SPANphos
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
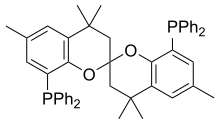
4,4,4',4',6,6'-Hexamethyl-2,2'-spirobichroman-8,8'-diylbis(diphenylphosphane) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C47H46O2P2 | |
| Molar mass | 704.814 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
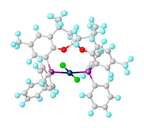
SPANphos is an organophosphorus compound used as a ligand in organometallic and coordination chemistry. This compound is a rare example of a trans-spanning ligand and rigidly links mutually trans coordination sites. By virtue of its C2-symmetric backbone, SPANphos forms a chiral cavity over the face of a square planar complexes, e.g. in MCl2(SPANphos) (M = Pd, Pt).
Synthesis
SPANphos can be prepared synthesized from relatively inexpensive reagents. In the first step 4,4,4',4',6,6'-hexamethyl-2,2'-spirobichromane is prepared via an acid-catalyzed reaction of p-cresol and acetone. The resultant spirocycle is halogenated with N-bromosuccinimide followed by lithium-bromide exchange using n-BuLi. Treatment of the resulting dilithio compound with chlorodiphenylphosphine completes the synthesis.[1]
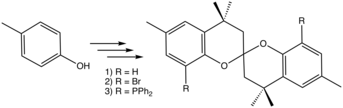 Preparation of SPANphos from p-cresol.
Preparation of SPANphos from p-cresol.
References
- 1 2 Z. Freixa, M. S. Beentjes, G. D. Batema, C. B. Dieleman, G. P. F. v. Strijdonck, J. N. H. Reek, P. C. J. Kamer, J. Fraanje, K. Goubitz and P. W. N. M. Van Leeuwen (2003). "SPANphos: A C2-Symmetric trans-Coordinating Diphosphane Ligand". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 42 (11): 1322–1325. doi:10.1002/anie.200390330. PMID 12645065.