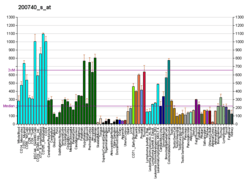
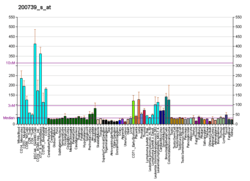
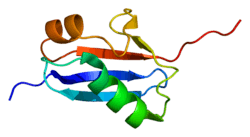Small ubiquitin-related modifier 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SUMO3 gene.[5][6]
Function
SUMO proteins, such as SUMO3, and ubiquitin (see MIM 191339) posttranslationally modify numerous cellular proteins and affect their metabolism and function. However, unlike ubiquitination, which targets proteins for degradation, sumoylation participates in a number of cellular processes, such as nuclear transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, and protein stability (Su and Li, 2002).[supplied by OMIM][6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000184900 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020265 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Lapenta V, Chiurazzi P, van der Spek P, Pizzuti A, Hanaoka F, Brahe C (March 1997). "SMT3A, a human homologue of the S. cerevisiae SMT3 gene, maps to chromosome 21qter and defines a novel gene family". Genomics. 40 (2): 362–6. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.4556. PMID 9119407.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: SUMO3 SMT3 suppressor of mif two 3 homolog 3 (S. cerevisiae)".
- ↑ Lee J, Lee Y, Lee MJ, Park E, Kang SH, Chung CH, Lee KH, Kim K (October 2008). "Dual modification of BMAL1 by SUMO2/3 and ubiquitin promotes circadian activation of the CLOCK/BMAL1 complex". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 28 (19): 6056–65. doi:10.1128/MCB.00583-08. PMC 2546997. PMID 18644859.
- ↑ Hardeland U, Steinacher R, Jiricny J, Schär P (March 2002). "Modification of the human thymine-DNA glycosylase by ubiquitin-like proteins facilitates enzymatic turnover". The EMBO Journal. 21 (6): 1456–64. doi:10.1093/emboj/21.6.1456. PMC 125358. PMID 11889051.
Further reading
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (January 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (October 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Saitoh H, Hinchey J (March 2000). "Functional heterogeneity of small ubiquitin-related protein modifiers SUMO-1 versus SUMO-2/3". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (9): 6252–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.9.6252. PMID 10692421.
- Tatham MH, Jaffray E, Vaughan OA, Desterro JM, Botting CH, Naismith JH, Hay RT (September 2001). "Polymeric chains of SUMO-2 and SUMO-3 are conjugated to protein substrates by SAE1/SAE2 and Ubc9". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (38): 35368–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104214200. PMID 11451954.
- Lin J, Johannsen E, Robertson E, Kieff E (January 2002). "Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C putative repression domain mediates coactivation of the LMP1 promoter with EBNA-2". Journal of Virology. 76 (1): 232–42. doi:10.1128/JVI.76.1.232-242.2002. PMC 135708. PMID 11739688.
- Kadoya T, Yamamoto H, Suzuki T, Yukita A, Fukui A, Michiue T, Asahara T, Tanaka K, Asashima M, Kikuchi A (June 2002). "Desumoylation activity of Axam, a novel Axin-binding protein, is involved in downregulation of beta-catenin". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 22 (11): 3803–19. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.11.3803-3819.2002. PMC 133821. PMID 11997515.
- Su HL, Li SS (August 2002). "Molecular features of human ubiquitin-like SUMO genes and their encoded proteins". Gene. 296 (1–2): 65–73. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(02)00843-0. PMID 12383504.
- Subramanian L, Benson MD, Iñiguez-Lluhí JA (March 2003). "A synergy control motif within the attenuator domain of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha inhibits transcriptional synergy through its PIASy-enhanced modification by SUMO-1 or SUMO-3". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (11): 9134–41. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210440200. PMID 12511558.
- Eaton EM, Sealy L (August 2003). "Modification of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-beta by the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) family members, SUMO-2 and SUMO-3". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (35): 33416–21. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305680200. PMID 12810706.
- Tatham MH, Kim S, Yu B, Jaffray E, Song J, Zheng J, Rodriguez MS, Hay RT, Chen Y (August 2003). "Role of an N-terminal site of Ubc9 in SUMO-1, -2, and -3 binding and conjugation". Biochemistry. 42 (33): 9959–69. doi:10.1021/bi0345283. PMID 12924945.
- Dobreva G, Dambacher J, Grosschedl R (December 2003). "SUMO modification of a novel MAR-binding protein, SATB2, modulates immunoglobulin mu gene expression". Genes & Development. 17 (24): 3048–61. doi:10.1101/gad.1153003. PMC 305257. PMID 14701874.
- Reverter D, Lima CD (August 2004). "A basis for SUMO protease specificity provided by analysis of human Senp2 and a Senp2-SUMO complex". Structure. 12 (8): 1519–31. doi:10.1016/j.str.2004.05.023. PMID 15296745.
- Ayaydin F, Dasso M (December 2004). "Distinct in vivo dynamics of vertebrate SUMO paralogues". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 15 (12): 5208–18. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-07-0589. PMC 532004. PMID 15456902.
- Xu Z, Au SW (March 2005). "Mapping residues of SUMO precursors essential in differential maturation by SUMO-specific protease, SENP1". The Biochemical Journal. 386 (Pt 2): 325–30. doi:10.1042/BJ20041210. PMC 1134797. PMID 15487983.
- Ding H, Xu Y, Chen Q, Dai H, Tang Y, Wu J, Shi Y (March 2005). "Solution structure of human SUMO-3 C47S and its binding surface for Ubc9". Biochemistry. 44 (8): 2790–9. doi:10.1021/bi0477586. PMID 15723523.
- Bossis G, Malnou CE, Farras R, Andermarcher E, Hipskind R, Rodriguez M, Schmidt D, Muller S, Jariel-Encontre I, Piechaczyk M (August 2005). "Down-regulation of c-Fos/c-Jun AP-1 dimer activity by sumoylation". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 25 (16): 6964–79. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.16.6964-6979.2005. PMC 1190241. PMID 16055710.
PDB gallery |
|---|
1u4a: Solution structure of human SUMO-3 C47S 1wm2: Crystal structure of human SUMO-2 protein 1wm3: Crystal structure of human SUMO-2 protein 1wz0: Solution Structure of Human SUMO-2 (SMT3B), a Ubiquitin-like Protein 2awt: Solution Structure of Human Small Ubiquitin-Like Modifier Protein Isoform 2 (SUMO-2) 2ckh: SENP1-SUMO2 COMPLEX 2d07: Crystal Structure of SUMO-3-modified Thymine-DNA Glycosylase 2io0: Crystal structure of human Senp2 in complex with preSUMO-2 2io1: Crystal structure of human Senp2 in complex with preSUMO-3 2io3: Crystal structure of human Senp2 in complex with RanGAP1-SUMO-2 2iyd: SENP1 COVALENT COMPLEX WITH SUMO-2 |