Screen of death
In computing, a screen of death is an informal term for a type of computer operating system error message, displayed onscreen when the system has experienced a fatal error. Computer users have dubbed these messages "screens of death" as they typically result in unsaved work being lost and often indicate serious problems with the system's hardware or software. These error screens are usually the result of a kernel panic, although the terms are frequently used interchangeably. Most screens of death are displayed on an even background color with a message advising the user to restart the computer.
Known screens of death
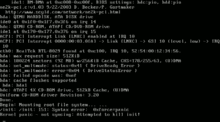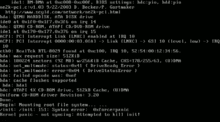

The Mac OS X kernel panic alert. This version was first used in Mac OS X 10.5.
- The Blue Screen of Death (also called BSoD, or stop error) is a common name for a screen displayed by the Microsoft Windows operating system when a critical system error occurs. By far, this is the most famous screen of death.
- Two Black Screen of Death are known: One is a failure mode of Windows 3.x. One appears when the bootloader for Windows Vista and later fails.
- A Green Screen of Death is a green screen that appears on a TiVo with a message that includes the words "a severe error has occurred". Its appearance often means that the hard drive of the device has failed.[1][2] Blue Screens of Death on the Windows Insider builds of Windows 10 appears as green instead of blue, starting with build 14997.[3]
- The Purple Screen of Death is used by VMware ESX Server, a server virtualization product by VMware, Inc. It is displayed in the event of a fatal kernel error. The screen provides error codes that can be used for debugging purposes.
- Two Red Screens of Death are known: One appears in early beta versions of Windows Vista. It later became a black screen. Another appeared in Windows 98 and is caused by Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI).
- A White Screen of Death appears on several other operating systems, content management systems[4] and BIOSes. One is in iOS 7, and the screen of death appears when a white iPhone 5 or later or a white iPod touch (5th generation) is frozen. Everything on the screen goes white, and a black Apple logo is all that's displayed on the screen.[5]
- A Yellow Screen of Death occurs when an ASP.NET web app encounters a problem and crashes.[6]
- A kernel panic is used primarily by Unix and Unix-like operating systems: the Unix equivalent of Microsoft's Blue Screen of Death. It is a routine called when the kernel detects irrecoverable errors in runtime correctness; in other words, when continued operation may risk escalating system instability, and a system reboot is easier than attempted recovery.
- A Sad Mac is a symbol used by older-generation Apple Macintosh computers, starting with the original Macintosh 128K, to indicate a severe hardware or software problem that prevented startup from occurring successfully. A similar symbol exists for the iPod.
- The Bomb icon is a symbol that was displayed when a classic Mac OS program had an application crash. The bomb symbols were also used by the Atari ST line of computers when the system encountered a fatal error. The number of bombs indicated the exact cause of the error.
- Guru Meditation is the name of the error that occurred on early versions of the Amiga computers when they crashed.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Screens of death. |
References
- ↑ Todd W. Carter; Michael Bellomo (2004). How to Do Everything with Your TiVo. McGraw Hill Professional. pp. 245, 246, 344. ISBN 978-0-07-223140-3.
- ↑ Krikorian. TiVo Hacks: 100 Industrial-Strength Tips & Tools. O'Reilly Media. 2003. Page 24.
- ↑ Warren, Tom (29 December 2016). "Windows 10 testers will now get a Green Screen of Death". The Verge. Vox Media.
- ↑ "Drupal White Screen of Death".
- ↑ Ulanoff, Lance (2006-09-12). "The Apple iPod's White Screen of Death". PCMag.com. Retrieved 2011-05-23.
- ↑ Busoli, Simone (November 15, 2007). "ELMAH - Error Logging Modules And Handlers".
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.