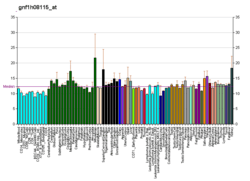
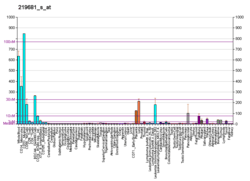
RAB11FIP1
Rab11 family-interacting protein 1 (Rab11-FIP1) also known as Rab-coupling protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAB11FIP1 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
Proteins of the large Rab GTPase family (see for example RAB1A) have regulatory roles in the formation, targeting, and fusion of intracellular transport vesicles. RAB11FIP1 is one of many proteins that interact with and regulate Rab GTPases.[6][7] RAB11FIP1 has been identified as a novel protein involved in the regulation of adiponectin trafficking and release from the adipocyte.[8] RAB11FIP1 expression, which is increased with increasing BMI in humans, inhibits the release of adiponectin from the adipocyte, potentially contributing to lower circulating levels of adiponectin observed in obese populations.[8]
Interactions
RAB11FIP1 has been shown to interact with RAB11A[5][6][9] and RAB4A.[5]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000156675 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000031488 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 3 Lindsay AJ, Hendrick AG, Cantalupo G, Senic-Matuglia F, Goud B, Bucci C, McCaffrey MW (Apr 2002). "Rab coupling protein (RCP), a novel Rab4 and Rab11 effector protein". J Biol Chem. 277 (14): 12190–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108665200. PMID 11786538.
- 1 2 3 Hales CM, Griner R, Hobdy-Henderson KC, Dorn MC, Hardy D, Kumar R, Navarre J, Chan EK, Lapierre LA, Goldenring JR (Oct 2001). "Identification and characterization of a family of Rab11-interacting proteins". J Biol Chem. 276 (42): 39067–75. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104831200. PMID 11495908.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: RAB11FIP1 RAB11 family interacting protein 1 (class I)".
- 1 2 Carson, Brian P.; Maria Del Bas, Josep; Moreno-Navarrete, Jose Maria; Fernandez-Real, Jose Manuel; Mora, Silvia (September 2013). "The Rab11 Effector Protein FIP1 Regulates Adiponectin". PLoS ONE. 8 (9): e74687. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074687. PMC 3770573. PMID 24040321.
- ↑ Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S, McBroom-Cerajewski L, Robinson MD, O'Connor L, Li M, Taylor R, Dharsee M, Ho Y, Heilbut A, Moore L, Zhang S, Ornatsky O, Bukhman YV, Ethier M, Sheng Y, Vasilescu J, Abu-Farha M, Lambert JP, Duewel HS, Stewart II, Kuehl B, Hogue K, Colwill K, Gladwish K, Muskat B, Kinach R, Adams SL, Moran MF, Morin GB, Topaloglou T, Figeys D (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3: 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
Further reading
- Wallace DM, Lindsay AJ, Hendrick AG, McCaffrey MW (2002). "The novel Rab11-FIP/Rip/RCP family of proteins displays extensive homo- and hetero-interacting abilities". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 292 (4): 909–15. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2002.6736. PMID 11944901.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Thériault C, Rochdi MD, Parent JL (2004). "Role of the Rab11-associated intracellular pool of receptors formed by constitutive endocytosis of the beta isoform of the thromboxane A2 receptor (TP beta)". Biochemistry. 43 (19): 5600–7. doi:10.1021/bi036268v. PMID 15134434.
- Peden AA, Schonteich E, Chun J, et al. (2005). "The RCP-Rab11 complex regulates endocytic protein sorting". Mol. Biol. Cell. 15 (8): 3530–41. doi:10.1091/mbc.E03-12-0918. PMC 491816. PMID 15181150.
- Lindsay AJ, McCaffrey MW (2004). "Characterisation of the Rab binding properties of Rab coupling protein (RCP) by site-directed mutagenesis". FEBS Lett. 571 (1–3): 86–92. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.06.068. PMID 15280022.
- Damiani MT, Pavarotti M, Leiva N, et al. (2005). "Rab coupling protein associates with phagosomes and regulates recycling from the phagosomal compartment". Traffic. 5 (10): 785–97. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2004.00220.x. PMID 15355514.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Marie N, Lindsay AJ, McCaffrey MW (2005). "Rab coupling protein is selectively degraded by calpain in a Ca2+-dependent manner". Biochem. J. 389 (Pt 1): 223–31. doi:10.1042/BJ20042116. PMC 1184555. PMID 15769254.
- Tajika Y, Matsuzaki T, Suzuki T, et al. (2006). "Differential regulation of AQP2 trafficking in endosomes by microtubules and actin filaments". Histochem. Cell Biol. 124 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1007/s00418-005-0010-3. PMID 16049696.
- Patil VS, Sachdeva G, Modi DN, et al. (2006). "Rab coupling protein (RCP): a novel target of progesterone action in primate endometrium". J. Mol. Endocrinol. 35 (2): 357–72. doi:10.1677/jme.1.01807. PMID 16216915.
- Jin M, Goldenring JR (2006). "The Rab11-FIP1/RCP gene codes for multiple protein transcripts related to the plasma membrane recycling system". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1759 (6): 281–95. doi:10.1016/j.bbaexp.2006.06.001. PMID 16920206.
- Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Gerber SA, et al. (2006). "A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization". Nat. Biotechnol. 24 (10): 1285–92. doi:10.1038/nbt1240. PMID 16964243.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.