Saarland state election, 2017
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
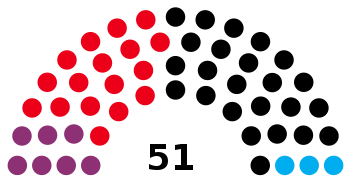
All 51 seats of the Landtag of the Saarland 26 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
State elections were held in Saarland on 26 March 2017.[2][3] All 51 seats in the Landtag of Saarland were up for election. The incumbent Minister-President Annegret Kramp-Karrenbauer went into the election leading a grand coalition of her Christian Democratic Union (CDU) and the Social Democratic Party (SPD),[4] seeking re-election after serving two terms as Minister-President.[5]
Background
The 2012 state election was a snap election called due to the collapse of the Jamaica coalition of CDU, Free Democrats (FDP) and the Green Party on 6 January 2012. The result of the election was a victory for the governing Christian Democrats, while the FDP suffered enormous losses. The party thus failed to achieve parliamentary representation. The Greens lost voters, but obtained seats by getting enough votes to reach the 5 percent threshold. The opposition Social Democrats led by Heiko Maas increased their number of seats and votes, but failed to become the largest party in parliament. The Left Party suffered moderate losses. The Pirate Party secured parliamentary representation for the first time in a Western German regional parliament.[6]
Parties and candidates
Opinion polling
| Publication date | Poll source | Others | Lead | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 Mar 2017 | 2017 election | 40.7 | 29.6 | 12.9 | 0.7 | 4.0 | 0.8 | 3.3 | 6.2 | 1.9 | 11.1 |
| 23 Mar 2017 | Forschungsgruppe Wahlen | 37 | 32 | 12.5 | – | 4.5 | – | 4 | 6 | 4 | 5 |
| 22 Mar 2017 | INSA | 35 | 33 | 13 | – | 4 | – | 5 | 6 | 4 | 2 |
| 17 Mar 2017 | Forschungsgruppe Wahlen | 37 | 32 | 12 | – | 4 | – | 4 | 7 | 4 | 5 |
| 16 Mar 2017 | Infratest dimap | 35 | 34 | 13 | – | 4.5 | – | 3 | 6.5 | 4 | 1 |
| 9 Mar 2017 | Forsa | 34 | 33 | 13 | – | 5 | – | 4 | 6 | 5 | 1 |
| 7 Mar 2017 | INSA | 36 | 33 | 12 | – | 4 | – | 4 | 7 | 4 | 3 |
| 26 Jan 2017 | Infratest dimap | 38 | 26 | 14 | – | 5 | – | 4 | 9 | 4 | 12 |
| 13 Jan 2017 | INSA | 35 | 24 | 16 | – | 6 | – | 5 | 10 | 2 | 11 |
| 15 Nov 2016 | Forsa | 37 | 26 | 15 | – | 6 | – | 3 | 9 | 4 | 11 |
| 11 May 2016 | Infratest dimap | 34 | 29 | 12 | – | 7 | – | 4 | 11 | 3 | 5 |
| 31 Mar 2015 | Infratest dimap | 40 | 33 | 10 | 1 | 6 | – | 2 | 4 | 4 | 7 |
| 25 May 2014 | EU Parliament election | 34.9 | 34.4 | 6.6 | 1.7 | 6.0 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 6.8 | 5.9 | 0.5 |
| 14 May 2014 | Infratest dimap | 37 | 34 | 13 | 2 | 5 | – | – | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| 22 Sep 2013 | Federal Election | 37.8 | 31.0 | 10.0 | 2.6 | 5.7 | 1.2 | 3.8 | 5.2 | 3.9 | 5.6 |
| 7 May 2013 | Infratest dimap | 39 | 36 | 10 | 2 | 6 | – | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 25 Mar 2012 | 2012 election | 35.2 | 30.6 | 16.1 | 7.4 | 5.0 | 1.7 | 1.2 | – | 4.4 | 4.6 |
- Preferred Minister-President
| Publication date | Poll source | Kramp-Karrenbauer |
Rehlinger |
Maas |
None |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 Mar 2017 | Forschungsgruppe Wahlen | 53.0 | 34.0 | – | 13.0 |
| 17 Mar 2017 | Forschungsgruppe Wahlen | 55.0 | 31.0 | – | 14.0 |
| 16 Mar 2017 | Infratest dimap | 51.0 | 32.0 | – | 7.0 |
| 26 Jan 2017 | Infratest dimap | 60.0 | 23.0 | – | 9.0 |
