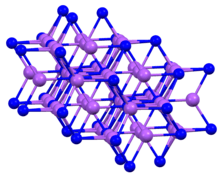
Sodium arsenide
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.762 |
| Properties | |
| Na3As | |
| Molar mass | 143,89 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | violet brown solid |
| Density | 2,36 g·cm−3 |
| hydrolysis | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | toxic |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sodium arsenide is the inorganic compound of sodium and arsenic with the formula Na3As. It is a dark colored solid that degrades upon contact with water or air. It is prepared by the reaction of the elements at 200–400 °C.[1] The compound is mainly of interest as exhibiting an archetypal structure. The normal pressure "sodium arsenide" phase is adopted by many alkali metal pnictides. At 3.6 gigapascals, Na3As adopts the Li3Bi structure, which is another archetypal structure.[2]
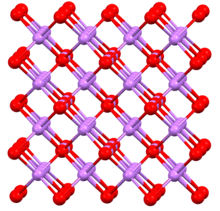
At high pressures, Na3As adopts this cubic structure (the so-called Li3Bi motif).
References
- ↑ E. Dönges "Alkali Metals" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, New York. p. 986.
- ↑ Beister, H.J.; Syassen, K.; Klein, J. "Phase transition of Na3As under pressure" Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B: Chemical Sciences 1990, volume 45, pp. 1388–1392. doi:10.1515/znb-1990-1007
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.