Siberian jay
| Siberian jay | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Corvidae |
| Genus: | Perisoreus |
| Species: | P. infaustus |
| Binomial name | |
| Perisoreus infaustus | |
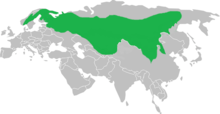 | |
| Current approximate range according to the IUCN | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
The Siberian Jay (Perisoreus infaustus) is a small jay with a widespread distribution within the coniferous forests in North Eurasia.
Taxonomy and systematics
The Siberian jay shares its genus Perisoreus with the Sichuan jay of China and the North American Gray Jay. However, the Siberian jay differs from the other two species in group living behaviours. Unlike the other two species, where group individuals unrelated to breeding parents may help to provision the young[3] n, the group individuals that accompany a breeding pair of Siberian jays do not help raise the offspring.[4] This absence of extra parental care despite group living may be because cooperative breeding has been selected against in the Siberian jay;[5] probably as an anti-predator strategy to avoid predator attention.[3]
Three Siberian jay subspecies occur west of Ural, with P.i.infaustus from Fennoscandia and Kola Peninsula grading into P.i.ostjakorum and ruthenus eastwards[6] (Cramp and Perrins, 1994). About 13 further subspecies have been reported further east.[7] With the arrival of coniferous forests in Scandinavia just after the last ice age, the Siberian jay probably expanded its range from east to west in response to the new suitable habitat emerged from climate warming.[7]
Description
The Siberian jay is the smallest of the western Palearctic corvids, weighing 75-90g[8] and measuring about 30 cm in length.[9] The adult plumage is greyish brown, with a dark brown head, paler forehead and buff breast. The rump is yellowish and the chin and throat are grey. There is also rufous streaking on the outer feathers, and the bill and legs are black.[10] Its overall colouration is fairly inconspicuous to visually conceal it from predators i within its forest habitat.[11] The plumage is also very soft and fluffy for insulation against extreme cold in winter.[10] There is one moult per year, which lasts from mid-June to mid-September.[10] An individual can live for up to 20 years,[12] although the average lifespan has been reported as 7.1 years.[13]
Newly hatched young are almost bare and are closely covered by the female. Juveniles look similar to adults, but the former have paler heads.[10]
The Siberian jay appears to be specially adapted in flight to navigating dense forest, whilst it is a rather cumbersome flyer in open terrain; which may explain its vulnerability to raptor predators outside forests.[14]
The Siberian jay is mostly silent but can utter a loud scream which resembles that of a buzzard (Buteo spp.). The song, which is given by both sexes; mainly in the breeding season and heard only from a short distance, comprises many different sounds. These range from soft and harsh notes, whistling, creaking, trilling and mimicked song of other birds.[11][10]
Habitat and distribution
The Siberian jay is resident in the northern boreal forests of spruce, pine, cedar and larch stretching from Scandinavia to northern Russia and Siberia.[11] It has an extensive range estimated at 19300000 km^2[13] and is native to Norway, Sweden, Finland, Russia, Mongolia, Kazakhstan and China.[13] It is vagrant in Belarus, Estonia, Latvia, Poland, Slovakia and Ukraine.[13] Although the species is largely sedentary, some individuals in the east of the range may move southwards in winter.[15]
This jay favours dense, mature forest habitat with closed canopy within lowlands and foothills.[15] Spruce forest is the preferred foraging and nesting habitat because the denser foliage of spruce than other local conifers offers greater concealment from predators.[16] Indeed, breeding success has been linked to higher foliage density; where eggs and nestlings are less likely to attract attention of predators.[8] Additionally, the benefit of increased predator evasion through more hiding space would probably outweigh the cost of making predators more difficult to see by the jays within the dense foliage.[17] The Siberian jay is notably selective in its choice of territory, with a typical territory comprising old dense spruce swamp with ample vegetation cover.[16] Territories also tend to be structurally diverse, comprising variably aged scrub, groves and flood meadows; so that active territories may be regarded as an indicator of high ecological diversity within the forest.[14]
Ecology
Feeding
The Siberian Jay is omnivorous and feeds mainly on berries, seeds, insects and spiders.[18] Flocks will also feed on large carcasses killed by mammalian predators such as wolves and wolverines.[8] Other occasional food items include eggs of small birds, tit nestlings, snails, slugs, small mammals and lizards.[11][14] In autumn and winter, berries (especially bilberries and cowberries) are typically collected and stored behind loose bark or in hanging beard lichen and between forked twigs.[11][10] Siberian jays distribute many different hidden food caches over a large area and are therefore known as scatter hoarders.[19] However, unlike in other corvids, this hidden food stash is not purposefully shared with siblings to increase inclusive fitness but is consumed by the hoarder or a pilferer for selfish use.[19] These food caches are critical to this species’ winter survival since foraging time is greatly restricted by the few hours of daylight.[9] To securely store food, Siberian jays have developed special saliva glands which they use to form sticky food clumps which they then adhere to beard moss or holes in tree bark; where they are readily accessible throughout the winter.[14] Because of their reliance on food stores during winter, they are territorial birds with reserves scattered around the territory, especially near to the nest.[14]
