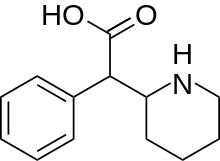
Ritalinic acid
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.039.094 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 219.28 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ritalinic acid is a substituted phenethylamine and an inactive major metabolite of the psychostimulant drugs methylphenidate and ethylphenidate.[1][2] When administered orally, methylphenidate is extensively metabolized in the liver by hydrolysis of the ester group yielding ritalinic acid.[1] The hydrolysis was found to be catalyzed by carboxylesterase 1 (CES1).[3]
Uses
Ritalinic acid is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of methylphenidate and its analogues, such as ethylphenidate and isopropylphenidate.
References
- 1 2 Faraj, B. A.; Israili, Z. H.; Perel, J. M.; Jenkins, M. L.; Holtzman, S. G.; Cucinell, S. A.; Dayton, P. G. (1974). "Metabolism and disposition of methylphenidate-14C: Studies in man and animals". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 191 (3): 535–47. PMID 4473537.
- ↑ Noelia Negreira; Claudio Erratico; Alexander L.N. van Nuijs; Adrian Covaci (January 2016). "Identification of in vitro metabolites of ethylphenidate by liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 117 (5): 474–484. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2015.09.029. PMID 26454340.
- ↑ Sun, Z.; Murry, D.; Sanghani, S.; Davis, W.; Kedishvili, N.; Zou, Q.; Hurley, T.; Bosron, W. (2004). "Methylphenidate is stereoselectively hydrolyzed by human carboxylesterase CES1A1". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 310 (2): 469–476. doi:10.1124/jpet.104.067116. PMID 15082749.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.