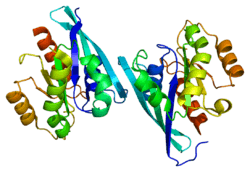
RAB9A
Ras-related protein Rab-9A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAB9A gene.[5][6]
Interactions
RAB9A has been shown to interact with RABEPK,[7] TIP47[8] and the Biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex 3.[9]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000123595 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000079316 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Davies JP, Cotter PD, Ioannou YA (May 1997). "Cloning and mapping of human Rab7 and Rab9 cDNA sequences and identification of a Rab9 pseudogene". Genomics. 41 (1): 131–4. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4644. PMID 9126495.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: RAB9A RAB9A, member RAS oncogene family".
- ↑ Díaz E, Schimmöller F, Pfeffer SR (July 1997). "A novel Rab9 effector required for endosome-to-TGN transport". J. Cell Biol. 138 (2): 283–90. doi:10.1083/jcb.138.2.283. PMC 2138197. PMID 9230071.
- ↑ Carroll KS, Hanna J, Simon I, Krise J, Barbero P, Pfeffer SR (May 2001). "Role of Rab9 GTPase in facilitating receptor recruitment by TIP47". Science. 292 (5520): 1373–6. doi:10.1126/science.1056791. PMID 11359012.
- ↑ Kloer DP, Rojas R, Ivan V, Moriyama K, van Vlijmen T, Murthy N, Ghirlando R, van der Sluijs P, Hurley JH, Bonifacino JS (March 2010). "Assembly of the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex-3 (BLOC-3) and its interaction with Rab9". J. Biol. Chem. 285 (10): 7794–7804. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.069088. PMC 2844223. PMID 20048159.
Further reading
- Shapiro AD, Pfeffer SR (1995). "Quantitative analysis of the interactions between prenyl Rab9, GDP dissociation inhibitor-alpha, and guanine nucleotides". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (19): 11085–90. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.19.11085. PMID 7744738.
- Soldati T, Riederer MA, Pfeffer SR (1993). "Rab GDI: a solubilizing and recycling factor for rab9 protein". Mol. Biol. Cell. 4 (4): 425–34. doi:10.1091/mbc.4.4.425. PMC 300943. PMID 8389620.
- Díaz E, Schimmöller F, Pfeffer SR (1997). "A novel Rab9 effector required for endosome-to-TGN transport". J. Cell Biol. 138 (2): 283–90. doi:10.1083/jcb.138.2.283. PMC 2138197. PMID 9230071.
- de Leeuw HP, Koster PM, Calafat J, Janssen H, van Zonneveld AJ, van Mourik JA, Voorberg J (1998). "Small GTP-binding proteins in human endothelial cells". Br. J. Haematol. 103 (1): 15–9. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.1998.00965.x. PMID 9792283.
- Shisheva A, Chinni SR, DeMarco C (1999). "General role of GDP dissociation inhibitor 2 in membrane release of Rab proteins: modulations of its functional interactions by in vitro and in vivo structural modifications". Biochemistry. 38 (36): 11711–21. doi:10.1021/bi990200r. PMID 10512627.
- Carroll KS, Hanna J, Simon I, Krise J, Barbero P, Pfeffer SR (2001). "Role of Rab9 GTPase in facilitating receptor recruitment by TIP47". Science. 292 (5520): 1373–6. doi:10.1126/science.1056791. PMID 11359012.
- Orzaez D, de Jong AJ, Woltering EJ (2001). "A tomato homologue of the human protein PIRIN is induced during programmed cell death". Plant Mol. Biol. 46 (4): 459–68. doi:10.1023/A:1010618515051. PMID 11485202.
- Michel F, Soler-Lopez M, Petosa C, Cramer P, Siebenlist U, Müller CW (2002). "Crystal structure of the ankyrin repeat domain of Bcl-3: a unique member of the IkappaB protein family". EMBO J. 20 (22): 6180–90. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.22.6180. PMC 125740. PMID 11707390.
- Barbero P, Bittova L, Pfeffer SR (2002). "Visualization of Rab9-mediated vesicle transport from endosomes to the trans-Golgi in living cells". J. Cell Biol. 156 (3): 511–8. doi:10.1083/jcb.200109030. PMC 2173336. PMID 11827983.
- Hanna J, Carroll K, Pfeffer SR (2002). "Identification of residues in TIP47 essential for Rab9 binding". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (11): 7450–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.112198799. PMC 124251. PMID 12032303.
- Walter M, Davies JP, Ioannou YA (2004). "Telomerase immortalization upregulates Rab9 expression and restores LDL cholesterol egress from Niemann-Pick C1 late endosomes". J. Lipid Res. 44 (2): 243–53. doi:10.1194/jlr.M200230-JLR200. PMID 12576506.
- Seaman MN (2004). "Cargo-selective endosomal sorting for retrieval to the Golgi requires retromer". J. Cell Biol. 165 (1): 111–22. doi:10.1083/jcb.200312034. PMC 2172078. PMID 15078902.
- Chen L, DiGiammarino E, Zhou XE, Wang Y, Toh D, Hodge TW, Meehan EJ (2004). "High resolution crystal structure of human Rab9 GTPase: a novel antiviral drug target". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (38): 40204–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M407114200. PMID 15263003.
- Ganley IG, Carroll K, Bittova L, Pfeffer S (2005). "Rab9 GTPase regulates late endosome size and requires effector interaction for its stability". Mol. Biol. Cell. 15 (12): 5420–30. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-08-0747. PMC 532021. PMID 15456905.
- Ganley IG, Pfeffer SR (2006). "Cholesterol accumulation sequesters Rab9 and disrupts late endosome function in NPC1-deficient cells". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (26): 17890–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M601679200. PMC 3650718. PMID 16644737.
- Aivazian D, Serrano RL, Pfeffer S (2006). "TIP47 is a key effector for Rab9 localization". J. Cell Biol. 173 (6): 917–26. doi:10.1083/jcb.200510010. PMC 2063917. PMID 16769818.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.