Stieglitz rearrangement
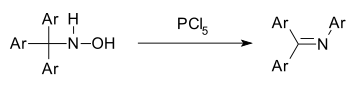
The Stieglitz rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction of a trityl hydroxylamine Ar3CNHOH to a triaryl imine.[1][2] The reaction is related to the Beckmann rearrangement as both reaction involve a carbon to nitrogen shift. It is catalyzed by PCl5.
References
- ↑ Julius Stieglitz, Paul Nicholas Leech (1914). "The molecular Rearrangement of Triarylmethyl-Hydroxylamines and the Beckmann Rearrangement of Ketoximes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 36 (2): 272–301. doi:10.1021/ja02179a008.
- ↑ Bert Allen Stagner (1914). "The molecular Rearrangement of Triarylmethyl-Hydroxylamines". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 36 (2): 2069–2081. doi:10.1021/ja02267a018.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.