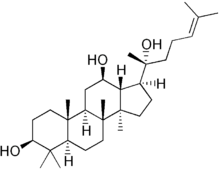
Protopanaxadiol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3S,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R,17S)-17-[(2S)-2-hydroxy-6-methylhept-5-en-2-yl]-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-2,3,5,6,7,9,11,12,13,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol | |
| Other names
Dammar-24-ene-3β,12β,20-triol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | PPD |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.208.650 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H52O3 | |
| Molar mass | 460.74 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Protopanaxadiol (PPD) is an organic compound characterizing a group of ginsenosides. It is a dammarane-type tetracyclic terpene sapogenin found in ginseng (Panax ginseng) and in notoginseng (Panax pseudoginseng).[1][2]
Just what protopanaxadiol's metabolites do inside the human body is still unclear. One study suggests it has rapid, non-genomic effects on endothelial cells, binding to the glucocorticoid and oestrogen beta receptors. The study also showed an increase of intracellular calcium ion concentration.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Shibata, S.; Tanaka, O.; Sado, M.; Tsushima, S. (1963). "The genuine sapogenin of ginseng". Tetrahedron Letters. 4 (12): 795–800. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)90718-X.
- ↑ Tanaka, O.; Nagai, M.; Shibata, S. (1964). "Stereochemistry of protopanaxadiol, a genuine sapogenin of ginseng". Tetrahedron Letters. 5 (33–34): 2291–7. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)71705-9.
- ↑ Leung; et al. "Protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol bind to glucocorticoid and oestrogen receptors in endothelial cells". British Journal of Pharmacology. Wiley Online Library. Retrieved 29 October 2012.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.