Rectified 6-orthoplexes
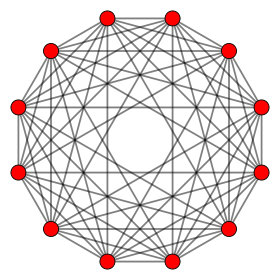 6-orthoplex |
 Rectified 6-orthoplex |
 Birectified 6-orthoplex | |
 Birectified 6-cube |
 Rectified 6-cube |
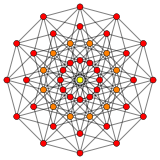 6-cube | |
| Orthogonal projections in B6 Coxeter plane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
In six-dimensional geometry, a rectified 6-orthoplex is a convex uniform 6-polytope, being a rectification of the regular 6-orthoplex.
There are unique 6 degrees of rectifications, the zeroth being the 6-orthoplex, and the 6th and last being the 6-cube. Vertices of the rectified 6-orthoplex are located at the edge-centers of the 6-orthoplex. Vertices of the birectified 6-orthoplex are located in the triangular face centers of the 6-orthoplex.
Rectified 6-orthoplex
| Rectified hexacross | |
|---|---|
| Type | uniform 6-polytope |
| Schläfli symbols | t1{34,4} or r{34,4} r{3,3,3,31,1} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams | |
| 5-faces | 76 total: 64 rectified 5-simplex 12 5-orthoplex |
| 4-faces | 576 total: 192 rectified 5-cell 384 5-cell |
| Cells | 1200 total: 240 octahedron 960 tetrahedron |
| Faces | 1120 total: 160 and 960 triangles |
| Edges | 480 |
| Vertices | 60 |
| Vertex figure | 16-cell prism |
| Petrie polygon | Dodecagon |
| Coxeter groups | B6, [3,3,3,3,4] D6, [33,1,1] |
| Properties | convex |
The rectified 6-orthoplex is the vertex figure for the demihexeractic honeycomb.



















Alternate names
- rectified hexacross
- rectified hexacontitetrapeton (acronym: rag) (Jonathan Bowers)
Construction
There are two Coxeter groups associated with the rectified hexacross, one with the C6 or [4,3,3,3,3] Coxeter group, and a lower symmetry with two copies of pentacross facets, alternating, with the D6 or [33,1,1] Coxeter group.
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a rectified hexacross, centered at the origin, edge length are all permutations of:
- (±1,±1,0,0,0,0)
Images
| Coxeter plane | B6 | B5 | B4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graph |  |
 |
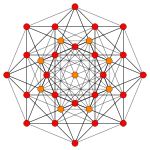 |
| Dihedral symmetry | [12] | [10] | [8] |
| Coxeter plane | B3 | B2 | |
| Graph | 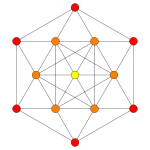 |
 | |
| Dihedral symmetry | [6] | [4] | |
| Coxeter plane | A5 | A3 | |
| Graph |  |
 | |
| Dihedral symmetry | [6] | [4] |
Root vectors
The 60 vertices represent the root vectors of the simple Lie group D6. The vertices can be seen in 3 hyperplanes, with the 15 vertices rectified 5-simplices cells on opposite sides, and 30 vertices of an expanded 5-simplex passing through the center. When combined with the 12 vertices of the 6-orthoplex, these vertices represent the 72 root vectors of the B6 and C6 simple Lie groups.
