SIL1
| SIL1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | SIL1, BAP, MSS, ULG5, SIL1 nucleotide exchange factor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1932040 HomoloGene: 32544 GeneCards: SIL1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 5: 138.95 – 139.29 Mb | Chr 18: 35.27 – 35.5 Mb | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
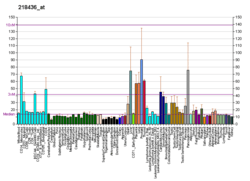
Nucleotide exchange factor SIL1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIL1 gene.[5][6][7][8]
This gene encodes a resident endoplasmic reticulum (ER), N-linked glycoprotein with an N-terminal ER targeting sequence, 2 putative N-glycosylation sites, and a C-terminal ER retention signal. This protein functions as a nucleotide exchange factor for another unfolded protein response protein. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Marinesco-Sjogren syndrome. Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized.[8]
Interactions
SIL1 has been shown to interact with Binding immunoglobulin protein.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000120725 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024357 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Tyson JR, Stirling CJ (Dec 2000). "LHS1 and SIL1 provide a lumenal function that is essential for protein translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum". EMBO J. 19 (23): 6440–52. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.23.6440. PMC 305876. PMID 11101517.
- 1 2 Chung KT, Shen Y, Hendershot LM (Nov 2002). "BAP, a mammalian BiP-associated protein, is a nucleotide exchange factor that regulates the ATPase activity of BiP". J Biol Chem. 277 (49): 47557–63. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208377200. PMID 12356756.
- ↑ Senderek J, Krieger M, Stendel C, Bergmann C, Moser M, Breitbach-Faller N, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Blaschek A, Wolf NI, Harting I, North K, Smith J, Muntoni F, Brockington M, Quijano-Roy S, Renault F, Herrmann R, Hendershot LM, Schroder JM, Lochmuller H, Topaloglu H, Voit T, Weis J, Ebinger F, Zerres K (Nov 2005). "Mutations in SIL1 cause Marinesco-Sjogren syndrome, a cerebellar ataxia with cataract and myopathy". Nat Genet. 37 (12): 1312–4. doi:10.1038/ng1678. PMID 16282977.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: SIL1 SIL1 homolog, endoplasmic reticulum chaperone (S. cerevisiae)".
External links
Further reading
- Keats B, Ott J, Conneally M (1989). "Report of the committee on linkage and gene order". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 51 (1–4): 459–502. doi:10.1159/000132805. PMID 2791656.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Clark HF, Gurney AL, Abaya E, et al. (2003). "The secreted protein discovery initiative (SPDI), a large-scale effort to identify novel human secreted and transmembrane proteins: a bioinformatics assessment". Genome Res. 13 (10): 2265–70. doi:10.1101/gr.1293003. PMC 403697. PMID 12975309.
- Lagier-Tourenne C, Tranebaerg L, Chaigne D, et al. (2004). "Homozygosity mapping of Marinesco-Sjögren syndrome to 5q31". Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 11 (10): 770–8. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201068. PMID 14512967.
- Colland F, Jacq X, Trouplin V, et al. (2004). "Functional proteomics mapping of a human signaling pathway". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1324–32. doi:10.1101/gr.2334104. PMC 442148. PMID 15231748.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Anttonen AK, Mahjneh I, Hämäläinen RH, et al. (2006). "The gene disrupted in Marinesco-Sjögren syndrome encodes SIL1, an HSPA5 cochaperone". Nat. Genet. 37 (12): 1309–11. doi:10.1038/ng1677. PMID 16282978.
- Otsuki T, Ota T, Nishikawa T, et al. (2007). "Signal sequence and keyword trap in silico for selection of full-length human cDNAs encoding secretion or membrane proteins from oligo-capped cDNA libraries". DNA Res. 12 (2): 117–26. doi:10.1093/dnares/12.2.117. PMID 16303743.
- Karim MA, Parsian AJ, Cleves MA, et al. (2006). "A novel mutation in BAP/SIL1 gene causes Marinesco-Sjögren syndrome in an extended pedigree". Clin. Genet. 70 (5): 420–3. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.2006.00695.x. PMID 17026626.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.