Senegambia
Senegambia is a region of West Africa that encompasses the modern states of Senegal, The Gambia, and Guinea-Bissau, as well as portions of Mauritania, Mali, and Guinea. The region spans beyond the borders of the Senegambia Confederation and was described by Boubacar Barry as historically "the main gateway to Sudan, the cradle of the great empires of Ghana, Mali and Songhai" and "the centre of gravity for West Africa."[1]
History
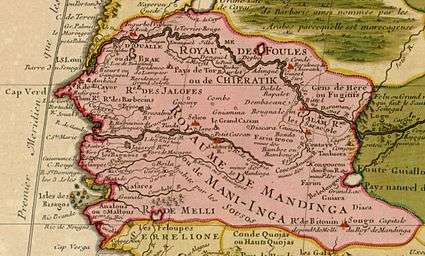
The region became a focus of Franco-British-Portuguese rivalry from the 15th century onwards. The Portuguese were the first to arrive in the region in the 1450s. Until the 16th century, they held a monopoly on trade.[2]
In 1677, the French took the island of Gorée, and in 1681 they took control of Albreda on the Gambia River. This began a rivalry with the English, and in 1692 they briefly confiscated Gorée and Saint-Louis. In 1758, during the Seven Years War, Gorée was captured by the British, who held it until 1763. In 1765, the British formed the Senegambia Province. In 1778, during the American War of Independence, the French went on the offensive, and razed James Island in the River Gambia. In 1783, the Treaty of Versailles recognised British claims to The Gambia and French claims to Saint-Louis and Gorée, dissolving the Senegambia Province.[1]
The French pursued a policy of expansion and saw The Gambia as an obstacle. In the late 19th century, they proposed ceding Dadou, Grand Bassam, and Assinie in return for The Gambia. The negotiations broke down but were repeatedly brought up again. After the failed 1981 coup d'etat in The Gambia, a Senegambia Confederation was proposed and accepted. This lasted until 1989.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 "The historical perspective of Senegambia: The prospects and the way forward". The Standard. 5 June 2014. Archived from the original on June 2017. Retrieved 3 September 2018.
- ↑ "Senegambia". Atlast of the Gambia. Archived from the original on November 2017. Retrieved 3 September 2018.