Proximity ligation assay

Proximity ligation assay (in situ PLA) is a technology that extends the capabilities of traditional immunoassays to include direct detection of proteins, protein interactions and modifications with high specificity and sensitivity.[1] Protein targets can be readily detected and localized with single molecule resolution and objectively quantified in unmodified cells and tissues. Utilizing only a few cells, sub-cellular events, even transient or weak interactions, are revealed in situ and sub-populations of cells can be differentiated. Within hours, results from conventional co-immunoprecipitation and co-localization techniques can be confirmed.[2]
The PLA principle
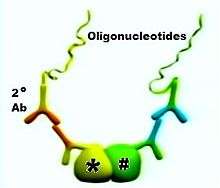
Two primary antibodies raised in different species recognize the target antigen on the proteins of interest. Secondary antibodies (2o Ab) directed against the constant regions of the different primary antibodies, called PLA probes, bind to the primary antibodies.
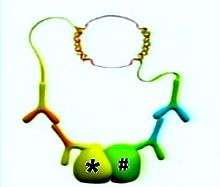
Each of the PLA probes has a unique short DNA strand attached to it, If the PLA probes are in close proximity (that is, if the two original proteins of interest are in close proximity, or part of a protein complex, as shown in the figures), the DNA strands can participate in rolling circle DNA synthesis when appropriate substrates and enzymes are added.
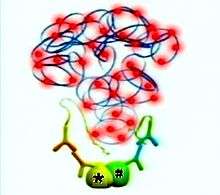
The DNA synthesis reaction results in several-hundredfold amplification of the DNA circle. Next, fluorescent-labeled complementary oligonucleotide probes are added, and they bind to the amplified DNA. The resulting high concentration of fluorescence is easily visible as a distinct bright spot when viewed with a fluorescence microscope.[3] In the specific case shown, the nucleus is enlarged because this is a B-cell lymphoma cell. The 2 proteins of interest are a B cell receptor and MYD88. The finding of interaction in the cytoplasm was interesting because B cell receptors are thought of as being located in the cell membrane.[4]

Applications
PLA as described above has been used to study aspects of animal development[5][6] and breast cancer[7][8] among many other topics. A variation of the technique (rISH-PLA) has been used to study the association of protein and RNA.[9]
References
- ↑ Gullberg M, Gústafsdóttir SM, Schallmeiner E, Jarvius J, Bjarnegård M, Betsholtz C, Landegren U, Fredriksson S (June 2004). "Cytokine detection by antibody-based proximity ligation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (22): 8420–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400552101. PMC 420409. PMID 15155907.
- ↑ Söderberg O, Gullberg M, Jarvius M, Ridderstråle K, Leuchowius KJ, Jarvius J, Wester K, Hydbring P, Bahram F, Larsson LG, Landegren U (December 2006). "Direct observation of individual endogenous protein complexes in situ by proximity ligation". Nature Methods. 3 (12): 995–1000. doi:10.1038/nmeth947. PMID 17072308.
- ↑ Gustafsdottir SM, Schallmeiner E, Fredriksson S, Gullberg M, Söderberg O, Jarvius M, Jarvius J, Howell M, Landegren U (October 2005). "Proximity ligation assays for sensitive and specific protein analyses". Analytical Biochemistry. 345 (1): 2–9. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2005.01.018. PMID 15950911.
- ↑ Staudt, Louis. "Therapy of lymphoma inspired by functional and structural genomics". videocast.nih.gov. National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ↑ Wang S, Yoo S, Kim HY, Wang M, Zheng C, Parkhouse W, Krieger C, Harden N (January 2015). "Detection of in situ protein-protein complexes at the Drosophila larval neuromuscular junction using proximity ligation assay". Journal of Visualized Experiments (95): 52139. doi:10.3791/52139. PMC 4354543. PMID 25650626.
- ↑ Kwon J, Jeong SM, Choi I, Kim NH (2016). "ADAM10 Is Involved in Cell Junction Assembly in Early Porcine Embryo Development". PLOS ONE. 11 (4): e0152921. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0152921. PMC 4820119. PMID 27043020.
- ↑ Karamouzis MV, Dalagiorgou G, Georgopoulou U, Nonni A, Kontos M, Papavassiliou AG (February 2016). "HER-3 targeting alters the dimerization pattern of ErbB protein family members in breast carcinomas". Oncotarget. 7 (5): 5576–97. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.6762. PMC 4868707. PMID 26716646.
- ↑ Vincent A, Berthel E, Dacheux E, Magnard C, Venezia NL (April 2016). "BRCA1 affects protein phosphatase 6 signalling through its interaction with ANKRD28". The Biochemical Journal. 473 (7): 949–60. doi:10.1042/BJ20150797. PMID 27026398.
- ↑ Roussis IM, Guille M, Myers FA, Scarlett GP (2016). "RNA Whole-Mount In situ Hybridisation Proximity Ligation Assay (rISH-PLA), an Assay for Detecting RNA-Protein Complexes in Intact Cells". PLOS ONE. 11 (1): e0147967. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0147967. PMC 4732756. PMID 26824753.