When foraging, Siberian jays often stay within closed forest to avoid visual detection by predators,[9] although they may occasionally forage for insects in wet tussocky open areas.[11] They forage in flocks comprising 3-5 individuals within their large territory.[19] Especially in winter, Siberian jays will also venture into increasingly open areas to take and store small rodents for food when the latter are abundant.[9]
The young are fed a high proportion of insect larvae, which is collected by the male and stored in his oesophagus, until he returns to the nest to regurgitate it to feed to the young.[10] In the first week of brooding, the male provides the female and young with all their food, and the female takes an increasing share of the work thereafter.[11]
Breeding
Siberian Jays are strictly monogamous and an established pair will stay together and hold the same territory for life.[11] Mate guarding in both sexes has been observed in this species, whereby males and females become increasingly aggressive toward same-sex conspecifics[20] (Ruth, 2016). This may prevent extra-pair mating opportunities for the partner and thereby preserve inclusive fitness for both pair members.[20] The territory of the size is 1–4 km^2, which is slightly enlarged in autumn and winter.[11][12] Although territories are firmly established, the jays can shift them to a neighbouring site if this is in a better quality habitat where breeding success will be higher.[21][8] Widowed individuals have been observed to establish new pair bonds.[12]
The nest is situated in a pine or spruce tree 4-6m above ground[11] within dense foliage to minimise detection by nest predators.[22] The nest comprises a loose cup of dry twigs broken off trees by the jays[11] and is thickly lined with beard lichen moss, down feathers, cobwebs, reindeer fur and wasp nest fragments; which is necessary insulation against the extreme winter cold.[10] Nest material is hoarded in winter long before building takes place.[11] Nest building then begins in late March and lasts about three weeks.[10] Both partners collect nest material; but only the female builds the nest.[11]
The eggs are pale green, blue or grey and spotted with grey and brown. Average egg dimensions are 31.6 x 22.9mm.[23] They are laid 31 March – 22 April, with a variable clutch size of 1-5 (and incubation period of about 19 days (Coombes, 1978, Eggers, 2006). The eggs are incubated entirely by the female,[22] whilst the male provides all the food for the brooding female and the chicks.[24] The Siberian jay is single brooded and does not relay in a breeding season even after nest failure, but will wait until next year.[22] A new nest is also built for every breeding attempt.[22]
The young fledge in mid-May to early June and leave the nest around this time, 18–24 days after the first chick has hatched;[10][12][24] although they usually hide within tree branches on the territory until able to fly.[14] Parents continue to feed them for about three weeks after fledging and all remain in a family group throughout summer, autumn and winter.[11] Most mature young disperse from the natal territory in their first summer 4–8 weeks after fledging to join new groups which are usually more than four territories away from the natal territory.[25] These early dispersers are generally subordinates which have been out-competed and displaced by one or a few socially dominant offspring that are retained.[4][8] If offspring have not yet dispersed by the time they are eight weeks old, they usually remain in the natal territory at least through the first winter.[8] The retained, socially dominant offspring which remain on the natal territory may wait for up to five years before dispersing when a breeding opportunity arises.[20] Retained offspring can also claim their natal territory, but only if both parents disappear within a short time, which is rare.[8] Offspring may inherit and breed at a new territory to which they disperse.[8] However, if there are no vacant territories to occupy, juveniles can join a different family group to gain feeding advantages and may attempt to establish own territory at an age of 2–3 years.[14]
Other behaviours
The species has a complex and unusual social structure.[4] Siberian jays live in small flocks of 2-7 individuals, with the dominant breeding pair at the centre of the group;[26][27] alongside retained multigenerational offspring and unrelated immigrants.[4][27] Within a group, there is a dominance hierarchy; whereby males are dominant over females and breeders are dominant over non-breeders; with some male non-breeders being dominant over female breeders.[28] Flock composition varies, with some comprising only family members, families associated with nonrelated immigrants, and others containing only nonrelated individuals.[26] Immigrated unrelated individuals can be tolerated within the territory outside nesting areas.[10]
