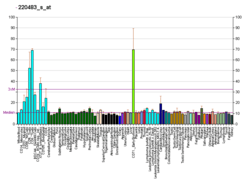
RNF19A
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF19A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNF19A gene.[5][6][7]
The protein encoded by this gene contains two RING-finger motifs and an IBR (in between RING fingers) motif. This protein is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that is localized in Lewy bodies (LBs), neuronal inclusions characteristic of Parkinson's disease (PD). This protein interacts with UBE2L3/UBCH7 and UBE2E2/UBCH8, but not other ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. This protein is found to bind and ubiquitylate synphilin 1 (SNCAIP), which is an interacting protein of alpha-synuclein in neurons, and a major component of LB. Alternatively-spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been reported.[7]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000034677 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000022280 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Niwa J, Ishigaki S, Doyu M, Suzuki T, Tanaka K, Sobue G (Mar 2001). "A novel centrosomal ring-finger protein, dorfin, mediates ubiquitin ligase activity". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 281 (3): 706–13. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4414. PMID 11237715.
- ↑ Gunther M, Laithier M, Brison O (Dec 2000). "A set of proteins interacting with transcription factor Sp1 identified in a two-hybrid screening". Mol Cell Biochem. 210 (1–2): 131–42. doi:10.1023/A:1007177623283. PMID 10976766.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: RNF19 ring finger protein 19".
Further reading
- Niwa J, Ishigaki S, Hishikawa N, et al. (2002). "Dorfin ubiquitylates mutant SOD1 and prevents mutant SOD1-mediated neurotoxicity". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (39): 36793–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206559200. PMID 12145308.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ito T, Niwa J, Hishikawa N, et al. (2003). "Dorfin localizes to Lewy bodies and ubiquitylates synphilin-1". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (31): 29106–14. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302763200. PMID 12750386.
- Hishikawa N, Niwa J, Doyu M, et al. (2003). "Dorfin Localizes to the Ubiquitylated Inclusions in Parkinson's Disease, Dementia with Lewy Bodies, Multiple System Atrophy, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis". Am. J. Pathol. 163 (2): 609–19. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63688-7. PMC 1868225. PMID 12875980.
- Paces-Fessy M, Boucher D, Petit E, et al. (2004). "The negative regulator of Gli, Suppressor of fused (Sufu), interacts with SAP18, Galectin3 and other nuclear proteins". Biochem. J. 378 (Pt 2): 353–62. doi:10.1042/BJ20030786. PMC 1223961. PMID 14611647.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Takeuchi H, Niwa J, Hishikawa N, et al. (2004). "Dorfin prevents cell death by reducing mitochondrial localizing mutant superoxide dismutase 1 in a neuronal cell model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis". J. Neurochem. 89 (1): 64–72. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02289.x. PMID 15030390.
- Ishigaki S, Hishikawa N, Niwa J, et al. (2005). "Physical and functional interaction between Dorfin and Valosin-containing protein that are colocalized in ubiquitylated inclusions in neurodegenerative disorders". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (49): 51376–85. doi:10.1074/jbc.M406683200. PMID 15456787.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Huang Y, Niwa J, Sobue G, Breitwieser GE (2006). "Calcium-sensing receptor ubiquitination and degradation mediated by the E3 ubiquitin ligase dorfin". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (17): 11610–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M513552200. PMID 16513638.
- Ishigaki S, Niwa J, Yamada S, et al. (2007). "Dorfin-CHIP chimeric proteins potently ubiquitylate and degrade familial ALS-related mutant SOD1 proteins and reduce their cellular toxicity". Neurobiol. Dis. 25 (2): 331–41. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2006.09.017. PMID 17157513.
External links
- RNF19A+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.