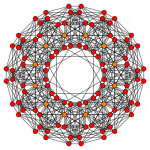
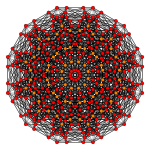
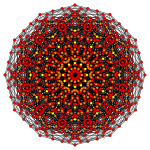
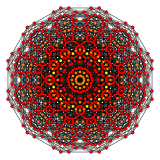
The 60 roots of D6 can be geometrically folded into H3 (Icosahedral symmetry), as ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
| Rectified 6-orthoplex | 2 icosidodecahedra | |
|---|---|---|
| 3D (H3 projection) | A4/B5/D6 Coxeter plane | H2 Coxeter plane |
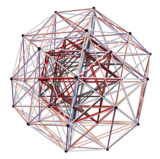 |
 |
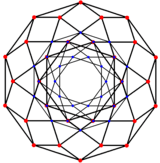 |
Birectified 6-orthoplex
| Birectified 6-orthoplex | |
|---|---|
| Type | uniform 6-polytope |
| Schläfli symbols | t2{34,4} or 2r{34,4} t2{3,3,3,31,1} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams | |
| 5-faces | 76 |
| 4-faces | 636 |
| Cells | 2160 |
| Faces | 2880 |
| Edges | 1440 |
| Vertices | 160 |
| Vertex figure | {3}×{3,4} duoprism |
| Petrie polygon | Dodecagon |
| Coxeter groups | B6, [3,3,3,3,4] D6, [33,1,1] |
| Properties | convex |
The birectified 6-orthoplex can tessellation space in the trirectified 6-cubic honeycomb.
Alternate names
- birectified hexacross
- birectified hexacontitetrapeton (acronym: brag) (Jonathan Bowers)
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a rectified hexacross, centered at the origin, edge length are all permutations of:
- (±1,±1,±1,0,0,0)
Images
| Coxeter plane | B6 | B5 | B4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graph |  |
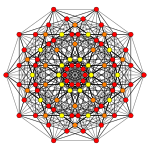 |
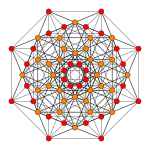 |
| Dihedral symmetry | [12] | [10] | [8] |
| Coxeter plane | B3 | B2 | |
| Graph | 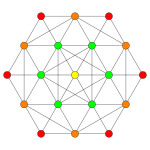 |
 | |
| Dihedral symmetry | [6] | [4] | |
| Coxeter plane | A5 | A3 | |
| Graph |  |
 | |
| Dihedral symmetry | [6] | [4] |
It can also be projected into 3D-dimensions as ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Related polytopes
These polytopes are a part a family of 63 Uniform 6-polytopes generated from the B6 Coxeter plane, including the regular 6-cube or 6-orthoplex.
Notes
- ↑ Icosidodecahedron from D6 John Baez, January 1, 2015
References
- H.S.M. Coxeter:
- H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 3rd Edition, Dover New York, 1973
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995,
ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6
- (Paper 22) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi Regular Polytopes I, [Math. Zeit. 46 (1940) 380-407, MR 2,10]
- (Paper 23) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes II, [Math. Zeit. 188 (1985) 559-591]
- (Paper 24) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes III, [Math. Zeit. 200 (1988) 3-45]
- Norman Johnson Uniform Polytopes, Manuscript (1991)
- N.W. Johnson: The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs, Ph.D.
- Klitzing, Richard. "6D uniform polytopes (polypeta)". o3x3o3o3o4o - rag, o3o3x3o3o4o - brag
External links
Fundamental convex regular and uniform polytopes in dimensions 2–10 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family | An | Bn | I2(p) / Dn | E6 / E7 / E8 / F4 / G2 | Hn | |||||||
| Regular polygon | Triangle | Square | p-gon | Hexagon | Pentagon | |||||||
| Uniform polyhedron | Tetrahedron | Octahedron • Cube | Demicube | Dodecahedron • Icosahedron | ||||||||
| Uniform 4-polytope | 5-cell | 16-cell • Tesseract | Demitesseract | 24-cell | 120-cell • 600-cell | |||||||
| Uniform 5-polytope | 5-simplex | 5-orthoplex • 5-cube | 5-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 6-polytope | 6-simplex | 6-orthoplex • 6-cube | 6-demicube | 122 • 221 | ||||||||
| Uniform 7-polytope | 7-simplex | 7-orthoplex • 7-cube | 7-demicube | 132 • 231 • 321 | ||||||||
| Uniform 8-polytope | 8-simplex | 8-orthoplex • 8-cube | 8-demicube | 142 • 241 • 421 | ||||||||
| Uniform 9-polytope | 9-simplex | 9-orthoplex • 9-cube | 9-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 10-polytope | 10-simplex | 10-orthoplex • 10-cube | 10-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform n-polytope | n-simplex | n-orthoplex • n-cube | n-demicube | 1k2 • 2k1 • k21 | n-pentagonal polytope | |||||||
| Topics: Polytope families • Regular polytope • List of regular polytopes and compounds | ||||||||||||