At least one offspring usually remains with the parents after successful reproduction and regularly accompanies the pair for at least a year before dispersing;[19] although some retained offspring delay dispersal for up to five years.[21][25] These are the dominant offspring, which out-compete and expel their subordinate siblings.[26] The dispersed subordinate individuals (which disperse in their first summer) settle as non-breeding immigrants in other existing flocks[29][25][30] and tend to disperse much further than their dominant siblings, which more often move straight into a breeding position in a new territory.[30] Unusually for a group living species of Corvidae, group members do not help the parents raise younger siblings in future cohorts (there is no cooperative breeding) and so offspring retention is not explained by cooperative breeding.[4] Groups also unusually stay together outside the breeding season.[21][12]
Retention of some offspring in the natal territory after fledging is probably explained by nepotism which parents show toward them.[29] Parents provide retained offspring with reliable access to resources and antipredator protection,[17] thereby imparting to them a survival advantage[26][8] (in turn with an inclusive fitness advantage to the parents). Although delayed dispersal of offspring may be explained by “queueing” for available high-quality territories for the offspring to occupy,[21] the influence of nepotism has been shown experimentally. In removal experiments in which a father alpha male in a group was replaced with a new male unrelated to the offspring, the offspring were more likely to disperse prematurely; probably because the new male did not impart the same nepotistic advantages to the now unrelated young.[29] Although retained offspring may incur an initial cost of postponing breeding, this may be offset by enhanced breeding success later in life as a result of resource advantages gained from nepotistic parents;[8] and late dispersers have been found to have higher lifetime reproductive success than early dispersers.[31]
Siberian jays also display nepotistic alarming calling and these calls may function as a warning to conspecifics of an approaching predator.[32] Warning calls have been shown experimentally to decrease reaction time in response in an approaching predator and improve survival within non-breeding individuals.[32] However, females seem more able than males to differentiate between kin and non-kin(Griesser and Ekman, 2004). Alongside direct warning to family group members, nepotistic alarm calling by a breeding female may also function to divert predator attention away from her offspring.[33]
Siberian jays are aggressive to non-related intruders on their territory. Two different aggressive responses from territory holders within feeding grounds have been observed:(1) the intruder is approached and forced away (2) or is chased in flight; although the latter behaviour is more costly to the aggressor.[4] Although breeders show considerably more aggression toward immigrants than retained offspring,[4] aggressive responses appear to be modified by social dominance within groups.[27] For example, females have been found to receive notably more aggression than males because males show more resistance owing to their higher social dominance, therefore leading to higher energy cost by the aggressor.[27] Siberian jays also appear to recognise their own young through associative learning as opposed to genetic cues, as shown by experiments in which Siberian jays did not differentiate between own and fostered offspring.[27]
Threats
Birds of prey, especially hawks such the goshawk and sparrowhawk, are the main predators of Siberian jays.[26][9] Most Siberian jay predators detect prey visually, so that ample forest cover together with the jays’ cryptic colouration and secretive nesting help render the jays inconspicuous to predators.[34] Predators of this species’ eggs and young include squirrels, ravens, hooded crows, magpies and Eurasian jays. As an antipredator measure, the nest is built in the dense foliage to minimize predator attention. Females also appear to lay smaller clutches under higher predation pressure, and this may minimise predator attention to the nest through fewer necessary nest visits by the parent.[22] Further, in higher cover nests, chicks are fed by the parent more evenly than in exposed nests more detectable by predators; so that chicks raised in well-concealed nests are expected to have better growth.[22]
