Simple Bus Architecture

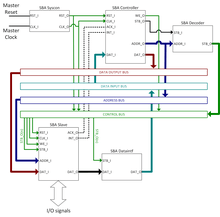
The Simple Bus Architecture[1] (SBA) is a form of computer architecture. It is made up software tools and intellectual property cores (IP Core) interconnected by buses using simple and clear rules, that allow the implementation of an embedded system (SoC). Basic templates are provided to accelerate design. The VHDL code that implements this architecture is portable.
Master core
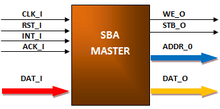
The master core is a finite state machine (FSM) and performs basic data flow and processing, similar to a microprocessor, but with lower consumption of logic resources. One possible way to implement FSMs is to have a controller that acts as a switch box. When the thread of execution executes FSM code, it runs the controller that evaluates/determines the current state, usually through the use of a switch (case) statement or if-then-else statements. Once the current state is determined, its code is executed, performing actions and setting the state transitions for the next FSM execution. The controller may be a simple switch statement, but an implementation may have the controller perform pre-processing of inputs and triggering of state transitions before-hand.
Wishbone
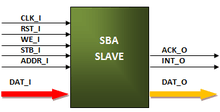
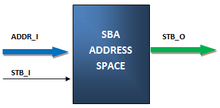
SBA is an application and a simplified version of the Wishbone[2] specification. SBA implements the minimum essential subset of the Wishbone signals interface. It can be connected with simple Wishbone IP Cores. SBA defines three types of cores: masters, slaves, and auxiliaries. Several slave IP Cores were developed following the SBA architecture, many to implement virtual instruments.
References
- ↑ "SBA - Simple Bus Architecture". Sba.accesus.com. Retrieved 2014-05-15.
- ↑ OpenCores. (2011) “Wishbone, Revision B.4 Specification