Phenylglycine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-2-phenylacetic acid | |
| Other names
2-Phenylglycine; Aminophenylacetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 608018 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number | 200-719-1 220-608-1 |
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H9NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 151.17 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 290 °C (554 °F; 563 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
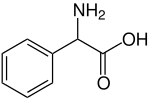
Phenylglycine is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH(NH2)CO2H. It is a non-proteinogenic alpha amino acid related to alanine, but with a phenyl group in place of methyl. It is a white solid. The compound exhibits some biological activity.[1]
Preparation
It is prepared from benzaldehyde by amino cyanation (Strecker synthesis).[2] It can also be prepared from glyoxal[3] and by reductive amination of phenylpyruvic acid.
Ester
The ester methyl α‐phenylglycinate is used to convert carboxylic acids into homologated unsaturated ketones. These reactions proceed via cyclization of phenylglycinamides to oxazolones, which can be reductively cleaved with chromous reagents.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Watkins, Jeff; Collingridge, Graham (1994). "Phenylglycine derivatives as antagonists of metabotropic glutamate receptors". Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 15: 333–42. doi:10.1016/0165-6147(94)90028-0.
- ↑ Robert E. Steiger (1942). "dl-α-Aminophenylacetic Acid". Org. Synth. 22: 23. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.022.0023.
- ↑ Agami, Claude; Couty, Francois; Puchot-Kadouri, Cathy (1998). "Asymmetric synthesis of α-amino acids from a chiral masked form of glyoxal". Synlett: 449–456. doi:10.1055/s-1998-1685.
- ↑ Wolfgang Steglich Stefan Jaroch (2001). "Methyl α‐Phenylglycinate". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rm229.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.