Sarcochilus
| Sarcochilus | |
|---|---|
.jpg) | |
| Sarcochilus fitzgeraldii 1882 illustration[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Orchidaceae |
| Subfamily: | Epidendroideae |
| Tribe: | Vandeae |
| Subtribe: | Aeridinae |
| Genus: | Sarcochilus R.Br. (1810) |
| Type species | |
| Sarcochilus falcatus | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
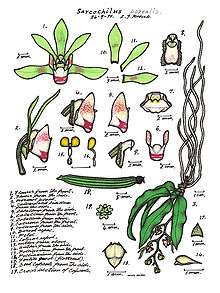
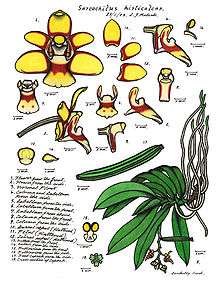

Sarcochilus, commonly known as butterfly orchids or fairy bells is a genus of about twenty five species of flowering plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae and which are found in Australia and New Caledonia.[2] Butterfly orchids are mostly epiphytes but a few species grow on rocks or in leaf litter. The leaves are arranged disticiously and not originating from a pseudobulb. The axillary, racemose inflorescence is pendant to arching with a few to many, successive opening flowers with free petals and sepals. The colour of the flowers is variable and goes from pure white (S. falcatus) to white and red (S. fitzgeraldii). The trilobed, fleshy labellum is saccate ( = pouch-like) and articulate to the apex of the column foot. The large side lobes are erect and curved. The small midlobe is attached to a short spur. Some of these species can form keikis, forming large clumps with age.
The name Sarcochilus is derived from the Ancient Greek words sarkos meaning "flesh"[3]:47 and cheilos meaning "lip".[3]:200 referring to the fleshy labellum of these orchids.
The genus Sarcochilus has been shown to be non-monophyletic.[4]
Sarcochilus is abbreviated as "Sarco." in the horticultural trade. Many species have become endangered or vulnerable, due to illegal collecting.
Species
The following is a list of Sarcochilus species recognised by the World Checklist of Selected Plant Families as at January 2018. The common names in the list below are those used by David Jones.[2][5]
- Sarcochilus argochilus D.L.Jones & M.A.Clem., 2006 northern lawyer orchid
- Sarcochilus australis (Lindl.) Rchb.f. in Walp., 1863 butterfly orchid, Gunn's tree orchid
- Sarcochilus borealis (Nicholls) D.L.Jones & M.A.Clem., 1989 small lawyer orchid
- Sarcochilus ceciliae F.Muell., 1865 fairy bells (mostly a lithophyte)
- Sarcochilus chrysanthus Schltr., 1913
- Sarcochilus dilatatus F.Muell., 1859 brown butterfly orchid (epiphyte)
- Sarcochilus falcatus R.Br., 1810 orange blossom orchid (epiphyte)
- Sarcochilus fitzgeraldii F.Muell., 1870 ravine orchid (mainly lithophytic)
- Sarcochilus gildasii N.Hallé, 1986
- Sarcochilus hartmannii F.Muell., 1874 large boulder orchid (almost completely lithophytic)
- Sarcochilus hillii (F.Muell.) F.Muell, 1860 myrtle bells
- Sarcochilus hillii var. hillii.
- Sarcochilus hillii var. thycola N.Hallé, 1986
- Sarcochilus hirticalcar (Dockrill) M.A.Clem. & B.J.Wallace, 1998 harlequin orchid
- Sarcochilus iboensis Schltr., 1913
- Sarcochilus koghiensis Schltr., 1911
- Sarcochilus odoratus Schltr., 1913
- Sarcochilus parviflorus Lindl., 1838 southern lawyer orchid
- Sarcochilus rarus Schltr., 1906
- Sarcochilus roseus (Clemesha) Clemesha, 1969 northern fairy bells (true lithophyte)
- Sarcochilus serrulatus D.L.Jones, 1972 banded butterfly orchid
- Sarcochilus spathulatus R.S.Rogers, 1927 small butterfly orchid
- Sarcochilus tricalliatus (Rupp) Rupp, 1951
- Sarcochilus uniflorus Schltr., 1913
- Sarcochilus weinthalii F.M.Bailey, 1903 blotched butterfly orchid (epiphyte)
Hybrids
The species S. falcatus, S. fitzgeraldii and S. hartmannii have been hybridized, often with S. australis, producing rounder, cherry-red flowers. A few examples are : S. Fitzhart (hartmannii × fitzgeraldii), S. Heidi (Fitzhart × hartmannii), S. Arcadia (Lois × Fitzhart) and S. George Colthup (Melba × hartmannii).
Intrageneric hybrids include
- × Aeridochilus (Aerides × Sarcochilus)
- × Gastrosarcochilus (Gastrochilus × Sarcochilus)
- × Luichilus (Luisia × Sarcochilus)
- × Malcolmcampbellara (Drymoanthus × Plectorrhiza × Sarcochilus)
- × Parachilus (Parasarcochilus × Sarcochilus)
- × Plectochilus (Plectorrhiza × Sarcochilus)
- × Pomatochilus (Pomatocalpa × Sarcochilus)
- × Porterara (Rhynchostylis × Sarcochilus × Vanda)
- × Rhinochilus (Rhinerrhiza × Sarcochilus)
- × Sarcocentrum (Ascocentrum × Sarcochilus)
- × Sarcomoanthus (Sarcochilus × Drymoanthus)
- × Sarconopsis (Phalaenopsis × Sarcochilus)
- × Sarcorhiza (Rhinerrhiza × Sarcochilus)
- × Sarcothera (Renanthera × Sarcochilus)
- × Sarcovanda (Sarchilus × Vanda)
- × Sartylis (Rhynchostylis × Sarcochilus)
- × Sladeara (Doritis × Phalaenopsis × Sarcochilus)
- × Uptonara (Phalaenopsis × Rhynchostylis × Sarcochilus)
References
- ↑ Fitzgeraldi, R. D., Thomas Richards, Government Printer. Sidney (editors) - Schweizerische Orchideenstiftung am Herbarium Jany Renz
- 1 2 3 Kew World Checklist of Selected Plant Families
- 1 2 Brown, Roland Wilbur (1956). The Composition of Scientific Words. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press.
- ↑ Topik Hidayat, Tomohisa Yukawa and Motomi Ito (August 2005). "Molecular phylogenetics of subtribe Aeridinae (Orchidaceae): insights from plastid matK and nuclear ribosomal ITS sequences". Journal of Plant Research. 118 (4): 271–284. doi:10.1007/s10265-005-0217-3. PMID 16025359.
- ↑ Jones, David L. (2006). A complete guide to native orchids of Australia including the island territories. Frenchs Forest, N.S.W.: New Holland. pp. 447–452. ISBN 1877069124.
- Upton, Walter T. (1992). Sarcochilus Orchids of Australia. Double U Orchids, Balmain. pp. 119 p. ISBN 0-646-09734-2.
External links

