Raft

A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water.[1] It is the most basic of boat design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Although there are cross-over boat types that blur this definition, rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrels, or inflated air chambers (such as pontoons), and are typically not propelled by an engine.
Human-made rafts
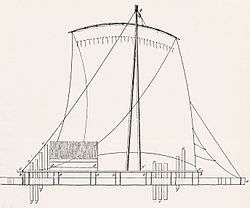
Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood or reeds. Modern rafts may also use pontoons, drums, or extruded polystyrene blocks. Inflatable rafts up to the 20th century used flotation chambers made of goat- or buffalo-skins, but most now use durable, multi-layered rubberized fabrics. Depending on its use and size, it may have a superstructure, masts, or rudders. Timber rafting is used by the logging industry for the transportation of logs, by tying them together into rafts and drifting or pulling them down a river. This method was very common up until the middle of the 20th century but is now used only rarely.

Large rafts made of balsa logs and using sails for navigation were important in maritime trade on the Pacific Ocean coast of South America from pre-Columbian times until the 19th century. Voyages were made to locations as far away as Mexico, and many trans-Pacific voyages using replicas of ancient rafts have been undertaken to demonstrate possible contacts between South America and Polynesia.[2]
The type of raft used for recreational rafting is almost exclusively an inflatable boat, manufactured of flexible materials for use on whitewater.
Natural rafts
In biology, particularly in island biogeography, non-manmade rafts are an important concept. Such rafts consist of matted clumps of vegetation that has been swept off the dry land by a storm, tsunami, tide, earthquake or similar event; in modern times they sometimes also incorporate other kind of flotsam and jetsam, e.g. plastic containers. They stay afloat by its natural buoyancy and can travel for hundreds, even thousands of miles and are ultimately destroyed by wave action and decomposition, or make landfall.
Rafting events are important means of oceanic dispersal for non-flying animals. For small mammals, amphibians and reptiles in particular, but for many invertebrates as well, such rafts of vegetation are often the only means by which they could reach and – if they are lucky – colonize oceanic islands before human-built vehicles provided another mode of transport.
Image gallery





See also
References
External links
| Look up raft in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rafts. |