The European range of the population is threatened by habitat degradation through forestry, road building, settlements and agriculture.[35] Modern European forestry practices in particular may be decreasing breeding habitat quality for the Siberian jay primarily through reduced foliage cover.[22] This may occur through forest thinning, whereby lower-quality trees are regularly removed from forest stands. Excessive clearcutting has been linked with increased territory abandonment by Siberian jays and in turn strong decreases in the species’ breeding success in affected areas.[36] Another practice which may threaten the Siberian jay has been the large-scale removal of stands of native spruce to be replaced with pine, potentially leading to loss of sufficient visual cover of nesting activity from predators with removal of spruce.[16] In Finland, spruce has also been declining faster than other forest types and loss and fragmentation of spruce forests through forestry has been linked with population declines here.[37] Anthropogenic habitat loss may be interacting with natural threats from predators. The Siberian jay population has declined more than can be explained by anthropogenic forest clearance alone,[38] which may be attributable to increased nest exposure to avian predators and other human activities favouring these predatory species.[34] Human activity may also lead to increases in nest predators such as Eurasian jays through activities such as supplemental feeding and refuse dumpling, in turn compounding the predation pressure on Siberian jays through increased exposure.[34] Finally, destruction by felling of winter food storages in trees near territories during winter may also destroy winter food caches.[14]
Alongside increased predator attention, the open land exposed as a result of forest habitat fragmentation also presents an apparently large dispersal barrier which the jays find difficult to cross given their apparent cumbersomeness at traversing open land.[14] Siberian jays are also apparently unable to evolve fast enough to adapt to these anthropogenic habitat and predator population changes.[34] Because this species is markedly sedentary, there appear to several genetically isolated subpopulations.[7] Given this jay’s high site fidelity, gene flow between subpopulations may have been low even before onset of modern forestry practices which have created the strong dispersal barriers.[7]
In culture and relationship with humans
Siberian jays are reported to be fearless in human company, and with repeated provision of food by humans in the same place may become tame enough to take food from the hand.[11] This was especially the case formerly when forestry workers regularly left patches of food scraps in the forest for the jays to take; with the same being true around campfires.[11] The Siberian jay has now gained flagship status as a conservation concern both because of threats from modern forestry and because active territories are considered a sign of high-quality biodiverse forest.[14]
Status
The Siberian jay is evaluated as Least Concern by the IUCN because of the species’ exceptionally large range.[13] Although the world population is decreasing, the magnitude of this decrease is not considered sufficiently large to render the species Vulnerable.[13] The world population is very large and estimated at 4295000-7600000 mature individuals.[13] Population declines have been reported to be strongest in the southernmost part of the range.[13]
Gallery
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2012). "Perisoreus infaustus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ↑ "Siberian Jay Perisoreus infaustus (Linnaeus, 1758)". Avibase. Denis Lepage. Retrieved 2 July 2017.
- 1 2 Jing Y, Fang Y, Strickland D, Lu N, Sun Y-H. 2009. Alloparenting in the rare Sichuan jay (Perisoreus internigrans). The Condor 111: 662-667.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Ekman J, Sklepkovych B. 1994. Conflict of interest between the sexes in Siberian jay winter flocks. Animal Behaviour 48: 485-487
- ↑ Ekman J, Ericson PGP. 2006. Out of Gondwanaland; the evolutionary history of cooperative breeding and social behaviour among crows, magpies, jays and allies. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 273: 1117-1125.
- ↑ Cramp S, Perrins C. 1994. Handbook of the Birds of Europe, the Middle East and North Africa. The Birds of the Western palearctic, Vol. 8 – Oxford University Press, pp. 40-42.
- 1 2 3 4 Uimaniemi L, Orell M, Mӧnkkӧnen M, Huhta E, Jukka J, Lumme J. 2000. Genetic diversity in the Siberian jay Perisoreus infaustus in fragmented old-growth forests of Fennoscandia. Ecography 23: 669-677.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Ekman, Jan; Griesser, Michael (2016). "Siberian jays: delayed dispersal in the absence of cooperative breeding". In Walt Koenig; Janis L Dickinson. Cooperative breeding in vertebrates: studies of ecology, evolution, and behavior. Cambridge University Press. pp. 6–18. doi:10.1017/CBO9781107338357.002. ISBN 9781107043435.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Hogstad O. 2016. Hunting strategies by Siberian jays Perisoreus infaustus on wintering small rodents. Ornis Norvegica 39: 25-28.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Coombes F. 1978. The Crows, a Study of the Corvids of Europe. BT Batsford Limited
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Blomgren A. 1971. Studies of less familiar birds, 162: Siberian jay. British Birds 64: 25-28.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Lillandt B-G, Bensch S, von Schantz T. 2003. Family structure in the Siberian jay as revealed by microsatellite analysis. The Condor 105: 505-514.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Birdlife International. 2016. Perisoreus infaustus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. e.T22705775A87356809. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22705775A87356809.en
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Fabritius H. 2010. Effective population size and the viability of the Siberian jay population of Suupohja, Finland. Master’s thesis, University of Helsinki.
