| Pyuria |
|---|
 |
|
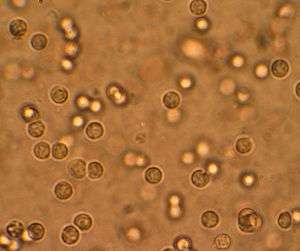
White blood cells seen under a microscope from a urine sample. |
| Pronunciation |
|
|---|
| Specialty |
Urology  |
|---|
Pyuria is the condition of urine containing white blood cells or pus. Defined as the presence of 6-10 or more neutrophils per high power field of unspun, voided mid-stream urine. It can be a sign of a bacterial urinary tract infection. Pyuria may be present in the people with sepsis, or in older people with pneumonia.
Sterile pyuria,[1] is urine which contains white blood cells while appearing sterile by standard culturing techniques. It is often caused by sexually transmitted infections, such as gonorrhea, or viruses which will not grow in bacterial cultures. Sterile pyuria is listed as a side effect from some medications such as paracetamol (acetaminophen). Its occurrence is also associated with certain disease processes, such as Kawasaki disease and genitourinary tuberculosis.[2] However, there are many known causes, including systemic or infectious disease, structural and physiological reasons, intrinsic kidney pathology, or drugs.[2]
External links
| Classification |
|
|---|
| External resources |
|
|---|
 |
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pyuria. |