| 15 Nov 2016 | Forsa | 54.0 | 19.0 | – | – |
| 11 May 2016 | Infratest dimap | 59.0 | 26.0 | – | 10.0 |
| 31 Mar 2015 | Infratest dimap | 62.0 | 18.0 | – | 9.0 |
| 14 May 2014 | Infratest dimap | 53.0 | – | 35.0 | 6.0 |
| 7 May 2013 | Infratest dimap | 53.0 | – | 36.0 | 7.0 |
Results
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Christian Democratic Union||217,275 | 40.7 | 24 | +5 | ||
| Social Democratic Party||157,841 | 29.6 | 17 | 0 | ||
| The Left||68,566 | 12.9 | 7 | –2 | ||
| Alternative for Germany||32,935 | 6.2 | 3 | New | ||
| Alliance '90/The Greens||21,392 | 4.0 | 0 | –2 | ||
| Free Democratic Party||17,419 | 3.3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Family Party||4,433 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Pirate Party||3,979 | 0.7 | 0 | –4 | ||
| National Democratic Party||3,744 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Free Voters||2,146 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Liberal Conservative Reformers||1,179 | 0.2 | 0 | New | ||
| The Reformers | 883 | 0.2 | 0 | New | |
| Unity | 872 | 0.2 | 0 | New | |
| Democratic Citizens of Germany | 539 | 0.1 | 0 | New | |
| Basic Income Alliance | 286 | 0.1 | 0 | New | |
| Free Citizens Union | 51 | 0.0 | 0 | New | |
| Invalid/blank votes | 6,561 | – | – | – | |
| Total | 540,091 | 100 | 51 | 0 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 774,947 | 69.69 | – | – | |
| Source: Wahlrecht | |||||
Reactions and aftermath
Pre-election polls suggested a close contest between the CDU and SPD, but the CDU surprised observers by exceeding pre-vote predictions.[7] After the election, several commentators described the results as a boost for the September 2017 electoral prospects of German Chancellor Angela Merkel and the CDU,[8][9][10] and as a setback for SPD leader Martin Schulz.[11]
As both the CDU and SPD refused to coalition with AfD, the CDU and SPD coalition reached an agreement to continue governing together after the election.[12]
References
- ↑ The party leader: Annegret Kramp-Karrenbauer, cdu-saar.de (German)
- ↑ Election dates in Germany, wahlrecht.de (German)
- ↑ Vor dem Wahlkampf: Elefantenrunde ohne Berührungsängste, Saarbrücker Zeitung (German), 13 February 2016
- ↑ Kramp-Karrenbauer für Fortsetzung der großen Koalition im Saarland, focus.de (German), 2 Oct 2014
- ↑ Die „rote Charlotte“ hält sich bereit, Frankfurter Allgemeine (German), 29 May 2015
- ↑ Merkel's party wins German state election, AlJazeera (English), 25 March 2012
- ↑ Delcker, Janosch (27 March 2017). "Merkel: Embracing 'Grand Coalition' Helped Us Win Saarland". Politico. Retrieved 27 March 2017.
- ↑ Chase, Jefferson (27 March 2017). "Merkel's CDU Savors Local Election Win". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 27 March 2017.
- ↑ Carrel, Paul; Erdem, Hakan (26 March 2017). "Merkel's Conservatives Win Saarland Vote in Boost for National Campaign". Reuters. Retrieved 27 March 2017.
- ↑ Smale, Alison (26 March 2017). "Angela Merkel's Re-election Bid Is Buoyed by Widely Watched State Election". The New York Times. Retrieved 27 March 2017.
- ↑ Carrel, Paul (27 March 2017). "Germany's 'Schulz Effect' Fails to Deliver in First Election Test". U.S. News & World Report (from Reuters). Retrieved 27 March 2017.
- ↑ https://www.handelsblatt.com/politik/deutschland/saarland-cdu-und-spd-unterschreiben-koalitionsvertrag/19809446.html


_in_Hamm_(10571425525).jpg)
