 1997". Diabetes Care. 21 (2): 310–14. doi:10.2337/diacare.21.2.310. PMID 9540000.
- ↑ Keebler ME & McGuire DK 2003 Subclinical diabetes mellitus: is it really “sub-clinical”? American Heart Journal 146 210–12. doi:10.1016/S0002-8703(03)00236-9
- ↑ Kulkarni RN 2012 "Identifying Biomarkers of Subclinical Diabetes". Diabetes 61 1925–26. doi:10.2337/db12-0599
- ↑ Lima LMTR 2017 "Prediabetes definitions and clinical outcomes". The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 5 92–93. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30011-6
- ↑ Hanley AJG, Williams K, Stern MP & Haffner SM 2002 "Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance in relation to the incidence of cardiovascular disease: the San Antonio Heart Study. Diabetes Care 25 1177–84.
- ↑ Valenti V, Hartaigh B ó, Cho I, Schulman-Marcus J, Gransar H, Heo R, Truong QA, Shaw LJ, Knapper J, Kelkar AA et al. 2016 Absence of Coronary Artery Calcium Identifies Asymptomatic Diabetic Individuals at Low Near-Term But Not Long-Term Risk of Mortality A 15-Year Follow-Up Study of 9715 Patients. Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging 9 e003528. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.115.003528
- ↑ DECODE Study Group, European Diabetes Epidemiology Group 2003 "Is the current definition for diabetes relevant to mortality risk from all causes and cardiovascular and noncardiovascular diseases?" Diabetes Care 26 688–696.
- ↑ Colagiuri S, Lee CMY, Wong TY, Balkau B, Shaw JE, Borch-Johnsen K & Group the D-2 CW 2011 "Glycemic Thresholds for Diabetes-Specific Retinopathy Implications for diagnostic criteria for diabetes". Diabetes Care 34 145–50. doi:10.2337/dc10-1206
- ↑ Goto A, Noda M, Sawada N, Kato M, Hidaka A, Mizoue T, Shimazu T, Yamaji T, Iwasaki M, Sasazuki S et al. 2016 "High hemoglobin A1c levels within the non-diabetic range are associated with the risk of all cancers". International Journal of Cancer 138 1741–53. doi:10.1002/ijc.29917
- ↑ Muti P, Quattrin T, Grant BJB, Krogh V, Micheli A, Schünemann HJ, Ram M, Freudenheim JL, Sieri S, Trevisan M et al. 2002 "Fasting glucose is a risk factor for breast cancer: a prospective study". Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention: A Publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, Cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology 11 1361–68.
- ↑ Sieri S, Muti P, Claudia A, Berrino F, Pala V, Grioni S, Abagnato CA, Blandino G, Contiero P, Schunemann HJ et al. 2012 "Prospective study on the role of glucose metabolism in breast cancer occurrence". International Journal of Cancer 130 921–29. doi:10.1002/ijc.26071
- ↑ Crane PK, Walker R, Hubbard RA, Li G, Nathan DM, Zheng H, Haneuse S, Craft S, Montine TJ, Kahn SE et al. 2013 "Glucose Levels and Risk of Dementia". New England Journal of Medicine 369 540–48. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1215740
- ↑ Luchsinger JA, Tang M-X, Shea S & Mayeux R 2004 "Hyperinsulinemia and risk of Alzheimer disease". Neurology 63 1187–92.