- 1 2 Madge S. 2009. Siberian Jay (Perisoreus infaustus). In: del Hoyo J, Elliot A, Sargatal J. Christie DA, de Jauna E.(eds). Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive. Lynx Edicions, Barcelona.
- 1 2 3 Edenius L, Meyer C. 2002. Activity budgets and microhabitat use in the Siberian Jay Perisoreus infaustus in managed and unmanaged forest. Ornis Fennica 79: 26-33.
- 1 2 Nystrand M. 2006. Influence of age, kinship, and large-scale habitat quality on local foraging choices of Siberian jays. Behavioural Ecology 17: 503-509.
- ↑ Virkkala R. 1988. Foraging niches of foliage-gleaning birds in he northernmost taiga in Finland. Ornis Fennica 65: 104-113.
- 1 2 3 4 Ekman J, Brodin A, Bylin A, Sklepkovych B. 1996. Selfish long-term benefits of hoarding in the Siberian jay. Behavioural Ecology 7: 140-144.
- 1 2 3 Ruth L. 2016. Mate-guarding in the Siberian jay (Perisoreus infaustus). Biology Independent Research Project, Karlstads Universitet.
- 1 2 3 4 Ekman J, Eggers S, Griesser M, Tegelstrӧm H. 2001. Queueing for preferred territories: delayed dispersal of Siberian jays. Journal of Animal Ecology 70:317-324.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Eggers S, Griesser M, Nystrand M, Ekman J. 2006. Predation risk induces changes in nest-site selection and clutch size in the Siberian jay. Proc. R. Soc. B 273: 701-706.
- ↑ Harrison C. 1975. A Field Guide to the Nests, Eggs and Nestlings of British and European Birds. London
- 1 2 Eggers S. 2002. Behaviour and life-history responses to chick provisioning under the risk of nest predation. PhD dissertation, Uppsala University.
- 1 2 3 Griesser M, Nystrand M, Eggers S, Ekman J. 2008. Social constraints limit dispersal and settlement decisions in a grouplivingbird species. Behavioral Ecology 19: 317–324.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Griesser M. 2003. Nepotistic vigilance behaviour in Siberian jay parents. Behavioural Ecology 14: 246-250.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Griesser M, Halvarsson P, Drobniak SM, Vila C. 2015. Fine-scale kin recognition in the absence of social familiarity in the Siberian jay a monogamous bird species. Molecular ecology 24.22: 5726-5738.
- ↑ Ekman J, Sklepkovych B. 1994. Conflict of interest between the sexes in Siberian jay winter flocks. Animal Behaviour 48: 485-487.
- 1 2 3 Ekman J, Griesser M. 2002. Why offspring delay dispersal: experimental evidence for a role of parental tolerance. Proceedings for the Royal Society of London B 269: 1709-1713.
- 1 2 Griesser M, Halvarson P, Sahlman T, Ekman J. 2014. What are the strengths and limitations of direct and indirect assessment of dispersal? Insight from a long-term field study in a group-living species. Behavioural Ecology and Sociobiology 68.3: 485-497.
- ↑ Ekman J, Bylin A, Tegelstrom H. 1999. Increased lifetime reproductive success for Siberian jay Perisoreus infaustus males with delayed dispersal. Proc. R. Soc. Lond B 266: 911-915
- 1 2 Griesser M. 2013. Do warning calls boost survival of signal recipients? Evidence from a field experiment in a group-living bird species. Frontiers in Zoology 10: 49
- ↑ Griesser M, Ekman J. 2004. Nepotistic alarm calling in the Siberian jay, Perisoreus infaustus. Animal Behaviour 67: 933-939
- 1 2 3 4 Eggers S, Griesser M, Andersson T, Ekman J. 2005. Nest predation and habitat change interact to influence Siberian jay numbers. OIKOS 111: 150-158.
- ↑ Hagemeijer, EJM, Blair MJ. 1997. The EBCC Atlas of European breeding Birds: their Distribution and Abundance. T. and A. D. Poyser, London.
- ↑ Griesser M, Nystrand M, Eggers S, Ekman J. 2007. Impact of forestry practices on fitness correlates and population productivity in an open-nesting bird species. Conservation Biology 21: 767-774.
- ↑ Muukonen P, Angervuori A, Virtanen T, Kuparinen A. 2012. Loss and fragmentation of Siberian jay (Perisoreus infaustus) habitats. Boreal Environment Research 17: 59-71.
- ↑ Helle P, Jarvinen O. 1986. Population trends of North Finnish land birds in relation to their habitat selection and changes in forest structure. OIKOS 46: 107-115