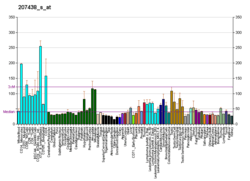
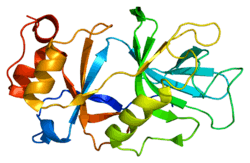Snurportin1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNUPN gene.[5][6]
The nuclear import of the spliceosomal snRNPs U1, U2, U4 and U5, is dependent on the presence of a complex nuclear localization signal. The latter is composed of the 5'-2,2,7-terminal trimethylguanosine (m3G) cap structure of the U snRNA and the Sm core domain. The protein encoded by this gene interacts specifically with m3G-cap and functions as an snRNP-specific nuclear import receptor. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified for this gene.[6]
Further reading
- Paraskeva E, Izaurralde E, Bischoff FR, et al. (1999). "CRM1-mediated recycling of snurportin 1 to the cytoplasm". J. Cell Biol. 145 (2): 255–64. doi:10.1083/jcb.145.2.255. PMC 2133107. PMID 10209022.
- Narayanan U, Ospina JK, Frey MR, et al. (2003). "SMN, the spinal muscular atrophy protein, forms a pre-import snRNP complex with snurportin1 and importin beta". Hum. Mol. Genet. 11 (15): 1785–95. doi:10.1093/hmg/11.15.1785. PMC 1630493. PMID 12095920.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Strasser A, Dickmanns A, Lührmann R, Ficner R (2005). "Structural basis for m3G-cap-mediated nuclear import of spliceosomal UsnRNPs by snurportin1". EMBO J. 24 (13): 2235–43. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600701. PMC 1173142. PMID 15920472.
- Ospina JK, Gonsalvez GB, Bednenko J, et al. (2006). "Cross-talk between snurportin1 subdomains". Mol. Biol. Cell. 16 (10): 4660–71. doi:10.1091/mbc.E05-04-0316. PMC 1237072. PMID 16030253.
- Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, et al. (2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell. 122 (6): 957–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. PMID 16169070.
External links
PDB gallery |
|---|
1xk5: Crystal structure of the m3G-cap-binding domain of snurportin1 in complex with a m3GpppG-cap dinucleotide |