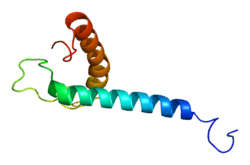Further reading
- Toggas SM, Krady JK, Billingsley ML (July 1992). "Molecular neurotoxicology of trimethyltin: identification of stannin, a novel protein expressed in trimethyltin-sensitive cells". Molecular Pharmacology. 42 (1): 44–56. PMID 1635553.
- Dejneka NS, Patanow CM, Polavarapu R, Toggas SM, Krady JK, Billingsley ML (December 1997). "Localization and characterization of stannin: relationship to cellular sensitivity to organotin compounds". Neurochemistry International. 31 (6): 801–15. doi:10.1016/S0197-0186(97)00034-X. PMID 9413842.
- Horrevoets AJ, Fontijn RD, van Zonneveld AJ, de Vries CJ, ten Cate JW, Pannekoek H (May 1999). "Vascular endothelial genes that are responsive to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in vitro are expressed in atherosclerotic lesions, including inhibitor of apoptosis protein-1, stannin, and two novel genes". Blood. 93 (10): 3418–31. PMID 10233894.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (November 2000). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination". Genome Research. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, Gassenhuber J, Glassl S, Ansorge W, Böcher M, Blöcker H, Bauersachs S, Blum H, Lauber J, Düsterhöft A, Beyer A, Köhrer K, Strack N, Mewes HW, Ottenwälder B, Obermaier B, Tampe J, Heubner D, Wambutt R, Korn B, Klein M, Poustka A (March 2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs". Genome Research. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- Ballif BA, Villén J, Beausoleil SA, Schwartz D, Gygi SP (November 2004). "Phosphoproteomic analysis of the developing mouse brain". Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 3 (11): 1093–101. doi:10.1074/mcp.M400085-MCP200. PMID 15345747.
- Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, Wellenreuther R, Schleeger S, Mehrle A, Bechtel S, Sauermann M, Korf U, Pepperkok R, Sültmann H, Poustka A (October 2004). "From ORFeome to biology: a functional genomics pipeline". Genome Research. 14 (10B): 2136–44. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC 528930. PMID 15489336.
- Mehrle A, Rosenfelder H, Schupp I, del Val C, Arlt D, Hahne F, Bechtel S, Simpson J, Hofmann O, Hide W, Glatting KH, Huber W, Pepperkok R, Poustka A, Wiemann S (January 2006). "The LIFEdb database in 2006". Nucleic Acids Research. 34 (Database issue): D415–8. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj139. PMC 1347501. PMID 16381901.
PDB gallery |
|---|
1zza: Solution NMR Structure of the Membrane Protein Stannin |